10-K: Annual report pursuant to Section 13 and 15(d)
Published on March 17, 2010
Table of Contents
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
| þ | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2009
OR
| o | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
Commission file number 001-33528
OPKO HEALTH, INC.
(Exact Name of Registrant as Specified in Its Charter)
| DELAWARE | 75-2402409 | |
| (State or Other Jurisdiction of Incorporation or Organization) | (I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) |
4400 Biscayne Blvd., FL 33137
(Address of Principal Executive Offices, Zip Code)
(Address of Principal Executive Offices, Zip Code)
Registrants Telephone Number, Including Area Code: (305) 575-4100
Securities registered pursuant to section 12(b) of the Act:
| Title of Each Class Common Stock, $.01 par value per share |
Name of Each Exchange on Which Registered NYSE Amex |
Securities registered pursuant to section 12(g) of the Act:
None
None
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule
405 of the Securities Act. Yes o No þ
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section
13 or Section 15(d) of the Act. Yes o No þ
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed
by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or
for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been
subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes þ No o
Indicate by check mark whether the Registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its
corporate Website, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant
to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the
registrant was required to submit and post such files). Yes o No o
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation
S-K is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of registrants knowledge, in
definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K
or any amendment to this Form 10-K. o
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated
filer, a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company. See the definitions of large
accelerated filer, Accelerated filer and smaller reporting company in Rule 12b-2 of the
Exchange Act.
| Large Accelerated filer o | Accelerated filer þ | Non-Accelerated filer o | Smaller Reporting Company o | |||
| (Do not check if a smaller reporting company) |
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of
the Act).Yes o No þ
The aggregate market value of the voting and non-voting common equity held by non-affiliates
computed by reference to the price at which the common equity was last sold, as of the last
business day of the registrants most recently completed second fiscal quarter was: $196,865,850.
As of March 8, 2010 the registrant had 255,406,078 shares of common stock outstanding.
Documents Incorporated by Reference
Portions of the registrants definitive proxy statement for its 2010 Annual Meeting of
Stockholders are incorporated by reference in Items 10, 11, 12, 13, and 14 of Part III of this
Annual Report on Form 10-K.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
| Page | ||||||||
| Part I. | ||||||||
| Item 1. | 6 | |||||||
| Item 1A. | 22 | |||||||
| Item 1B. | 40 | |||||||
| Item 2. | 40 | |||||||
| Item 3. | 41 | |||||||
| Item 4. | 41 | |||||||
| Part II. | ||||||||
| Item 5. | 42 | |||||||
| Item 6. | 44 | |||||||
| Item 7. | 44 | |||||||
| Item 7A. | 51 | |||||||
| Item 8. | 52 | |||||||
| Item 9. | 83 | |||||||
| Item 9A. | 84 | |||||||
| Item 9B. | 84 | |||||||
| Part III. | ||||||||
| Item 10. | 85 | |||||||
| Item 11. | 85 | |||||||
| Item 12. | 85 | |||||||
| Item 13. | 85 | |||||||
| Item 14. | 85 | |||||||
| Part IV. | ||||||||
| Item 15. | 86 | |||||||
| Signatures | 89 | |||||||
| Certifications | ||||||||
| EX-10.24 | ||||||||
| EX-10.25 | ||||||||
| EX-21 | ||||||||
| EX-23.1 | ||||||||
| EX-31.1 | ||||||||
| EX-31.2 | ||||||||
| EX-32.1 | ||||||||
| EX-32.2 | ||||||||
2
Table of Contents
CAUTIONARY STATEMENTS REGARDING FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
This Annual Report on Form 10-K contains forward-looking statements, as that term is defined
under the Private Securities Reform Act of 1995, or PSLRA, Section 27A of the Securities Act of
1933, as amended, and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended.
Forward-looking statements include statements about our expectations, beliefs or intentions
regarding our product development efforts, business, financial condition, results of operations,
strategies or prospects. You can identify forward-looking statements by the fact that these
statements do not relate strictly to historical or current matters. Rather, forward-looking
statements relate to anticipated or expected events, activities, trends or results as of the date
they are made. Because forward-looking statements relate to matters that have not yet occurred,
these statements are inherently subject to risks and uncertainties that could cause our actual
results to differ materially from any future results expressed or implied by the forward-looking
statements. Many factors could cause our actual activities or results to differ materially from
the activities and results anticipated in forward-looking statements. These factors include those
described below and in Item 1A-Risk Factors of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. We do not
undertake any obligation to update forward-looking statements. We intend that all forward-looking
statements be subject to the safe-harbor provisions of the PSLRA. These forward-looking statements
are only predictions and reflect our views as of the date they are made with respect to future
events and financial performance.
Risks and uncertainties, the occurrence of which could adversely affect our business, include
the following:
| | We have a history of operating losses and we do not expect to become profitable in the near future. | ||
| | Our technologies are in an early stage of development and are unproven. | ||
| | Our drug research and development activities may not result in commercially viable products. | ||
| | The results of previous clinical trials may not be predictive of future results, and our current and planned clinical trials may not satisfy the requirements of the FDA or other non-U.S. regulatory authorities. | ||
| | We will require substantial additional funding, which may not be available to us on acceptable terms, or at all. | ||
| | We expect to finance future cash needs primarily through public or private offerings, debt financings or strategic collaborations, which may dilute your stockholdings in the Company. | ||
| | If our competitors develop and market products that are more effective, safer or less expensive than our future product candidates, our commercial opportunities will be negatively impacted. | ||
| | The regulatory approval process is expensive, time consuming and uncertain and may prevent us or our collaboration partners from obtaining approvals for the commercialization of some or all of our product candidates. | ||
| | Failure to recruit and enroll patients for clinical trials may cause the development of our product candidates to be delayed. | ||
| | Even if we obtain regulatory approvals for our product candidates, the terms of approvals and ongoing regulation of our products may limit how we manufacture and market our product candidates, which could materially impair our ability to generate anticipated revenues. | ||
| | We may not meet regulatory quality standards applicable to our manufacturing and quality processes. | ||
| | Even if we receive regulatory approval to market our product candidates, the market may not be receptive to our products. | ||
| | If we fail to attract and retain key management and scientific personnel, we may be unable to successfully develop or commercialize our product candidates. |
3
Table of Contents
| | In the event that we successfully evolve from a company primarily involved in development to a company also involved in commercialization, we may encounter difficulties in managing our growth and expanding our operations successfully. | ||
| | If we fail to acquire and develop other products or product candidates, at all or on commercially reasonable terms, we may be unable to diversify or grow our business. | ||
| | We have no experience manufacturing our pharmaceutical product candidates other than our Mexican facility and we therefore rely on third parties to manufacture and supply our pharmaceutical product candidates, and would need to meet various standards necessary to satisfy FDA regulations if and when we commence manufacturing. | ||
| | We currently have no pharmaceutical marketing, sales or distribution organization. If we are unable to develop our sales and marketing and distribution capability on our own or through collaborations with marketing partners, we will not be successful in commercializing our pharmaceutical product candidates. | ||
| | Independent clinical investigators and contract research organizations that we engage to conduct our clinical trials may not be diligent, careful or timely. | ||
| | The success of our business is dependent on the actions of our collaborative partners. | ||
| | If we are unable to obtain and enforce patent protection for our products, our business could be materially harmed. | ||
| | If we are unable to protect the confidentiality of our proprietary information and know-how, the value of our technology and products could be adversely affected. | ||
| | We will rely heavily on licenses from third parties. | ||
| | We license patent rights to certain of our technology from third-party owners. If such owners do not properly maintain or enforce the patents underlying such licenses, our competitive position and business prospects will be harmed. | ||
| | Our commercial success depends significantly on our ability to operate without infringing the patents and other proprietary rights of third parties. | ||
| | Adverse results in material litigation matters or governmental inquiries could have a material adverse effect upon our business and financial condition. | ||
| | Medicare prescription drug coverage legislation and future legislative or regulatory reform of the health care system may affect our ability to sell our products profitably. | ||
| | Failure to obtain regulatory approval outside the United States will prevent us from marketing our product candidates abroad. | ||
| | We may not have the funding available to pursue acquisitions. | ||
| | Acquisitions may disrupt our business, distract our management and may not proceed as planned; and we may encounter difficulties in integrating acquired businesses. | ||
| | Non-U.S. governments often impose strict price controls, which may adversely affect our future profitability. | ||
| | Our business may become subject to legal, economic, political, regulatory and other risks associated with international operations. | ||
| | The market price of our common stock may fluctuate significantly. |
4
Table of Contents
| | Directors, executive officers, principal stockholders and affiliated entities own a significant percentage of our capital stock, and they may make decisions that you do not consider to be in your best interests or in the best interests of our stockholders. | ||
| | Compliance with changing regulations concerning corporate governance and public disclosure may result in additional expenses. | ||
| | If we are unable to satisfy the requirements of Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, as they apply to us, or our internal controls over financial reporting are not effective, the reliability of our financial statements may be questioned and our common stock price may suffer. | ||
| | We may be unable to maintain our listing on the NYSE Amex, which could cause our stock price to fall and decrease the liquidity of our common stock. | ||
| | Future issuances of common stock and hedging activities may depress the trading price of our common stock. | ||
| | Provisions in our charter documents and Delaware law could discourage an acquisition of us by a third party, even if the acquisition would be favorable to you. | ||
| | We do not intend to pay cash dividends on our common stock in the foreseeable future. |
5
Table of Contents
PART I
Unless the context otherwise requires, all references in this Annual Report on Form 10-K to
the Company, OPKO, we, our, ours, and us refers to OPKO Health, Inc., a Delaware
corporation, including our wholly-owned subsidiaries.
ITEM 1. BUSINESS
OVERVIEW
We are a specialty healthcare company focused on the discovery, development and
commercialization of proprietary pharmaceutical products, vaccines, diagnostic technologies, and
imaging systems. Initially focused on the treatment and management of ophthalmic diseases and
conditions, OPKO has since expanded into other areas of major unmet medical need. Our business
presently consists of the development of a broad range of pharmaceutical products and diagnostic
tests, and the development, commercialization and sale of ophthalmic diagnostic and imaging systems
and instrumentation products, as well as the sale of pharmaceutical products, over-the-counter
products and medical devices to government, private and institutional markets in Chile and Mexico.
Our objective is to establish industry-leading positions in large and rapidly growing medical
markets by leveraging our preclinical and development expertise and our novel and proprietary
technologies. We also actively explore opportunities to acquire complementary pharmaceuticals,
compounds, technologies, and businesses, which could, individually or in the aggregate, materially
increase the scale of our business.
GROWTH STRATEGY
We expect our future growth to come from:
| | leveraging our proprietary technology and research and development strengths to develop our pharmaceutical product pipeline; | ||
| | discovering and developing and/or acquiring or licensing new products; and | ||
| | being opportunistic and pursuing complementary, accretive, or strategic acquisitions and investments. |
Leverage Proprietary Technology and Development Strengths
We have a broad and diversified portfolio of small molecules, vaccines and biologicals
targeting a broad range of unmet medical needs. We intend to continue to leverage our proprietary
technology and our strengths in all phases of pharmaceutical research and development to further
develop and commercialize our portfolio of proprietary pharmaceutical and diagnostic products.
Key elements of our strategy are to:
| | Obtain regulatory approval for our most advanced product candidates; | ||
| | Develop a focused commercialization capability in the United States; | ||
| | Strategically utilize our research and development resources to advance our product pipeline; | ||
| | Develop and grow our instrumentation business beyond diagnostic and imaging systems to include drug delivery devices and other therapeutic devices and technologies; and | ||
| | Expand into other medical markets which provide significant opportunities and which we believe are complementary to and synergistic with our business. |
Discovery and Development and/or Acquisition of New Products
Acquisitions and licenses of new products have in the past helped us to build our company, and
we expect that new products that we discover, develop, acquire, or license will provide a
cornerstone for our future growth. In November 2009, we acquired rolapitant, our lead
pharmaceutical product candidate, and other neurokinin-1 (NK-1) assets from Schering Plough
Corporation. Rolapitant, a potent and selective competitive antagonist of the NK-1 receptor, has
successfully completed Phase II clinical testing for prevention of chemotherapy induced nausea and
vomiting and post-operative induced nausea and vomiting. We intend to pursue final
development and commercialization of rolapitant for both indications. Phase I clinical testing has
also been completed for a second compound in the same class, which is being considered for further
development in other indications.
6
Table of Contents
In June 2009, we acquired exclusive, worldwide rights to a new platform technology for the
rapid identification of molecules that can be useful in the creation of new, important diagnostic
tests as well as the development of vaccines and therapeutic agents. The first diagnostic product
we are pursuing is a simple blood test for Alzheimers Disease.
In July 2009, we acquired worldwide rights from Academia Sinica in Taipei, Taiwan, for a new
technology to develop protein vaccines against influenza and other viral infections. We believe
this innovative technology will, among other things, permit the development of a molecular protein
based flu vaccine that will cross react with H1, H3 or H5 flu variances. Instead of the typical
method of making a cocktail of inactivated viruses for annual flu shots, this new approach to
anti-viral vaccines is designed to recognize and destroy new strains of flu virus before the virus
has a chance to mutate. OPKO has formed a subsidiary in Taiwan to collaborate closely with
Academia Sinica in the development of a universal flu vaccine.
In March 2010, we acquired worldwide rights from Academia Sinica for a new technology to
target cancer cells and deliver chemotherapeutic agents to the target site to treat various forms
of cancer. We also acquired worldwide rights from Academia Sinica to certain alpha-galactosyl
ceramide analogs which are believed to be useful as vaccines or vaccine adjuvants for a wide
variety of disorders including cancer, infectious disease and autoimmune disease.
We are working in conjunction with Academia Sinica to advance and
develop compounds under these technologies.
Pursue Complementary, Accretive and Strategic Acquisitions and Investments
We expect to use well-timed, carefully selected acquisitions and investments to continue to
drive our growth. We intend to pursue acquisitions that will complement our existing businesses
and provide new product and market opportunities, improve the bottom line, leverage our existing
assets, and contribute to our own organic growth. In assessing strategic opportunities, we will
consider whether the acquisition target:
| | is a mature profit-generating business accretive to our bottom line; | ||
| | allows us to leverage our expertise in our existing areas of therapeutic focus by adding new products or product development capabilities; | ||
| | will help us further our own organic growth; and | ||
| | offers geographic expansion opportunities into key strategic markets. |
In February 2010, we completed the acquisition of Pharmacos Exakta S.A. de C.V. (Pharmacos
Exakta), a Mexican pharmaceutical business engaged in the manufacture, marketing, sale, and
distribution of ophthalmic and other pharmaceutical products in Mexico. In October 2009, we
completed the acquisition of Pharma Genexx, S.A. (Pharma Genexx), a privately owned Chilean
company engaged in the marketing, sale, and distribution of pharmaceutical products, devices, and
over-the-counter products for government, private, and institutional markets in Chile.
In September 2009, we made an investment in Cocrystal Discovery, Inc., a privately held
biopharmaceutical company (Cocrystal) in exchange for shares of Cocrystals Convertible Series A
Preferred Stock. In June 2009, we invested in Sorrento Therapeutics, Inc. (Sorrento), a
development-stage biopharmaceutical company focused on applying its proprietary technology platform
for the discovery and development of human therapeutic antibodies for the treatment of a variety of
disease conditions, including cancer, inflammation, metabolic disease and infectious disease.
We may make investments in other early stage companies that we perceive to have valuable
proprietary technology and significant upside potential in creating value for OPKO as a
shareholder.
7
Table of Contents
Corporate Information
We were originally incorporated in Delaware in October 1991 under the name Cytoclonal
Pharmaceutics, Inc., which was later changed to eXegenics, Inc. On March 27, 2007, we were part of
a three-way merger with Froptix Corporation, or Froptix, a research and development company, and
Acuity Pharmaceuticals, Inc., or Acuity, a research and development company. This transaction was
accounted for as a reverse merger between Froptix and eXegenics, with the combined company then
acquiring Acuity. eXegenics was previously involved in the research, creation, and development of
drugs for the treatment and prevention of cancer and infectious diseases; however, eXegenics had
been a public shell company without any operations since 2003. On June 8, 2007, we changed our
name to OPKO Health, Inc.
On November 28, 2007, we acquired Ophthalmic Technologies, Inc. (OTI), an Ontario
corporation pursuant to a definitive share purchase agreement with OTI and its shareholders. As a
result of this agreement, we entered the ophthalmic instrumentation market and began
generating revenue from this business.
On May 6, 2008, we completed the acquisition of Vidus Ocular, Inc. (Vidus), a privately-held
company that is developing Aquashunt, a device for the treatment of refractory open angle
glaucoma. In January 2009, we began treating patients in a clinical trial designed to assess the
safety and efficacy of the Aquashunt.
In October 2009, we acquired Pharma Genexx, a Chilean company engaged in the marketing, sale,
and distribution of pharmaceutical products, over-the-counter products and medical devices for
government, private and institutional markets in Chile.
In February 2010, we completed the acquisition of Pharmacos Exakta, a Mexican pharmaceutical
business engaged in the manufacture, marketing, sale, and distribution of ophthalmic and other
pharmaceutical products in Mexico.
Our shares are publicly traded on the NYSE Amex under the ticker OPK. Our principal
executive offices are located in Miami, Florida. We also have offices in Santiago, Chile, a
research and development branch office in Kingston, Ontario, Canada, a manufacturing facility in
Hialeah, Florida, and a research and development office in the United Kingdom at the University of
Kent. As a result of our recent acquisition of Pharmacos Exakta, we also have offices and a
manufacturing facility in Guadalajara, Mexico. Our Internet website address is www.OPKO.com.
We currently manage our operations in two reportable segments, pharmaceutical and
instrumentation segments. The pharmaceutical segment consists of two operating segments, (i) our
pharmaceutical research and development segment which is focused on the research and development of
pharmaceutical products, diagnostic tests, and vaccines, and (ii) the pharmaceutical operations we
acquired in Chile through the acquisition of Pharma Genexx. The instrumentation segment consists
of ophthalmic instrumentation devices and the activities related to the research, development,
manufacture, and commercialization of those products. Additional business segment information is
set forth in Part II, Item 8 Financial Statements and Note 16Segments to the Consolidated
Financial Statements of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
PHARMACEUTICAL BUSINESS
Current Product Candidates and Related Markets
We presently have several compounds and technologies in research and development for the
pharmaceutical and diagnostic markets for a broad range of indications and conditions. The
following table lists our most advanced product candidates, the initial indications that we plan to
address through their development, and their development stage.
8
Table of Contents
| Product Candidate | Initial Indication | Development Stage | ||
| Rolapitant | Emesis
|
Phase III | ||
| Alzheimers Test | Alzheimers Diagnostic
|
Pre-Clinical | ||
| Flu Vaccine | Pan-Influenza (e.g. H1, H3, H5)
|
Pre-Clinical | ||
| Bevasiranib | Wet AMD
|
Phase III | ||
| Doxovir | Viral Conjunctivitis
|
Phase II | ||
| SCH 900978 | Emesis
|
Phase II | ||
| OPK-HVB-004 | Wet AMD/Diabetic Retinopathy/Diabetic Macular Edema |
Pre-Clinical | ||
| OPK-HVB-010 | Wet AMD/Diabetic
Retinopathy/Diabetic Macular Edema |
Pre-Clinical |
All of our product development candidates are in an early stage of development. There can be
no assurance that we will be able to successfully formulate any of these product candidates under
development as planned, or that we will be successful in demonstrating the safety and efficacy of
such products under development in human clinical trials. Thus, there can be no assurances that
any of these product candidates will be developed and commercialized in a timely manner, or in
accordance with our plans or projections, or at all. We may determine to discontinue the
development of any or all of our products under development at any time.
NK-1 Program
Rolapitant. Our lead product candidate, rolapitant, a potent and selective competitive
antagonist of the NK-1 receptor, has successfully completed Phase II clinical testing for
prevention of chemotherapy induced nausea and vomiting and post-operative induced nausea and
vomiting. We intend to pursue final development and commercialization of rolapitant for both
indications. NK-1 receptors are highly concentrated in the brain and are also found in other
tissues of the body. Activation of NK-1 receptors leads to the release of neurotransmitters and
other signaling molecules that play a central role in controlling nausea and vomiting and other
basic functions. Phase I clinical testing has also been completed for a second compound in the
same class, which is being considered for further development in other indications.
The emesis market is estimated to be in excess of $2 billion. There are more than two million
chemotherapy patients each year in the United States, Europe, and Japan alone, and there are more
than 23 million surgery patients in the United States and Europe. NK-1 receptor antagonists and
5HT3 receptor antagonists are major classes of drugs used for prevention of nausea and vomiting.
In general, NK-1 inhibitors are complementary to 5HT3 inhibitors with potential for additive
effects in post operative nausea and vomiting and demonstrated additive effects in chemotherapy
induced nausea and vomiting. While there are several approved 5HT3 receptor antagonists
(palonosetron (Aloxi), ondansetron (Zocor), and other generics), there is only one NK-1 receptor
antagonist approved for commercial use, aprepitant (Emend®).
Molecular Diagnostics
In June 2009, we acquired exclusive, worldwide rights to a new platform technology for the
rapid identification of molecules that can be useful as vaccines and new drugs, and to create new
diagnostic tests. The first diagnostic product we are pursuing utilizing this technology is a
simple blood test for Alzheimers Disease. The test is designed to detect elevated levels of
antibodies that are unique to Alzheimers Disease and could be useful in stratifying patients for
ongoing clinical trials of potential Alzheimers drugs as well as to confirm the diagnosis in a
clinical setting. The Alzheimer Disease-specific antibodies were discovered using this novel
proprietary platform that we believe is capable of identifying biomarkers for any disease to which
the immune system reacts, including cancer, autoimmune disease, neurodegenerative disease and
infectious disease.
Currently it is estimated that over five million people in the United States, and almost 35
million worldwide, have Alzheimers disease and the national cost of caring for people with
Alzheimers is estimated to exceed $148 billion annually. By 2050, it is estimated that 16 million
people in the United States will have Alzheimers, and the global prevalence of Alzheimers is
expected to be greater than 115 million. Currently there are no approved early diagnostic tests to
detect Alzheimers disease and follow its progression. Confirmation of diagnosis is performed
through a series of behavioral measurements and brain scans. Definitive diagnosis can be made
only from examination of postmortem brain tissue samples. An effective early diagnostic blood test
would provide a significant breakthrough in supporting definitive early diagnosis.
9
Table of Contents
Ophthalmics
In the developed world, major vision threatening disorders include cataracts, glaucoma, and
Age Related Macular Degeneration, or AMD. The ophthalmic pharmaceuticals market for these
disorders and other conditions of the eye, such as ocular allergies, among others, represent key
markets with significant unmet needs.
SiRNA Product Candidates. We have invested significant resources to address ophthalmic
disease in large and growing markets by employing a powerful and rapidly progressing technology,
known as RNAi, to develop pharmaceutical product candidates. In October 2006, the Nobel Prize in
Medicine was awarded to the two individuals who discovered RNAi. We have taken advantage of this
major scientific breakthrough by inventing and developing siRNAs that shut down the production of
proteins that cause ophthalmic diseases.
We believe we are a pioneer in this area as we conducted the first clinical trials ever with a
siRNA and obtained the first clinical proof of concept with a siRNA. Bevasiranib, a drug candidate
in development for the treatment of Wet AMD, is a first in class siRNA drug designed to silence the
genes that cause vascular endothelial growth factor, or VEGF, which is believed to be largely
responsible for the vision loss associated with Wet AMD, and other related ocular conditions. AMD
is a back-of-the-eye disease involving the retina, macula and fovea, which is characterized by loss
of central visual acuity. Untreated AMD can significantly impact an affected individuals quality
of life. AMD accounts for approximately 55% of blindness in the United States. Direct and
indirect costs attributed to the treatment of AMD in the United States are approximately $30 to $40
billion annually, according to the National Eye Institute, a division of the National Institutes of
Health. Age is the primary risk factor for AMD, and the number of cases of AMD is expected to
increase significantly as the population ages.
In July 2007, we initiated the first of two required pivotal Phase III trials for bevasiranib,
however, on March 6, 2009, following the recommendation of an independent data monitoring committee
(IDMC), we determined to terminate the Phase III clinical trial of bevasiranib. Review of the
data by the IDMC had indicated that the trial as structured was unlikely to meet its primary end
point. We are continuing to evaluate the clinical data in an effort to determine appropriate next
steps regarding the development of bevasiranib. Our willingness to continue to develop bevasiranib
will depend on our understanding of the trial data and the efficacy of the underlying technology.
We intend to continue development of our other siRNA product candidates targeting VEGF. We
are using our expertise in ophthalmology and RNAi technology in the development of our next
generation of anti-VEGFA siRNA molecules, including without limitation, OPK-HVB-004 and
OPK-HVB-010, which are designed to inhibit the angiogenic isoform VEGF165 but spare the
anti-angiogenic isoform VEGF165b. We believe that RNAi based drugs have the potential
to be a significant advancement over the VEGF inhibitors presently on the market because they block
the synthesis of VEGF as opposed to merely neutralizing existing VEGF. In addition, RNAi based
drugs have the potential to require less frequent administration than VEGF inhibitors and have a
better safety profile.
We also have a worldwide exclusive license to commercialize ACU-HHY-011, which is an siRNA
targeting HIF-1a, believed to be the most important transcription factor involved in the cellular
response to hypoxia, a key step in the neovascularization process which occurs in Wet AMD. HIF-1a
is upstream of the target for bevasiranib and preclinical data suggests that targeting HIF-1a may
have advantages over other approaches to treating Wet AMD. HIF-1a modulates the expression of more
than 60 genes, including multiple angiogenic factors under hypoxic conditions, such as VEGF,
angiopoietin-1, angiopoietin-2, placental growth factor, and platelet-derived growth factor-B.
We have a worldwide exclusive license to commercialize siRNAs targeting transforming growth
factor-b receptor Type II, or TbRII, which is an important mediator of wound healing and has been
shown to play a significant causative role in ocular inflammation and scarring. This compound may
have a therapeutic application as an eye drop to prevent complications from ocular surgery, and
could also be developed as an adjunct therapy to bevasiranib or ACU-HHY-011 in Wet AMD patients to
reduce the damage caused by the fibrotic component of Wet AMD.
In addition to bevasiranib and our other siRNA molecules, including and our next generation
siRNA molecules, we are developing a broad range of product candidates for additional ophthalmic
diseases and conditions. These
products address eye diseases with large markets and major unmet medical needs, and range in
developmental stage from clinical to preclinical.
10
Table of Contents
Doxovir. In June 2008, we acquired exclusive worldwide rights in the field of ophthalmology
to a novel small molecule agent in Phase II clinical development for the treatment of viral
conjunctivitis and other viral infections. The agent, CTC-96, also known as Doxovir, was
developed by Redox Pharmaceutical Corporation. Viral conjunctivitis is a highly contagious
epidemic disease and the most common source of acute care visits to eye care professionals in the
United States. Symptoms of viral conjunctivitis include redness, swelling, discharge from the eye,
sticking of eyelids, pain or discomfort in the eye and light sensitivity. We are currently
enrolling patients in a Phase II clinical trial for Doxovir.
Compounds for the Treatment of Dry AMD. We have worldwide exclusive licenses to commercialize
compounds from the University of Florida Research Foundation which have potential to treat Dry AMD
by eliminating disease-causing accumulations of protein molecules at the back of the eye. Proteins
must fold into their correct three-dimensional conformation to achieve their biological function.
The loss of vision associated with Dry AMD is thought to be caused by the destructive effects of
the misfolded protein and debris aggregates like lipofuscin. Autophagy is a cellular process by
which cellular protein aggregates and dysfunctional organelles like mitochondria are degraded. If
methods for increasing autophagy were available, they might enhance the elimination of misfolded
proteins, and eliminate the destructive effects associated with their accumulation. These
compounds may mitigate retinal degeneration by causing the elimination or reduction of drusen in
patients with Dry AMD.
Academia
Sinica Licenses
We
have licensed in several innovative technologies from Academia
Sinica, the most prestigious academic institution in Taiwan, and have
formed a subsidiary in Taiwan to work with Academia Sinica to advance
these technologies and develop products to prevent and treat a
variety of serious medical problems. A description of these
technologies is set forth below:
In July 2009, we acquired worldwide rights from Academia Sinica for a new technology to develop protein vaccines against influenza and other viral
infections. The technology was discovered by Dr. Chi-Huey Wong, a renowned biological chemist, and
his team at Academia Sinica. We are working with
Academia Sinica to develop the first product, a universal flu vaccine, to surmount the problem of
the emergence of new strains against which vaccines produced with presently available technology do
not provide satisfactory protection. We believe this innovative technology will, among other
things, permit the development of a molecular protein based flu vaccine that will cross react with
H1, H3 or H5 flu variances. Instead of the typical method of making a cocktail of inactivated
viruses for annual flu shots, this new approach to anti-viral vaccines is designed to recognize and
destroy new strains of flu virus before the virus has a chance to mutate.
The world-wide seasonal influenza market place is projected to exceed $6 billion by 2013.
Influenza results in more than 200,000 hospitalizations and 46,000 deaths each year in the United
States alone, with economic costs in excess of $80 billion per year. Although there are several
significant companies in the vaccine market, there are unmet needs related to effectiveness in
certain populations, speed to market and reliable and cost effective supply.
In March
2010, we acquired worldwide rights from Academia Sinica for a new technology to target cancer
cells and deliver chemotherapeutic agents to the target site to treat various forms of cancer.
We also acquired worldwide rights from Academia Sinica to certain alpha-galactosyl ceramide
analogs which are believed to be useful as vaccines or vaccine adjuvants for a wide variety of
disorders including cancer, infectious disease and autoimmune disease. We are working in
conjunction with Academia Sinica to advance and develop compounds
under these technologies.
Latin American Operations
In the fourth quarter of 2009, we commenced selling and distributing pharmaceutical products,
over-the-counter products and medical devices for government, private and institutional markets in
Chile through our subsidiary, Pharma Genexx. Pharma Genexx was established in 2006 by FASA, the
largest drugstore chain in Latin America, and Laboratorios Volta S.A., a Chilean pharmaceutical
company. Pharma Genexx sells a broad range of products to the private, hospital and institutional
markets in Chile for a wide range of indications, including without limitation, cardiovascular
products, vaccines, antibiotics, gastro-intestinal products, and hormones, among others. Since its
inception, Pharma Genexx has enjoyed continued growth in sales and profits.
11
Table of Contents
As a result of our acquisition of Pharmacos Exakta, the Mexican pharmaceutical business we
acquired in February 2010, we have also commenced the manufacture, marketing, sale, and
distribution of a broad range of ophthalmic and other pharmaceutical products to private and public
customers in Mexico.
INSTRUMENTATION BUSINESS
Our instrumentation business consists of the development, commercialization and sale of
ophthalmic diagnostic and imaging systems and instrumentation products. Currently, the
instrumentation business is primarily based on the technology platform established by OTI, which
offers innovative systems with advanced diagnostic imaging capabilities and tools to meet the needs
of eye care professionals. We plan to utilize our expertise and resources to expand our business
to include other types of ophthalmic products. These efforts may lead to our acquiring or
developing products which aid in the prevention, diagnosis, treatment, and management of ocular
diseases and conditions. The product types may include diagnostic and imaging equipment, other
instrumentation products, and drug delivery systems and technologies.
Current Product Candidates
We presently market four ophthalmic diagnostic systems and instrumentation products, including
our Spectral OCT SLO Combination Imaging System and ultrasound products, in over 50 countries
worldwide. We offer innovative systems with advanced imaging capabilities and tools designed to
meet the needs of eye care professionals. This complete line of advanced imaging and ultrasound
products provide physicians key information needed for treatment decisions and are used by eye care
professionals in both routine screening and specialized care involving management of major eye
diseases. We believe that our instrumentation products complement our therapeutic products; in the
future, for example, we expect that patient outcomes will be significantly optimized by the use of
our instrumentation products in individualizing treatment as well as monitoring and tracking
disease progression and treatment outcomes over time.
Optical Coherence Tomography / Confocal Scanning Ophthalmoscopy. We currently market a
spectral imaging system which combines Spectral Optical Coherence Tomography, together with a
Confocal Scanning Ophthalmoscope, or Spectral OCT SLO, in a single platform that is used in the
diagnosis, treatment and management of a variety of ocular disorders. The Spectral OCT SLO is
indicated for in vivo viewing, axial cross-sectional, and three-dimensional imaging and measurement
of posterior ocular structures including: retina, macula, retina nerve fiber layer and optic disk.
We currently market and sell the Spectral OCT SLO device in the international and U.S. markets.
We believe the Spectral OCT SLO is an innovative product that offers significant advantages
over current technology in resolution and functionality. OCT technology is being rapidly adopted
by the eye care community for diagnosing AMD, glaucoma and diabetic retinopathy and also tracking
the course of treatment. Our OCT SLO product is unique in that it offers microperimetry
capability, which provides the physician with the ability to correlate loss of visual function with
abnormalities in the retina. Additionally, the OCT SLO diagnostic platform offers a foundation
upon which to build a multitude of diagnostic tests. In the future, we plan to incorporate a
number of imaging and other diagnostic test modalities into the OCT SLO platform.
Ultrasound. We also develop, manufacture, market and sell a full line of advanced ophthalmic
ultrasound systems used by eye care professionals for both routine and specialized care. Our
ultrasound systems include A-scans, B-scans, and Ultrasound Bio-microscope, or UBM, high frequency
B-scan systems. A-scan technology is principally used for eye axial length measurement in the
calculation of the power for an intraocular lens implant. These systems are routinely used prior
to cataract surgery.
The B-scan system displays internal structures of the eye, often when these structures are not
visible by traditional light-based imaging methods. This system has the ability to pass through
opacities and reveal internal structures.
The UBM system is a high frequency ultrasound device that provides detailed structural
assessment of the anterior segment of the eye and is typically used in glaucoma evaluation and
certain refractive surgeries that require precise positioning of lens implantation.
12
Table of Contents
Aquashunt. In addition to our innovative diagnostic and imaging products, we are also
developing the Aquashunt, an innovative shunt used in the treatment of refractory open angle
glaucoma. Glaucoma occurs when
fluid accumulating in the eye raises the intraocular pressure and causes the optic nerve to
degenerate, potentially leading to irreversible vision loss. Glaucoma is increasing in prevalence
as the population ages, currently affecting an estimated 2.4 million people in the United States
and about 60 million people worldwide. It is the leading cause of bilateral, irreversible
blindness.
In January 2009, we began treating patients in a small clinical trial conducted in the
Dominican Republic and Mexico designed to assess the safety and efficacy of the Aquashunt. The
efficacy measures for the study include (i) the percentage change in intraocular pressure from
baseline to 6 months and 12 months post-implantation and (ii) the change in the number of glaucoma
medications from baseline at 6 and 12 months post-implantation. In September, 2009, we had
enrolled and implanted our device in 15 patients, which will be the total number of patients
enrolled.
Ophthalmic Instrumentation Market
The market for ophthalmic instrumentation, including imaging systems and other devices, is
more than $1 billion and growing annually. This growth is primarily driven by an aging patient
population, technological innovation and improvement in treatment options, as well as improved
awareness in patients actively seeking treatment. Ophthalmic instruments, imaging products, and
other medical devices are sold to a variety of eye care practitioners, including retinal and
glaucoma specialists, ophthalmologists, optometrists, retail optometry chain outlets, teaching
institutions, and military hospitals.
RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT EXPENSES
To date, the majority of our research and development expenses have been incurred to develop
our bevasiranib program. During the years ended December 31, 2009, 2008, and 2007, we incurred
$12.9 million, $21.6 million, and $10.9 million, respectively, in research and development expenses
for our various product candidates, primarily bevasiranib. In addition, during 2009, 2008 and 2007 we recorded $2.0 million, $1.4 million, and
$243.8 million for acquired in process research and development related to our acquisitions of the NK-1 compounds, Vidus, and
Acuity. As a result of our acquisition of rolapitant in November 2009, we expect our research and
development expenses will increase from 2009 expenditures as we move into clinical trials for
rolapitant.
INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY
We believe that technology innovation is driving breakthroughs in healthcare. We have adopted
a comprehensive intellectual property strategy which blends the efforts to innovate in a focused
manner with the efforts of our business development activities to strategically in-license
intellectual property rights. We develop, protect, and defend our own intellectual property rights
as dictated by the developing competitive environment. We value our intellectual property assets
and believe we have benefited from early and insightful efforts at understanding the disease and
the molecular basis of potential pharmaceutical intervention.
We actively seek, when appropriate and available, protection for our products and proprietary
information by means of United States and foreign patents, trademarks, trade secrets, copyrights,
and contractual arrangements. Patent protection in the pharmaceutical field, however, can involve
complex legal and factual issues. There can be no assurance that any steps taken to protect such
proprietary information will be effective.
Because the patent positions of pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies are highly
uncertain and involve complex legal and factual questions, the patents owned and licensed by the
Company, or any future patents, may not prevent other companies from developing similar or
therapeutically equivalent products or ensure that others will not be issued patents that may
prevent the sale of our products or require licensing and the payment of significant fees or
royalties. Furthermore, to the extent that any of our future products or methods are not
patentable, that such products or methods infringe upon the patents of third parties, or that our
patents or future patents fail to give us an exclusive position in the subject matter claimed by
those patents, we will be adversely affected. We may be unable to avoid infringement of third
party patents and may have to obtain a license, defend an infringement action, or challenge the
validity of the patents in court. A license may be unavailable on terms and conditions acceptable
to us, if at all. Patent litigation is costly and time consuming, and we may be unable to prevail
in any such patent litigation or devote sufficient resources to even pursue such litigation.
13
Table of Contents
LICENSES AND COLLABORATIVE RELATIONSHIPS
Our strategy is to develop a portfolio of product candidates through a combination of internal
development, acquisition, and external partnerships. Collaborations are key to our strategy and we
continue to build relationships and forge partnerships with companies both inside and outside of
ophthalmology. We completed strategic licensing transactions during 2009 with the University of
Texas Southwestern Medical Center at Dallas and Academia Sinica, and previously with the Trustees
of the University of Pennsylvania, the University of Florida Research Foundation, and Redox
Pharmaceuticals, among others.
COMPETITION
The pharmaceutical and instrumentation industries are highly competitive and require an
ongoing, extensive search for technological innovation. The industries are characterized by
rapidly advancing technologies, intense competition and a strong emphasis on proprietary products.
They also require, among other things, the ability to effectively discover, develop, test and
obtain regulatory approvals for products, as well as the ability to effectively commercialize,
market and promote approved products.
We intend to leverage our technological innovation and proprietary position to effectively
compete in the pharmaceutical market. Numerous companies, however, including major pharmaceutical
companies, specialty pharmaceutical companies and specialized biotechnology companies, are engaged
in the development, manufacture and marketing of pharmaceutical products competitive with those
that we intend to commercialize. Such companies include, among others, Merck, Genentech, Allergan,
Alcon Laboratories, Novartis, Helsinn Healthcare, and Alnylam. For example, Merck currently
markets Emend, an NK-1 compound for post-operative nausea and vomiting and chemotherapy induced
nausea and vomiting. In addition, Genentech, Allergan, Alcon Laboratories, Novartis, Alnylam,
Regeneron and QLT all have products or development programs for Wet AMD. There are also several
companies working to develop early diagnostic tests for Alzheimers disease and universal flu
vaccines. Moreover, there are several companies who either have a product currently on the market
or in development, for glaucoma, conjunctivitis, and other disease states of the eye.
Most of these companies have substantially greater financial and other resources, larger
research and development staffs and more extensive marketing and manufacturing organizations than
ours. This enables them, among other things, to make greater research and development investments
and efficiently utilize their research and development costs, as well as their marketing and
promotion costs, over a broader revenue base. This also provides our competitors with a
competitive advantage in connection with the highly competitive product acquisition and product
in-licensing process, which may include auctions in which the highest bidder wins. Our competitors
may also have more experience and expertise in obtaining marketing approvals from the Food and Drug
Administration (the FDA) and other regulatory authorities. In addition to product development,
testing, approval and promotion, other competitive factors in the pharmaceutical industry include
industry consolidation, product quality and price, product technology, reputation, customer service
and access to technical information.
Our ability to commercialize our pharmaceutical product candidates and compete effectively
will depend, in large part, on:
| | Our ability to meet all necessary regulatory requirements to advance our product candidates through clinical trials and the FDA approval process; | ||
| | the perception by physicians and other members of the health care community of the safety, efficacy and benefits of our products compared to those of competing products or therapies; | ||
| | our ability to manufacture products we may develop on a commercial scale; | ||
| | the effectiveness of our sales and marketing efforts; | ||
| | the willingness of physicians to adopt a new treatment regimen represented by our technology; | ||
| | our ability to secure reimbursement for our product candidates, | ||
| | the price of the products we may develop and commercialize relative to competing products; |
14
Table of Contents
| | our ability to accurately forecast and meet demand for our product candidates if regulatory approvals are achieved; | ||
| | our ability to develop a commercial scale infrastructure either on our own or with a collaborator, which would include expansion of existing facilities, including our manufacturing facilities, development of a distribution network and other operational and financial systems necessary to support our increased scale; | ||
| | our ability to maintain a proprietary position in our technologies; | ||
| | our ability to rapidly expand the existing information technology infrastructure and configure existing operational, manufacturing and financial systems (on our own or with third party collaborators) necessary to support our increased scale, which would include existing or additional facilities and or partners. |
We also face significant competition from competitors for our instrumentation products located
in the United States and abroad, which competitors include companies with a far more diverse
product offering and significantly greater market presence than ours, such as Carl Zeiss Meditec,
Topcon Corporation, and Heidelberg Engineering, as well as a number of smaller competitors and
smaller start-up companies that may also have competing technologies and products. We
differentiate our instrumentation products on the basis of scan quality, precise image
registration, software functionality, and on a diagnostic test known as microperimetry.
Microperimetry allows the clinician to obtain both structure and function from a single device.
Additionally, in the future we intend to couple diagnostic tests to further refine and guide
therapeutic treatments in clinical trials in order to further enhance our competitive position.
GOVERNMENT REGULATION OF OUR DRUG AND DEVICE DEVELOPMENT ACTIVITIES
The U. S. government regulates healthcare through various agencies, including but not limited
to the following: (i) the FDA, which administers the Federal Food, Drug and cosmetic Act (the
FDCA), as well as other relevant laws; (ii) the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (the
CMS), which administers the Medicare and Medicaid programs; (iii) the Office of Inspector General
(OIG), which enforces various laws aimed at curtailing fraudulent or abusive practices, including
by way of example, the Anti-Kickback Law, the Anti-Physician Referral Law, commonly referred to as
the Stark law, the Anti-Inducement Law, the Civil Money Penalty Law, and the laws that authorize
the OIG to exclude healthcare providers and others from participating in federal healthcare
programs; and (iv) the Office of Civil Rights, which administers the privacy aspects of the Health
Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 (HIPAA). All of the aforementioned are
agencies within the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). Healthcare is also provided
or regulated, as the case may be, by the Department of Defense through its TriCare program, the
Department of Veterans Affairs, especially through the Veterans Health Care Act of 1992, the Public
Health Service within HHS under Public Health Service Act § 340B (42 U.S.C. § 256b), the Department
of Justice through the Federal False Claims Act and various criminal statutes, and state
governments under the Medicaid and other state sponsored or funded programs and their internal laws
regulating all healthcare activities.
The testing, manufacture, distribution, advertising, and marketing of drug products and
medical devices are subject to extensive regulation by federal, state, and local governmental
authorities in the United States, including the FDA, and by similar agencies in other countries.
Any product that we develop must receive all relevant regulatory approvals or clearances, as the
case may be, before it may be marketed in a particular country. The pre-market approval (PMA)
clearance processes for drugs differ from those for devices.
The regulatory process, which includes overseeing preclinical studies and clinical trials of
each pharmaceutical compound to establish its safety and efficacy and confirmation by the FDA that
good laboratory, clinical, and manufacturing practices were maintained during testing and
manufacturing, can take many years, requires the expenditure of substantial resources, and gives
larger companies with greater financial resources a competitive advantage over us. Delays or
terminations of clinical trials that we undertake would likely impair our development of product
candidates. Delays or terminations could result from a number of factors, including stringent
enrollment criteria, slow rate of enrollment, size of patient population, having to compete with
other clinical trials for eligible patients, geographical considerations, and others.
15
Table of Contents
The FDA review processes can be lengthy and unpredictable, and we may encounter delays or
rejections of our applications when submitted. Generally, in order to gain FDA approval, we must
first conduct preclinical studies in
a laboratory and in animal models to obtain preliminary information on a compound and to
identify any safety problems. The results of these studies are submitted as part of an IND
application that the FDA must review before human clinical trials of an investigational drug can
commence.
Clinical trials are normally done in three sequential phases and generally take two to five
years or longer to complete. Phase I consists of testing the drug product in a small number of
humans, normally healthy volunteers, to determine preliminary safety and tolerable dose range.
Phase II usually involves studies in a limited patient population to evaluate the effectiveness of
the drug product in humans having the disease or medical condition for which the product is
indicated, determine dosage tolerance and optimal dosage, and identify possible common adverse
effects and safety risks. Phase III consists of additional controlled testing at multiple clinical
sites to establish clinical safety and effectiveness in an expanded patient population of
geographically dispersed test sites to evaluate the overall benefit-risk relationship for
administering the product and to provide an adequate basis for product labeling. Phase IV clinical
trials may be conducted after approval to gain additional experience from the treatment of patients
in the intended therapeutic indication.
After completion of clinical trials of a new drug product, FDA and foreign regulatory
authority marketing approval must be obtained. Assuming that the clinical data support the
products safety and effectiveness for its intended use, an NDA is submitted to the FDA for its
review. Generally, it takes one to three years to obtain approval. If questions arise during the
FDA review process, approval may take a significantly longer period of time. The testing and
approval processes require substantial time and effort and we may not receive approval on a timely
basis, if at all, or the approval that we receive may be for a narrower indication than we had
originally sought, potentially undermining the commercial viability of the product. Even if
regulatory approvals are obtained, a marketed product is subject to continual review, and later
discovery of previously unknown problems or failure to comply with the applicable regulatory
requirements may result in restrictions on the marketing of a product or withdrawal of the product
from the market as well as possible civil or criminal sanctions. For marketing outside the United
States, we also will be subject to foreign regulatory requirements governing human clinical trials
and marketing approval for pharmaceutical products. The requirements governing the conduct of
clinical trials, product licensing, pricing, and reimbursement vary widely from country to country.
None of our pharmaceutical products under development has been approved for marketing in the
United States or elsewhere. We may not be able to obtain regulatory approval for any such products
under development in a timely manner, if at all. Failure to obtain requisite governmental
approvals or failure to obtain approvals of the scope requested will delay or preclude us, or our
licensees or marketing partners, from marketing our products, or limit the commercial use of our
products, and thereby would have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition,
and results of operations. See Risk FactorsThe results of previous clinical trials may not be
predictive of future results, and our current and planned clinical trials may not satisfy the
requirements of the FDA or other non-U. S. regulatory authorities.
Devices are subject to varying levels of premarket regulatory control, the most comprehensive
of which requires that a clinical evaluation be conducted before a device receives approval for
commercial distribution. The FDA classifies medical devices into one of three classes: Class I
devices are relatively simple and can be manufactured and distributed with general controls; Class
II devices are somewhat more complex and require greater scrutiny; Class III devices are new and
frequently help sustain life.
In the United States, a company generally can obtain permission to distribute a new device in
one of two ways. The first applies to any device that is substantially equivalent to a device
first marketed prior to May 1976, or to another device marketed after that date, but which was
substantially equivalent to a pre-May 1976 device. These devices are either Class I or Class II
devices. To obtain FDA permission to distribute the device, the company generally must submit a
section 510(k) submission, and receive an FDA order finding substantial equivalence to a predicate
device (pre-May 1976 or post-May 1976 device that was substantially equivalent to a pre-May 1976
device) and permitting commercial distribution of that device for its intended use. A 510(k)
submission must provide information supporting a claim of substantial equivalence to the predicate
device. If clinical data from human experience are required to support the 510(k) submission,
these data must be gathered in compliance with investigational device exemption (IDE) regulations
for investigations performed in the United States. The 510(k) process is normally used for
products of the type that the Company proposes distributing. The FDA review process for premarket
notifications submitted pursuant to section 510(k) takes, on average, about 90 days, but it can
take substantially longer if the FDA has concerns, and there is no guarantee that the FDA will
clear the device for marketing, in which case the device cannot be distributed in the United
States. There is also no guarantee that the FDA will deem the applicable device subject to the
510(k) process, as opposed to the more time-consuming, resource-intensive and problematic, PMA
process described below.
16
Table of Contents
The second, more comprehensive, approval process applies to a new device that is not
substantially equivalent to a pre-1976 product or that is to be used in supporting or sustaining
life or preventing impairment. These devices are normally Class III devices. For example, most
implantable devices are subject to the approval process. Two steps of FDA approval are generally
required before a company can market a product in the United States that is subject to approval, as
opposed to clearance. First, a company must comply with IDE regulations in connection with any
human clinical investigation of the device. These regulations permit a company to undertake a
clinical study of a non-significant risk device without formal FDA approval. Prior express FDA
approval is required if the device is a significant risk device. Second, the FDA must review the
companys PMA application, which contains, among other things, clinical information acquired under
the IDE. The FDA will approve the PMA application if it finds there is reasonable assurance that
the device is safe and effective for its intended use. The PMA process takes substantially longer
than the 510(k) process and it is conceivable that the FDA would not agree with our assessment that
a device that we propose to distribute should be a Class I or Class II device. If that were to
occur we would be required to undertake the more complex and costly PMA process. However, for
either the 510(k) or the PMA process, the FDA could require us to run clinical trials, which would
pose all of the same risks and uncertainties associated with the clinical trials of drugs,
described above.
Even when a clinical study has been approved by the FDA or deemed approved, the study is
subject to factors beyond a manufacturers control, including, but not limited to the fact that the
institutional review board at a given clinical site might not approve the study, might decline to
renew approval which is required annually, or might suspend or terminate the study before the study
has been completed. Also, the interim results of a study may not be satisfactory; leading the
sponsor to terminate or suspend the study on its own initiative or the FDA may terminate or suspend
the study. There is no assurance that a clinical study at any given site will progress as
anticipated; there may be an insufficient number of patients who qualify for the study or who agree
to participate in the study or the investigator at the site may have priorities other than the
study. Also, there can be no assurance that the clinical study will provide sufficient evidence to
assure the FDA that the product is safe and effective, a prerequisite for FDA approval of a PMA, or
substantially equivalent in terms of safety and effectiveness to a predicate device, a prerequisite
for clearance under 510(k). Even if the FDA approves or clears a device, it may limit its intended
uses in such a way that manufacturing and distributing the device may not be commercially feasible.
After clearance or approval to market is given, the FDA and foreign regulatory agencies, upon
the occurrence of certain events, are authorized under various circumstances to withdraw the
clearance or approval or require changes to a device, its manufacturing process or its labeling or
additional proof that regulatory requirements have been met.
A manufacturer of a device approved through the PMA is not permitted to make changes to the
device which affect its safety or effectiveness without first submitting a supplement application
to its PMA and obtaining FDA approval for that supplement. In some instances, the FDA may require
clinical trials to support a supplement application. A manufacturer of a device cleared through
the 510(k) process must submit another premarket notification if it intends to make a change or
modification in the device that could significantly affect the safety or effectiveness of the
device, such as a significant change or modification in design, material, chemical composition,
energy source or manufacturing process. Any change in the intended uses of a PMA device or a
510(k) device requires an approval supplement or cleared premarket notification. Exported devices
are subject to the regulatory requirements of each country to which the device is exported, as well
as certain FDA export requirements.
A company that intends to manufacture medical devices is required to register with the FDA
before it begins to manufacture the device for commercial distribution. As a result, we and any
entity that manufactures products on our behalf will be subject to periodic inspection by the FDA
for compliance with the FDAs Quality System Regulation requirements and other regulations. In the
European Community, we will be required to maintain certain International Organization for
Standardization (ISO) certifications in order to sell products and we or our manufacturers
undergo periodic inspections by notified bodies to obtain and maintain these certifications. These
regulations require us or our manufacturers to manufacture products and maintain documents in a
prescribed manner with respect to design, manufacturing, testing and control activities. Further,
we are required to comply with various FDA and other agency requirements for labeling and
promotion. The Medical Device Reporting regulations require that we provide information to the FDA
whenever there is evidence to reasonably suggest that a device may have caused or contributed to a
death or serious injury or, if a malfunction were to occur, could cause or contribute to a death or
serious injury. In addition, the FDA prohibits us from promoting a medical device for unapproved
indications.
The FDA in the course of enforcing the FDCA Act may subject a company to various sanctions for
violating FDA regulations or provisions of the Act, including requiring recalls, issuing Warning
Letters, seeking to impose civil money penalties, seizing devices that the agency believes are
non-compliant, seeking to enjoin distribution of a
specific type of device or other product, seeking to revoke a clearance or approval, seeking
disgorgement of profits and seeking to criminally prosecute a company and its officers and other
responsible parties.
17
Table of Contents
The levels of revenues and profitability of biopharmaceutical companies may be affected by the
continuing efforts of government and third party payers to contain or reduce the costs of health
care through various means. For example, in certain foreign markets, pricing or profitability of
therapeutic and other pharmaceutical products is subject to governmental control. In the United
States, there have been, and we expect that there will continue to be, a number of federal and
state proposals to implement similar governmental control. In addition, in the United States and
elsewhere, sales of therapeutic and other pharmaceutical products are dependent in part on the
availability and adequacy of reimbursement from third party payers, such as the government or
private insurance plans. Third party payers are increasingly challenging established prices, and
new products that are more expensive than existing treatments may have difficulty finding ready
acceptance unless there is a clear therapeutic benefit. We cannot assure you that any of our
products will be considered cost effective, or that reimbursement will be available or sufficient
to allow us to sell them competitively and profitably.
Our instrumentation products are subject to regulation by the FDA and similar international
health authorities. We also have an obligation to adhere to the FDAs cGMP regulations.
Additionally, we are subject to periodic FDA inspections, quality control procedures, and other
detailed validation procedures. If the FDA finds deficiencies in the validation of our
manufacturing and quality control practices, they may impose restrictions on marketing specific
products until corrected.
We are also subject to various federal, state, and international laws pertaining to health
care fraud and abuse, including anti-kickback laws and false claims laws. Anti-kickback laws
make it illegal to solicit, offer, receive or pay any remuneration in exchange for, or to induce,
the referral of business, including the purchase or prescription of a particular drug or the use of
a service or device. Federal and state false claims laws prohibit anyone from knowingly and
willingly presenting, or causing to be presented for payment to third-party payors (including
Medicare and Medicaid), claims for reimbursed drugs or services that are false or fraudulent,
claims for items or services not provided as claimed, or claims for medically unnecessary items or
services. If the government were to allege against or convict us of violating these laws, there
could be a material adverse effect on us, including our stock price. Even an unsuccessful
challenge could cause adverse publicity and be costly to respond to, which could have a materially
adverse effect on our business, results of operations and financial condition. We will consult
counsel concerning the potential application of these and other laws to our business and our sales,
marketing and other activities and will make good faith efforts to comply with them. However,
given their broad reach and the increasing attention given by law enforcement authorities, we
cannot assure you that some of our activities will not be challenged or deemed to violate some of
these laws.
Foreign Corrupt Practices Act
We are also subject to the U.S. Foreign Corrupt Practices Act (FCPA), which prohibits
corporations and individuals from paying, offering to pay, or authorizing the payment of anything
of value to any foreign government official, government staff member, political party, or political
candidate in an attempt to obtain or retain business or to otherwise influence a person working in
an official capacity. The FCPA also requires public companies to make and keep books and records
that accurately and fairly reflect their transactions and to devise and maintain an adequate system
of internal accounting controls. Our international activities create the risk of unauthorized
payments or offers of payments by our employees, consultants, sales agents or distributors, even
though they may not always be subject to our control. We discourage these practices by our
employees and agents. However, our existing safeguards and any future improvements may prove to be
less than effective, and our employees, consultants, sales agents or distributors may engage in
conduct for which we might be held responsible. Any failure by us to adopt appropriate compliance
procedures and ensure that our employees and agents comply with the FCPA and applicable laws and
regulations in foreign jurisdictions could result in substantial penalties or restrictions on our
ability to conduct business in certain foreign jurisdictions.
18
Table of Contents
MANUFACTURING AND QUALITY
Other than our facility in Guadalajara, Mexico, we currently have no pharmaceutical
manufacturing facilities. We have entered into agreements with various third parties for the
formulation and manufacture of our pharmaceutical clinical supplies. These suppliers and their
manufacturing facilities must comply with FDA regulations, current good laboratory practices, or
cGLPs, and current good manufacturing practices, or cGMPs. We plan to outsource the manufacturing
and formulation of our clinical supplies.
We have instrumentation manufacturing facilities in Hialeah, Florida, which predominantly
perform high level assembly for our instrumentation products. Certain of our products components
and optical subsystems are produced by sub-contracted vendors that specialize in optical device
manufacturing.
On March 25, 2008, we received a warning letter in connection with a FDA inspection of the OTI
facility in Toronto, Canada, in July and August of 2007. The warning letter cited several
deficiencies in quality, record keeping, and reporting systems relating to certain of its products,
including the OTI Scan 1000, OTI Scan 2000, and OTI OCT SLO combination imaging system. The
warning letter noted that OTIs Toronto facility was not in compliance with cGMP. The FDA further
indicated that it issued an Import Alert and may refuse admission of these products into the United
States. Upon receipt of the warning letter, we immediately began to take corrective action to
address the FDAs concerns and to assure the quality of OTIs products. On September 18, 2008, we
received a letter from the FDA stating that our responses to the warning letter indicated that we
may have made adequate corrections to the deficiencies identified in the warning letter, and a
re-inspection by the FDA of the OTI facility in Toronto would be necessary. During January 2009,
the FDA re-inspected the Toronto facility, and we did not receive any citation of deficiency. We
closed the Toronto facility and relocated its operations to Hialeah, Florida in the fourth quarter
of 2009.
We are committed to providing high quality products to our customers, and we plan to meet this
commitment by working diligently to continue implementing updated and improved quality systems and
concepts throughout our organization.
SALES & MARKETING
We currently do not have pharmaceutical sales or marketing personnel in the United States and
have limited personnel in Chile and Mexico. In order to commercialize any pharmaceutical products
that are approved for commercial sale, we must either build a sales and marketing infrastructure or
collaborate with third parties with sales and marketing experience.
We intend to develop our own direct sales force in the United States to sell our
instrumentation products primarily to retinal and glaucoma specialists and ophthalmologists. Our
instrumentation division presently has a seven-person sales and marketing staff. We have offices
in Canada, the United States and the United Kingdom and a distributor network that currently covers
more than 50 countries. Our strategy is to increase sales of existing products through expansion
of our sales channel in the United States and to provide additional marketing resources to our
international distributor network.
SERVICE & SUPPORT
We currently offer service and telephone support for all of our marketed instrumentation
products. Warranties are given on all products against defects of labor and material. Extended
Service Contracts are available for purchase. Product repairs are performed onsite at our Hialeah
facility, and previously at our Toronto facility.
EMPLOYEES
As of December 31, 2009, we had 95 full-time employees worldwide. None of our employees are
represented by a collective bargaining agreement.
19
Table of Contents
MANAGEMENT
Executive Officers
The following table sets forth information concerning our current executive officers,
including their ages:
| Name | Age | Title | ||||
| Phillip Frost, M.D. | 73 | Chief Executive Officer and Chairman of the Board |
||||
| Jane H. Hsiao, Ph.D., MBA | 62 | Chief Technical Officer and Vice Chairman |
||||
| Steven D. Rubin | 49 | Executive Vice President Administration and
Director |
||||
| Rao Uppaluri, Ph.D. | 60 | Senior Vice President and Chief Financial Officer |
||||
Phillip Frost, M.D. Dr. Frost became the CEO and Chairman of OPKO Health, Inc. upon the
consummation of the merger of Acuity Pharmaceuticals Inc., Froptix Corporation and eXegenics, Inc.
on March 27, 2007 (referred to as the Acquisition). Dr. Frost was named the Chairman of the
Board of Teva Pharmaceutical Industries, Limited, or Teva, (NASDAQ:TEVA) in March 2010 and had
previously been Vice Chairman since January 2006 when Teva acquired IVAX Corporation, or IVAX. Dr.
Frost had served as Chairman of the Board of Directors and Chief Executive Officer of IVAX
Corporation since 1987. He was Chairman of the Department of Dermatology at Mt. Sinai Medical
Center of Greater Miami, Miami Beach, Florida from 1972 to 1986. Dr. Frost was Chairman of the
Board of Directors of Key Pharmaceuticals, Inc. from 1972 until the acquisition of Key
Pharmaceuticals by Schering Plough Corporation in 1986. Dr. Frost was named Chairman of the Board
of Ladenburg Thalmann Financial Services Inc. (NYSE Amex:LTS), an investment banking, asset
management, and securities brokerage firm providing services through its principal operating
subsidiary, Ladenburg Thalmann & Co. Inc., in July 2006 and has been a director of Ladenburg
Thalmann since March 2005. Dr. Frost also serves as Chairman of the Board of Directors of PROLOR
Biotech, Inc., a development stage biopharmaceutical company (OTCBB:MODG), and Castle Brands, a
developer and marketer of premium brand spirits (NYSE Amex:ROX). He serves on the Board of Regents
of the Smithsonian Institution, and is a member of the Board of Trustees of the University of
Miami, a Trustee of each of the Scripps Research Institutes, the Miami Jewish Home for the Aged,
and the Mount Sinai Medical Center. Dr. Frost is also a director of Continucare Corporation, a
provider of outpatient healthcare services, and Cocrystal Discovery, Inc., a privately held
biopharmaceutical company.
Jane H. Hsiao, Ph.D., MBA. Dr. Hsiao has served as Vice-Chairman and Chief Technical Officer
of the Company since May 2007. Dr. Hsiao served as the Vice Chairman-Technical Affairs of IVAX
from 1995 to January 2006, when Teva acquired IVAX. Dr. Hsiao served as IVAXs Chief Technical
Officer since 1996, and as Chairman, Chief Executive Officer and President of IVAX Animal Health,
IVAXs veterinary products subsidiary, since 1998. From 1992 until 1995, Dr. Hsiao served as
IVAXs Chief Regulatory Officer and Assistant to the Chairman. Dr. Hsiao has served as Chairman of
the Board of each of Safestitch Medical, Inc. (OTCBB:SFES) and Non-Invasive Monitoring Systems,
Inc. (OTCBB:NIMU), both medical device companies, since September 2007 and October 2008,
respectively. Dr. Hsiao is also a director of PROLOR Biotech, Inc., a development stage
biopharmaceutical company, Sorrento Therapeutics, Inc. (OTCBB:SRNE), a development-stage
biopharmaceutical company, Cocrystal Discovery, Inc., a privately held biopharmaceutical company,
and Neovasc, Inc. (TSXV:NVC), a company developing and marketing medical specialty vascular
devices.
Steven D. Rubin. Mr. Rubin has served as Executive Vice President Administration since May
2007 and a director of the Company since February 2007. Mr. Rubin served as the Senior Vice
President, General Counsel and Secretary of IVAX from August 2001 until September 2006. Mr. Rubin
currently serves on the board of directors of Dreams, Inc. (NYSE Amex:DRJ), a vertically integrated
sports licensing and products company, Safestitch Medical, Inc., a medical device company, PROLOR
Biotech, Inc., a development stage biopharmaceutical company, Kidville, Inc. (OTCBB:KVIL), which
operates large, upscale facilities, catering to newborns through five-year-old children and their
families and offers a wide range of developmental classes for newborns-5 year olds, Non-Invasive
Monitoring Systems, Inc., a medical device company, Cardo Medical, Inc., an early-stage orthopedic
medical device company specializing in designing, developing and marketing reconstructive joint
devices and spinal surgical devices (OTCBB:CDOM), Castle Brands, Inc., a developer and marketer of
premium brand spirits, SearchMedia Holdings Limited (NYSE Amex:IDI), a multi-platform media
advertising company in China, Cocrystal
Discovery, Inc., a privately held biopharmaceutical company, and Neovasc, Inc., a company
developing and marketing medical specialty vascular devices.
20
Table of Contents
Rao Uppaluri, Ph.D. Dr. Uppaluri has served as our Senior Vice President and Chief Financial
Officer since May 2007. Dr. Uppaluri served as the Vice President, Strategic Planning and
Treasurer of IVAX from 1997 until December 2006. Before joining IVAX, from 1987 to August 1996,
Dr. Uppaluri was Senior Vice President, Senior Financial Officer and Chief Investment Officer with
Intercontinental Bank, a publicly traded commercial bank in Florida. In addition, he served in
various positions, including Senior Vice President, Chief Investment Officer and Controller, at
Peninsula Federal Savings & Loan Association, a publicly traded Florida S&L, from October 1983 to
1987. His prior employment, during 1974 to 1983, included engineering, marketing and research
positions with multinational companies and research institutes in India and the United States. Dr.
Uppaluri currently serves on the board of directors of Kidville, Inc , which operates large,
upscale facilities, catering to newborns through five-year-old children and their families and
offers a wide range of developmental classes for newborns-5 year olds, Cardo Medical, Inc., an
early-stage orthopedic medical device company specializing in designing, developing and marketing
reconstructive joint devices and spinal surgical devices, Non-Invasive Monitoring Systems, Inc., a
medical devices company, and Winston Pharmaceuticals Inc. (OTCBB:WPHM), a specialty pharmaceutical
company engaged in the discovery and development of products for pain management.
Code of Ethics
We have adopted a Code of Business Conduct and Ethics. We require all employees, including
our principal executive officer and principal accounting officer and other senior officers and our
employee directors, to read and to adhere to the Code of Business Conduct and Ethics in discharging
their work-related responsibilities. Employees are required to report any conduct that they
believe in good faith to be an actual or apparent violation of the Code of Business Conduct and
Ethics. The Code of Business Conduct and Ethics is available on our website at
http://www.OPKO.com.
Available Information
We make available free of charge on or through our web site, at www.opko.com, our Annual Reports
on Form 10-K, Quarterly Reports on Form 10-Q, Current Reports on Form 8-K and all amendments
to those reports as soon as reasonably practicable after such material is electronically filed
with the SEC. Additionally, the public may read and copy any materials we file with the SEC
at the SECs Public Reference Room at 100 F Street, NE, Room 1580, Washington, D.C., 20549.
Information regarding operation of the Public Reference Room is available by calling the SEC
at 1-800-SEC-0330. Information that we file with the SEC is also available at the SECs Web
site at www.sec.gov.
21
Table of Contents
ITEM 1A. RISK FACTORS.
You should carefully consider the risks described below, as well as other information
contained in this report, including the consolidated financial statements and the notes thereto and
Managements Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations. The
occurrence of any of the events discussed below could significantly and adversely affect our
business, prospects, results of operations, financial condition, and cash flows.
RISKS RELATED TO OUR BUSINESS
We have a history of operating losses and we do not expect to become profitable in the near future.
We are a specialty healthcare company with a limited operating history. We are not profitable
and have incurred losses since our inception. We do not anticipate that we will generate revenue
from the sale of proprietary pharmaceutical products for the foreseeable future and we have
generated limited revenue from our instrumentation business. We have not yet submitted any
pharmaceutical products for marketing approval or clearance by regulatory authorities and we do not
currently have rights to any pharmaceutical product candidates that have been approved for
marketing, other than those products sold by our Chilean and Mexican subsidiaries. We continue to
incur research and development and general and administrative expenses related to our operations
and, to date, we have devoted most of our financial resources to research and development,
including our pre-clinical development activities and clinical trials. We expect to continue to
incur losses from our operations for the foreseeable future, and we expect these losses to increase
as we continue our research activities and conduct development of, and seek regulatory approvals
and clearances for, our product candidates, and prepare for and begin to commercialize any approved
or cleared products. If our product candidates fail in clinical trials or do not gain regulatory
approval or clearance, or if our product candidates do not achieve market acceptance, we may never
become profitable. In addition, if we are required by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, or
the FDA, to perform studies in addition to those we currently anticipate, our expenses will
increase beyond expectations and the timing of any potential product approval may be delayed. Even
if we achieve profitability in the future, we may not be able to sustain profitability in
subsequent periods.
Our technologies are in an early stage of development and are unproven.
We are engaged in the research and development of pharmaceutical products, drug delivery
technologies, and diagnostic systems and instruments for the treatment and prevention of various
diseases and conditions. The effectiveness of our technologies is not well-known in, or accepted
generally by, the clinical medical community. There can be no assurance that we will be able to
successfully employ our technologies as therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventative solutions for any
disease or condition. Our failure to establish the efficacy or safety of our technologies would
have a material adverse effect on our business.
In addition, we have a limited operating history. Our operations to date have been primarily
limited to organizing and staffing our company, developing our technology, and undertaking
pre-clinical studies and clinical trials of our product candidates. We have not yet obtained
regulatory approvals for any of our pharmaceutical product candidates. Consequently, any
predictions you make about our future success or viability may not be as accurate as they could be
if we had a longer operating history.
Our product research and development activities may not result in commercially viable products.
Most of our product candidates are in the very early stages of development and are prone to
the risks of failure inherent in drug and medical device product development. We will likely be
required to complete and undertake significant additional clinical trials to demonstrate that our
product candidates are safe and effective to the satisfaction of the FDA and other non-U.S.
regulatory authorities for their intended uses, or are substantially equivalent in terms of safety
and effectiveness to an existing, lawfully marketed non-premarket approved device. Clinical trials
are expensive and uncertain processes that often take years to complete. Failure can occur at any
stage of the process, and successful early positive results do not ensure that the entire clinical
trial or later clinical trials will be successful. Product candidates in clinical-stage trials may
fail to show desired efficacy and safety traits despite early promising results. If our research
and development activities do not result in commercially viable products, our business, results of
operations, and financial condition will be adversely affected.
22
Table of Contents
The results of pre-clinical trials and previous clinical trials may not be predictive of future
results, and our current and planned clinical trials may not satisfy the requirements of the FDA or
other non-U.S. regulatory authorities.
Positive results from pre-clinical studies and early clinical trial experience should not be
relied upon as evidence that later-stage or large-scale clinical trials will succeed. We will be
required to demonstrate with substantial evidence through well-controlled clinical trials that our
product candidates either (i) are safe and effective for use in a diverse population of their
intended uses or (ii) with respect to Class I or Class II devices only, are substantially
equivalent in terms of safety and effectiveness to devices that are already marketed under section
510(k) of the Food, Drug and Cosmetic Act. Success in early clinical trials does not mean that
future clinical trials will be successful because product candidates in later-stage clinical trials
may fail to demonstrate sufficient safety and efficacy to the satisfaction of the FDA and other
non-U.S. regulatory authorities despite having progressed through initial clinical trials.
Further, our drug candidates may not be approved or cleared even if they achieve their primary
endpoints in Phase III clinical trials or registration trials. In addition our device candidates
may not be approved or cleared, as the case may be, even though clinical or other data are, in our
view, adequate to support a device approval or clearance. The FDA or other non-U.S. regulatory
authorities may disagree with our trial design and our interpretation of data from pre-clinical
studies and clinical trials. In addition, any of these regulatory authorities may change
requirements for the approval or clearance of a product candidate even after reviewing and
providing comment on a protocol for a pivotal clinical trial that has the potential to result in
FDA and other non-U.S. regulatory authorities approval. Any of these regulatory authorities may
also approve or clear a product candidate for fewer or more limited indications or uses than we
request or may grant approval or clearance contingent on the performance of costly post-marketing
clinical trials. The FDA or other non-U.S. regulatory authorities may not approve the labeling
claims necessary or desirable for the successful commercialization of our product candidates.
The results of our clinical trials may show that our product candidates may cause undesirable
side effects, which could interrupt, delay or halt clinical trials, resulting in the denial of
regulatory approval by the FDA and other Non-U.S. regulatory authorities.
In light of widely publicized events concerning the safety risk of certain drug products,
regulatory authorities, members of Congress, the Government Accounting Office, medical
professionals, and the general public have raised concerns about potential drug safety issues.
These events have resulted in the withdrawal of drug products, revisions to drug labeling that
further limit use of the drug products, and establishment of risk management programs that may, for
instance, restrict distribution of drug products. The increased attention to drug safety issues
may result in a more cautious approach by the FDA to clinical trials. Data from clinical trials
may receive greater scrutiny with respect to safety, which may make the FDA or other regulatory
authorities more likely to terminate clinical trials before completion, or require longer or
additional clinical trials that may result in substantial additional expense and a delay or failure
in obtaining approval or approval for a more limited indication than originally sought.
We will require substantial additional funding, which may not be available to us on acceptable
terms, or at all.
We are advancing and intend to continue to advance multiple product candidates through
clinical and pre-clinical development. As a result of our entry into private placement
transactions during 2009 in which we raised $81 million, we believe we have the cash and cash
equivalents on hand sufficient to meet our anticipated cash requirements for operations and debt
service for the next 12 months. We have based this estimate on assumptions that may prove to be
wrong or subject to change, and we may be required to use our available capital resources sooner
than we currently expect. Because of the numerous risks and uncertainties associated with the
development and commercialization of our product candidates, we are unable to estimate the amounts
of increased capital outlays and operating expenditures associated with our current and anticipated
clinical trials. Our future capital requirements will depend on a number of factors, including the
continued progress of our research and development of product candidates, the timing and outcome of
clinical trials and regulatory approvals, the costs involved in preparing, filing, prosecuting,
maintaining, defending, and enforcing patent claims and other intellectual property rights, the
status of competitive products, the availability of financing, and our success in developing
markets for our product candidates.
23
Table of Contents
We will need to raise substantial additional capital to engage in and continue our clinical
and pre-clinical development, and commercialization activities. Until we can generate a sufficient
amount of product revenue to finance our cash requirements, which we may never do, we expect to
finance future cash needs primarily through public or private equity offerings, debt financings, or
strategic collaborations. Our ability to obtain additional capital
may depend on prevailing economic conditions and financial, business and other factors beyond
our control. The ongoing disruptions in the United States and global financial markets may
adversely impact the availability and cost of credit, as well as our ability to raise money in the
capital markets. Economic conditions have been, and continue to be volatile and, in the past two
years, the volatility has reached unprecedented levels. Continued instability in these market
conditions may limit our ability to replace, in a timely manner, maturing liabilities and access
the capital necessary to fund and grow our business. There can be no assurance that additional
capital will be available to us on acceptable terms, or at all, which could adversely impact our
business, results of operations, liquidity, capital resources and financial condition. If we are
not able to secure additional funding when needed, we may have to delay, reduce the scope of, or
eliminate one or more of our clinical trials or research and development programs. To the extent
that we raise additional funds by issuing equity securities, our stockholders may experience
additional significant dilution, and debt financing, if available, may involve restrictive
covenants. To the extent that we raise additional funds through collaboration and licensing
arrangements, it may be necessary to relinquish some rights to our technologies or our product
candidates or grant licenses on terms that may not be favorable to us. We may seek to access the
public or private capital markets whenever conditions are favorable, even if we do not have an
immediate need for additional capital at that time.
If our competitors develop and market products that are more effective, safer or less expensive
than our future product candidates, our commercial opportunities will be negatively impacted.
The life sciences industry is highly competitive, and we face significant competition from
many pharmaceutical, biopharmaceutical, biotechnology, and medical device companies that are
researching and marketing products designed to address the diseases and conditions our products are
designed to diagnose, treat, or prevent. We are currently developing therapeutic, diagnostic, and
preventative products that will compete with other drugs, therapies, and medical devices that
currently exist or are being developed. Products we may develop in the future are also likely to
face competition from other drugs, therapies, and medical devices. Many of our competitors have
significantly greater financial, manufacturing, marketing, and drug development resources than we
do. Large pharmaceutical companies, in particular, have extensive experience in clinical testing
and in obtaining regulatory approvals or clearances for drugs or medical devices. These companies
also have significantly greater research and marketing capabilities than we do. Some of the
pharmaceutical companies we expect to compete with include Merck, Genentech, Allergan, Alcon
Laboratories, Pfizer, Alnylam, and Bausch & Lomb, among others. In addition, many universities and
private and public research institutions are active in disease research. Compared to us, many of
our potential competitors have substantially greater capital resources, development resources,
including personnel and technology, clinical trial experience, regulatory experience, expertise in
prosecution of intellectual property rights, manufacturing and distribution experience, and sales
and marketing experience.
We believe that our ability to successfully compete will depend on, among other things:
| | the results of our clinical trials; | ||
| | our ability to recruit and enroll patients for our clinical trials; | ||
| | the efficacy, safety and reliability of our product candidates; | ||
| | the speed at which we develop our product candidates; | ||
| | our ability to design and successfully execute appropriate clinical trials; | ||
| | the timing and scope of regulatory approvals or clearances; | ||
| | our ability to commercialize and market any of our product candidates that may receive regulatory approval or clearance; | ||
| | appropriate coverage and adequate levels of reimbursement under private and governmental health insurance plans, including Medicare; | ||
| | our ability to protect intellectual property rights related to our products; | ||
| | our ability to have our partners manufacture and sell commercial quantities of any approved products to the market; and | ||
| | acceptance of future product candidates by physicians and other health care providers. |
24
Table of Contents
If our competitors market products that are more effective, safer, easier to use or less
expensive than our future product candidates, if any, or that reach the market sooner than our
future product candidates, if any, we may not achieve commercial success. In addition, both the
biopharmaceutical and medical device industries are characterized by rapid technological change.
Because our research approach integrates many technologies, it may be difficult for us to stay
abreast of the rapid changes in each technology. If we fail to stay at the forefront of
technological change, we may be unable to compete effectively. Technological advances or products
developed by our competitors may render our technologies or product candidates obsolete or less
competitive.
We may not continue to develop or be able to successfully commercialize bevasiranib, and our
failure to commercialize bevasiranib, or the experience of significant delays in doing so, may have
a material adverse effect on our business, results of operation, and financial condition.
On March 6, 2009, following the recommendation of the Independent Data Monitoring Committee,
or the IDMC, we determined to terminate the ongoing Phase III clinical trial of bevasiranib.
Review of the data by the IDMC indicated that the trial as structured was unlikely to meet its
primary end point. We have invested a significant portion of our efforts and financial resources
in the development of bevasiranib. We are continuing to evaluate the clinical data in an effort to
determine the factors causing this outcome. Our willingness to continue to develop bevasiranib
will depend on our understanding of the trial data and the efficacy of the underlying technology.
Our inability to timely assess and understand with certainty the factors causing the unfavorable
results of the Phase III trial, a decision not to further commercialize bevasiranib or our ultimate
inability to successfully commercialize bevasiranib could adversely affect our future business,
operating results and financial condition.
Our product development activities could be delayed or stopped.
We do not know whether our other current or planned clinical trials will be completed on
schedule, or at all. Furthermore, we cannot guarantee that our planned clinical trials will begin
on time or at all. The commencement of our planned clinical trials could be substantially delayed
or prevented by several factors, including:
| | a limited number of, and competition for, suitable patients with the particular types of disease required for enrollment in our clinical trials or that otherwise meet the protocols inclusion criteria and do not meet any of the exclusion criteria; | ||
| | a limited number of, and competition for, suitable sites to conduct our clinical trials; | ||
| | delay or failure to obtain FDA or other non-U.S. regulatory authorities approval or agreement to commence a clinical trial; | ||
| | delay or failure to obtain sufficient supplies of the product candidate for our clinical trials; | ||
| | requirements to provide the drugs or medical devices required in our clinical trial protocols or clinical trials at no cost or cost, which may require significant expenditures that we are unable or unwilling to make; | ||
| | delay or failure to reach agreement on acceptable clinical trial agreement terms or clinical trial protocols with prospective sites or investigators; and | ||
| | delay or failure to obtain institutional review board, or IRB, approval to conduct or renew a clinical trial at a prospective site. |
The completion of our clinical trials could also be substantially delayed or prevented by
several factors, including:
| | slower than expected rates of patient recruitment and enrollment; | ||
| | failure of patients to complete the clinical trial; | ||
| | unforeseen safety issues; |
25
Table of Contents
| | lack of efficacy evidenced during clinical trials; | ||
| | termination of our clinical trials by one or more clinical trial sites; | ||
| | inability or unwillingness of patients or medical investigators to follow our clinical trial protocols; and | ||
| | inability to monitor patients adequately during or after treatment. |
Our clinical trials may be suspended or terminated at any time by the FDA, other regulatory
authorities, the IRB for any given site, or us. Additionally, changes in regulatory requirements
and guidance may occur and we may need to amend clinical trial protocols to reflect these changes
with appropriate regulatory authorities. Amendments may require us to resubmit our clinical trial
protocols to IRBs for re-examination, which may impact the costs, timing, or successful completion
of a clinical trial. Any failure or significant delay in commencing or completing clinical trials
for our product candidates could materially harm our results of operations and financial condition,
as well as the commercial prospects for our product candidates.
The regulatory approval process is expensive, time consuming and uncertain and may prevent us or
our collaboration partners from obtaining approvals for the commercialization of some or all of our
product candidates.
The research, testing, manufacturing, labeling, approval, selling, marketing, and distribution
of drug products or medical devices are subject to extensive regulation by the FDA and other
non-U.S. regulatory authorities, which regulations differ from country to country. We are not
permitted to market our product candidates in the United States until we receive approval of a new
drug application, or NDA, a clearance letter under the premarket notification process, or 510(k)
process, or an approval of a pre-market approval, or PMA, from the FDA. We have not submitted a
NDA or PMA application or premarket notification, nor have we received marketing approval or
clearance for any of our proprietary pharmaceutical product candidates. Obtaining approval of a
NDA or PMA can be a lengthy, expensive, and uncertain process. With respect to medical devices,
while the FDA reviews and clears a premarket notification in as little as three months, there is no
guarantee that our products will qualify for this more expeditious regulatory process, which is
reserved for Class I and II devices, nor is there any assurance that even if a device is reviewed
under the 510(k) process that the FDA will review it expeditiously or determine that the device is
substantially equivalent to a lawfully marketed non-PMA device. If the FDA fails to make this
finding, then we cannot market the device. In lieu of acting on a premarket notification, the FDA
may seek additional information or additional data which would further delay our ability to market
the product. Furthermore, we are not permitted to make changes to a device approved through the
PMA or 510(k) which affects the safety or efficacy of the device without first submitting a
supplement application to the PMA and obtaining FDA approval or cleared premarket notification for
that supplement. In some cases, the FDA may require clinical trials to support a supplement
application. In addition, failure to comply with FDA, non-U.S. regulatory authorities, or other
applicable United States and non-U.S. regulatory requirements may, either before or after product
approval or clearance, if any, subject our company to administrative or judicially imposed
sanctions, including, but not limited to the following:
| | restrictions on the products, manufacturers, or manufacturing process; | ||
| | adverse inspectional observations (Form 483), warning letters, or non-warning letters incorporating inspectional observations; | ||
| | civil and criminal penalties; | ||
| | injunctions; | ||
| | suspension or withdrawal of regulatory approvals or clearances; | ||
| | product seizures, detentions, or import bans; | ||
| | voluntary or mandatory product recalls and publicity requirements; | ||
| | total or partial suspension of production; | ||
| | imposition of restrictions on operations, including costly new manufacturing requirements; and | ||
| | refusal to approve or clear pending NDAs or supplements to approved NDAs, applications or pre-market notifications. |
26
Table of Contents
Regulatory approval of an NDA or NDA supplement, PMA, PMA supplement or clearance pursuant to
a pre-market notification is not guaranteed, and the approval or clearance process, as the case may
be, is expensive and may, especially in the case of an NDA or PMA application, take several years.
The FDA also has substantial discretion in the drug and medical device approval and clearance
process. Despite the time and expense exerted, failure can occur at any stage, and we could
encounter problems that cause us to abandon clinical trials or to repeat or perform additional
pre-clinical studies and clinical trials. The number of pre-clinical studies and clinical trials
that will be required for FDA approval or clearance varies depending on the drug or medical device
candidate, the disease or condition that the drug or medical device candidate is designed to
address, and the regulations applicable to any particular drug or medical device candidate. The
FDA can delay, limit or deny approval or clearance of a drug or medical device candidate for many
reasons, including:
| | a drug candidate may not be deemed safe or effective; | ||
| | a medical device candidate may not be deemed to be substantially equivalent to a lawfully marketed non-PMA device, in the case of a premarket notification. | ||
| | FDA officials may not find the data from pre-clinical studies and clinical trials sufficient; | ||
| | the FDA might not approve our or our third-party manufacturers processes or facilities; or | ||
| | the FDA may change its approval or clearance policies or adopt new regulations. |
The Company may, at some future date, seek approval of one or more drugs under the Federal
Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act, Section 505(b)(2) which permits a manufacturer to submit an NDA for
an existing drug compound for intended uses that have already been approved by the FDA, but with
certain different characteristics, such as a different route of administration. Section 505(b)(2)
allows a company to reference the clinical data already collected by the NDA of the drug
supplemented by clinical trial results that address the change (e.g., route of administration).
The Company is not presently involved in clinical trials for a Section 505(b)(2) drug or the
submission of an NDA for such a drug, but could be in the future. If the Company were to submit an
NDA under that section, the Company could be sued for patent infringement by the pharmaceutical
company that owns the patent on the existing approved NDA drug. Such a suit would automatically
preclude the FDA from processing our NDA for 30 months and possibly longer. Defending such a suit
would be costly. If we were to lose the litigation, we could be precluded from marketing the
product until the NDA holders patent expires. Such an adverse result would interfere without
strategic plans and would therefore have adverse financial implications for the Company.
Our product candidates may have undesirable side effects and cause our approved drugs to be taken
off the market.
If a product candidate receives marketing approval and we or others later identify undesirable
side effects caused by such products:
| | regulatory authorities may require the addition of labeling statements, specific warnings, a contraindication, or field alerts to physicians and pharmacies; | ||
| | regulatory authorities may withdraw their approval of the product and require us to take our approved drug off the market; | ||
| | we may be required to change the way the product is administered, conduct additional clinical trials, or change the labeling of the product; | ||
| | we may have limitations on how we promote our drugs; | ||
| | sales of products may decrease significantly; | ||
| | we may be subject to litigation or product liability claims; and | ||
| | our reputation may suffer. |
27
Table of Contents
Any of these events could prevent us from achieving or maintaining market acceptance of the
affected product or could substantially increase our commercialization costs and expenses, which in
turn could delay or prevent us from generating significant revenues from its sale.
Our inability to address quality control issues in a timely manner could delay the production and
sale of our instrumentation products.
We previously received a warning letter in connection with a FDA inspection of the OTI
facility in Toronto, Canada on March 25, 2008 noting several deficiencies in OTIs, quality control
systems relating to certain products. Immediately upon receipt of the warning letter, we began to
take corrective action to address the FDAs concerns and to assure the quality of OTIs products.
On September 18, 2008, we received a letter from the FDA stating that our responses to the warning
letter indicated that we may have made adequate corrections to the deficiencies identified in the
warning letter, and a re-inspection by the FDA of the OTI facility in Toronto would be necessary.
During January 2009, the FDA re-inspected the Toronto facility, and we did not receive a citation
of deficiency. During the fourth quarter of 2009, we relocated operations from Toronto to our
Hialeah facility.
We are committed to providing high quality products to our customers, and we plan to meet this
commitment by working diligently to continue implementing updated and improved quality systems and
concepts throughout our organization. Although we believe we have properly addressed each of the
deficiencies cited by the FDA, we cannot assure you that we will not have quality control issues in
the future, which may result in future warning letters and citations from the FDA. If we receive
any warning letters from the FDA in the future, there can be no assurances regarding the length of
time or cost it will take us to resolve such quality issues to our satisfaction and to the
satisfaction of the FDA. If our remedial actions are not satisfactory to the FDA, we may have to
devote additional financial and human resources to our efforts, and the FDA may take further
regulatory actions against us including, but not limited to, assessing civil monetary penalties or
imposing a consent decree on us, which could result in further regulatory constraints, including
the governance of our quality system by a third party. Our inability to resolve these issues or
the taking of further regulatory action by the FDA may weaken our competitive position and have a
material adverse effect on our business, results of operations and financial condition.
We manufacture products in Mexico through our Mexican subsidiary. Any quality control issues
at our Mexican facility may weaken our competitive position and have a material adverse effect on
our business results of operations and financial condition.
We may not meet regulatory quality standards applicable to our manufacturing and quality processes,
which could have an adverse effect on our business, results of operations and financial condition.
As a medical device manufacturer, we are required to register with the FDA and are subject to
periodic inspection by the FDA for compliance with its Quality System Regulation (QSR)
requirements, which require manufacturers of medical devices to adhere to certain regulations,
including testing, quality control and documentation procedures. Compliance with applicable
regulatory requirements is subject to continual review and is monitored rigorously through periodic
inspections by the FDA. In addition, most international jurisdictions have adopted regulatory
approval and periodic renewal requirements for medical devices, and we must comply with these
requirements in order to market our products in these jurisdictions. In the European Community, we
are required to maintain certain ISO certifications in order to sell our products and must undergo
periodic inspections by notified bodies to obtain and maintain these certifications. Further, some
emerging markets rely on the FDAs Certificate for Foreign Government (CFG) in lieu of their own
regulatory approval requirements. Our, or our manufacturers failure to meet QSR ISO, or any other
regulatory requirements or industry standards could delay production of our products and lead to
fines, difficulties in obtaining regulatory clearances, recalls or other consequences, which could,
in turn, have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, and our financial
condition.
Even if we obtain marketing approvals or clearances for our product candidates, the terms of
approvals and ongoing regulation of our products may limit how we manufacture and market our
product candidates, which could materially impair our ability to generate anticipated revenues.
Once regulatory approval has been granted to market a product, the approved or cleared product
and its manufacturer are subject to continual review. Any approved or cleared product may only be
promoted for its indicated uses. In addition, if the FDA or other non-U.S. regulatory authorities
approve any of our product candidates for marketing, the labeling, packaging, adverse event
reporting, storage, advertising, and promotion for the product will be subject to extensive
regulatory requirements. We and the manufacturers of our products are also required to comply with
current Good Manufacturing Practicing, or cGMP regulations, or the FDAs QSR
regulations, which include requirements relating to quality control and quality assurance as
well as the corresponding maintenance of records and documentation. Moreover, device manufacturers
are required to report adverse events by filing Medical Device Reports with the FDA, which reports
are publicly available. Further, regulatory agencies must approve manufacturing facilities before
they can be used to manufacture our products, and these facilities are subject to ongoing
regulatory inspection. If we fail to comply with the regulatory requirements of the FDA and other
non-U.S. regulatory authorities, or if previously unknown problems with our products,
manufacturers, or manufacturing processes are discovered, we could be subject to administrative or
judicially imposed sanctions. Furthermore, any limitation on indicated uses for a product
candidate or our ability to manufacture and promote a product candidate could significantly and
adversely affect our business, results of operations, and financial condition.
28
Table of Contents
In addition, the FDA and other non-U.S. regulatory authorities may change their policies and
additional regulations may be enacted that could prevent or delay marketing approval or clearance
of our product candidates. We cannot predict the likelihood, nature or extent of government
regulation that may arise from future legislation or administrative action, either in the United
States or abroad. If we are not able to maintain regulatory compliance, we would likely not be
permitted to market our future product candidates and we may not achieve or sustain profitability,
which would materially impair our ability to generate anticipated revenues.
Even if we receive regulatory approval or clearance to market our product candidates, the market
may not be receptive to our products.
Even if our product candidates obtain marketing approval or clearance, our products may not
gain market acceptance among physicians, patients, health care payors and/or the medical community.
We believe that the degree of market acceptance will depend on a number of factors, including:
| | timing of market introduction of competitive products; | ||
| | the safety and efficacy of our product compared to other products; | ||
| | prevalence and severity of any side effects; | ||
| | potential advantages or disadvantages over alternative treatments; | ||
| | strength of marketing and distribution support; | ||
| | price of our products, both in absolute terms and relative to alternative treatments; | ||
| | availability of coverage and reimbursement from government and other third-party payors; | ||
| | potential product liability claims; | ||
| | limitations or warnings contained in a products regulatory authority-approved labeling; and | ||
| | changes in the standard of care for the targeted indications for any of our product candidates, which could reduce the marketing impact of any claims that we could make following applicable regulatory authority approval. |
In addition, our efforts to educate the medical community and health care payors on the
benefits of our product candidates may require significant resources and may never be successful.
If our products do not gain market acceptance, it would have a material adverse effect on our
business, results of operations, and financial condition.
If our future product candidates are not covered and eligible for reimbursement from government and
third party payors, we may not be able to generate significant revenue or achieve or sustain
profitability.
The coverage and reimbursement status of newly approved or cleared drugs or medical devices is
uncertain, and failure of our pharmaceutical products and procedures using our medical devices to
be adequately covered by insurance and eligible for adequate reimbursement could limit our ability
to market any future product candidates we may develop and decrease our ability to generate revenue
from any of our existing and future product candidates that may be approved or cleared.
29
Table of Contents
There is significant uncertainty related to the third-party coverage and reimbursement of
newly approved or cleared drugs or medical devices. Many medical devices are not directly covered
by insurance; instead, the procedure using the device is subject to a coverage determination by the
insurer. The commercial success of our existing and future product candidates in both domestic and
international markets will depend in part on the availability of coverage and adequate
reimbursement from third-party payors, including government payors, such as the Medicare and
Medicaid programs, managed care organizations, and other third-party payors. The government and
other third-party payors are increasingly attempting to contain health care costs by limiting both
insurance coverage and the level of reimbursement for new drugs or devices and, as a result, they
may not cover or provide adequate payment for our product candidates. These payors may conclude
that our product candidates are less safe, less effective, or less cost-effective than existing or
later-introduced products. These payors may also conclude that the overall cost of the procedure
using one of our devices exceeds the overall cost of the competing procedure using another type of
device, and third-party payors may not approve our product candidates for insurance coverage and
adequate reimbursement. The failure to obtain coverage and adequate or any reimbursement for our
product candidates, or health care cost containment initiatives that limit or restrict
reimbursement for our product candidates, may reduce any future product revenue. Even though a
drug (not administered by a physician) may be approved by the FDA, this does not mean that a
Prescription Drug Plan, or PDP, a private insurer operating under Medicare part D, will list that
drug on its formulary or will set a reimbursement level. PDPs are not required to make every
FDA-approved drug available on their formularies. If our drug products are not listed on
sufficient number of PDP formularies or if the PDPs levels of reimbursement are inadequate, the
Companys business, results of operations, and financial condition could be materially adversely
affected.
If we fail to attract and retain key management and scientific personnel, we may be unable to
successfully develop or commercialize our product candidates.
We will need to expand and effectively manage our managerial, operational, financial,
development, and other resources in order to successfully pursue our research, development, and
commercialization efforts for our product candidates. Our success depends on our continued ability
to attract, retain, and motivate highly qualified management and pre-clinical and clinical
personnel. The loss of the services or support of any of our senior management, particularly Dr.
Phillip Frost, our Chairman of the Board and Chief Executive Officer, could delay or prevent the
development and commercialization of our product candidates. We do not maintain key man
insurance policies on the lives of any of our employees. We will need to hire additional personnel
as we continue to expand our research and development activities and build a sales and marketing
function.
We have scientific and clinical advisors who assist us in formulating our research,
development, and clinical strategies. These advisors are not our employees and may have
commitments to, or consulting or advisory contracts with, other entities that may limit their
availability to us. In addition, these advisors may have arrangements with other companies to
assist those companies in developing products or technologies that may compete with ours.
We may not be able to attract or retain qualified management and scientific personnel in the
future due to the intense competition for qualified personnel among biotechnology, pharmaceutical,
medical device, and other similar businesses. If we are unable to attract and retain the necessary
personnel to accomplish our business objectives, we may experience constraints that will impede
significantly the achievement of our research and development objectives, our ability to raise
additional capital and our ability to implement our business strategy, which will adversely affect
our business, results of operations and financial condition. In particular, if we lose any members
of our senior management team, we may not be able to find suitable replacements in a timely fashion
or at all and our business may be harmed as a result.
As we evolve from a company primarily involved in development to a company also involved in
commercialization, we may encounter difficulties in managing our growth and expanding our
operations successfully.
As we advance our product candidates through clinical trials, research, and development we
will need to expand our development, regulatory, manufacturing, marketing, and sales capabilities
or contracts with third parties to provide these capabilities for us. As our operations expand, we
expect that we will need to manage additional relationships with such third parties, as well as
additional collaborators and suppliers. Maintaining these relationships and managing our future
growth will impose significant added responsibilities on members of our management. We must be
able to: manage our development efforts effectively; manage our clinical trials effectively; hire,
train and integrate additional management, development, administrative and sales and marketing
personnel; improve our managerial, development, operational and finance systems; implement and
manage an
effective marketing strategy; and expand our facilities, all of which may impose a strain on
our administrative and operational infrastructure.
30
Table of Contents
Furthermore, we may acquire additional businesses, products or product candidates that
complement or augment our existing business. Integrating any newly acquired business or product
could be expensive and time-consuming. We may not be able to integrate any acquired business or
product successfully or operate any acquired business profitably. Our future financial performance
will depend, in part, on our ability to manage any future growth effectively and our ability to
integrate any acquired businesses. We may not be able to accomplish these tasks, and our failure
to accomplish any of them could prevent us from successfully growing our company, which would have
a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations and financial condition.
If we fail to acquire and develop other products or product candidates at all or on commercially
reasonable terms, we may be unable to diversify or grow our business.
We intend to continue to rely on acquisitions and in-licensing as the source of our products
and product candidates for development and commercialization. The success of this strategy depends
upon our ability to identify, select, and acquire pharmaceutical products, drug delivery
technologies, and medical device product candidates. Proposing, negotiating, and implementing an
economically viable product acquisition or license is a lengthy and complex process. We compete
for partnering arrangements and license agreements with pharmaceutical, biotechnology and medical
device companies, and academic research institutions. Our competitors may have stronger
relationships with third parties with whom we are interested in collaborating and/or may have more
established histories of developing and commercializing products. Most of our competitors also
have substantially greater financial and other resources than us. As a result, our competitors may
have a competitive advantage in entering into partnering arrangements with such third parties, as
such partnering arrangements are often decided in an auction process in which the highest bidder
wins. In addition, even if we find promising product candidates, and generate interest in a
partnering or strategic arrangement to acquire such product candidates, we may not be able to
acquire rights to additional product candidates or approved products on terms that we find
acceptable, or at all.
We expect that any product candidate to which we acquire rights will require additional
development efforts prior to commercial sale, including extensive clinical testing and approval or
clearance by the FDA and other non-U.S. regulatory authorities. All product candidates are subject
to the risks of failure inherent in pharmaceutical or medical device product development, including
the possibility that the product candidate will not be shown to be sufficiently safe and effective
for approval by regulatory authorities. Even if the product candidates are approved or cleared for
marketing, we cannot be sure that they would be capable of economically feasible production or
commercial success. If we fail to acquire or develop other product candidates that are capable of
economically feasible production and commercial success, our business, results of operations and
financial condition and cash flows may be materially adversely affected.
We have no experience or capability manufacturing large clinical-scale or commercial-scale products
and have no pharmaceutical manufacturing facility other than our facility in Guadalajara, Mexico;
we therefore rely on third parties to manufacture and supply our pharmaceutical product candidates.
If our manufacturing partners are unable to produce our products in the amounts that we
require, we may not be able to establish a contract and obtain a sufficient alternative supply from
another supplier on a timely basis and in the quantities we require. We expect to continue to
depend on third-party contract manufacturers for the foreseeable future.
Our product candidates require precise, high quality manufacturing. Any of our contract
manufacturers will be subject to ongoing periodic unannounced inspection by the FDA and other
non-U.S. regulatory authorities to ensure strict compliance with QSR regulations for devices or
cGMPs for drugs, and other applicable government regulations and corresponding standards relating
to matters such as testing, quality control, and documentation procedures. If our contract
manufacturers fail to achieve and maintain high manufacturing standards in compliance with QSR or
cGMPs, we may experience manufacturing errors resulting in patient injury or death, product recalls
or withdrawals, delays or interruptions of production or failures in product testing or delivery,
delay or prevention of filing or approval of marketing applications for our products, cost
overruns, or other problems that could seriously harm our business.
31
Table of Contents
Any performance failure on the part of our contract manufacturers could delay clinical
development or regulatory approval or clearance of our product candidates or commercialization of
our future product candidates,
depriving us of potential product revenue and resulting in additional losses. In addition,
our dependence on a third party for manufacturing may adversely affect our future profit margins.
Our ability to replace an existing manufacturer may be difficult because the number of potential
manufacturers is limited and the FDA must approve any replacement manufacturer before it can begin
manufacturing our product candidates. Such approval would result in additional non-clinical
testing and compliance inspections. It may be difficult or impossible for us to identify and
engage a replacement manufacturer on acceptable terms in a timely manner, or at all.
We currently have limited marketing staff, no pharmaceutical sales or distribution capabilities and
have only recently commenced developing medical device sales capabilities in the United States. If
we are unable to develop our pharmaceutical sales and marketing and distribution capability and our
medical device sales and marketing capabilities in the United States on our own or through
collaborations with marketing partners, we will not be successful in commercializing our
pharmaceutical product candidates or our medical device product candidates in the United States.
We currently have no pharmaceutical marketing, sales or distribution capabilities other than
through our Mexican and Chilean subsidiaries for sales in those countries. We have only recently
commenced developing medical device sales capabilities in the United States. If our pharmaceutical
product candidates are approved, we intend to establish our sales and marketing organization with
technical expertise and supporting distribution capabilities to commercialize our product
candidates, which will be expensive and time-consuming. Any failure or delay in the development of
any of our internal sales, marketing, and distribution capabilities would adversely impact the
commercialization of our products. With respect to our existing and future pharmaceutical product
candidates, we may choose to collaborate with third parties that have direct sales forces and
established distribution systems, either to augment our own sales force and distribution systems or
in lieu of our own sales force and distribution systems. To the extent that we enter into
co-promotion or other licensing arrangements, our product revenue is likely to be lower than if we
directly marketed or sold our products. In addition, any revenue we receive will depend in whole
or in part upon the efforts of such third parties, which may not be successful and are generally
not within our control. If we are unable to enter into such arrangements on acceptable terms or at
all, we may not be able to successfully commercialize our existing and future product candidates.
If we are not successful in commercializing our existing and future product candidates, either on
our own or through collaborations with one or more third parties, our future product revenue will
suffer and we may incur significant additional losses.
Independent clinical investigators and contract research organizations that we engage to conduct
our clinical trials may not be diligent, careful or timely.
We depend on independent clinical investigators to conduct our clinical trials. Contract
research organizations may also assist us in the collection and analysis of data. These
investigators and contract research organizations will not be our employees, and we will not be
able to control, other than by contract, the amount of resources, including time, that they devote
to products that we develop. If independent investigators fail to devote sufficient resources to
the development of product candidates or clinical trials, or if their performance is substandard,
it will delay the marketing approval or clearance and commercialization of any products that we
develop. Further, the FDA requires that we comply with standards, commonly referred to as good
clinical practice, for conducting, recording and reporting clinical trials to assure that data and
reported results are credible and accurate and that the rights, integrity, and confidentiality of
trial subjects are protected. If our independent clinical investigators and contract research
organizations fail to comply with good clinical practice, the results of our clinical trials could
be called into question and the clinical development of our product candidates could be delayed.
Failure of clinical investigators or contract research organizations to meet their obligations to
us or comply with federal regulations and good clinical practice procedures could adversely affect
the clinical development of our product candidates and harm our business, results of operations,
and financial condition.
The success of our business may be dependent on the actions of our collaborative partners.
We expect to enter into collaborative arrangements with established multinational
pharmaceutical and medical device companies, which will finance or otherwise assist in the
development, manufacture and marketing of products incorporating our technology. We anticipate
deriving some revenues from research and development fees, license fees, milestone payments, and
royalties from collaborative partners. Our prospects, therefore, may depend to some extent upon
our ability to attract and retain collaborative partners and to develop technologies and products
that meet the requirements of prospective collaborative partners. In addition, our collaborative
partners may have the right to abandon research projects and terminate applicable agreements,
including funding obligations, prior to or upon the expiration of the agreed-upon research terms.
There can be no assurance that we will be successful in establishing collaborative arrangements on
acceptable terms or at all, that collaborative partners will not terminate
funding before completion of projects, that our collaborative arrangements will result in
successful product commercialization, or that we will derive any revenues from such arrangements.
To the extent that we are unable to develop and maintain collaborative arrangements, we would need
substantial additional capital to undertake research, development, and commercialization activities
on our own.
32
Table of Contents
If we are unable to obtain and enforce patent protection for our products, our business could be
materially harmed.
Our success depends, in part, on our ability to protect proprietary methods and technologies
that we develop or license under the patent and other intellectual property laws of the United
States and other countries, so that we can prevent others from unlawfully using our inventions and
proprietary information. However, we may not hold proprietary rights to some patents required for
us to commercialize our product candidates. Because certain U.S. patent applications are
confidential until patents issue, such as applications filed prior to November 29, 2000, or
applications filed after such date for which nonpublication has been requested, third parties may
have filed patent applications for technology covered by our pending patent applications without
our being aware of those applications, and our patent applications may not have priority over those
applications. For this and other reasons, we or our third-party collaborators may be unable to
secure desired patent rights, thereby losing desired exclusivity. If licenses are not available to
us on acceptable terms, we may not be able to market the affected products or conduct the desired
activities, unless we challenge the validity, enforceability, or infringement of the third-party
patent or otherwise circumvent the third-party patent.
Our strategy depends on our ability to rapidly identify and seek patent protection for our
discoveries. In addition, we will rely on third-party collaborators to file patent applications
relating to proprietary technology that we develop jointly during certain collaborations. The
process of obtaining patent protection is expensive and time-consuming. If our present or future
collaborators fail to file and prosecute all necessary and desirable patent applications at a
reasonable cost and in a timely manner, our business will be adversely affected. Despite our
efforts and the efforts of our collaborators to protect our proprietary rights, unauthorized
parties may be able to obtain and use information that we regard as proprietary.
The issuance of a patent does not guarantee that it is valid or enforceable. Any patents we
have obtained, or obtain in the future, may be challenged, invalidated, unenforceable, or
circumvented. Moreover, the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office, or USPTO, may commence interference
proceedings involving our patents or patent applications. In addition, court decisions may
introduce uncertainty in the enforceability or scope of patents owned by biotechnology,
pharmaceutical, and medical device companies. Any challenge to, finding of unenforceability or
invalidation or circumvention of, our patents or patent applications would be costly, would require
significant time and attention of our management, and could have a material adverse effect on our
business, results of operations and financial condition.
Our pending patent applications may not result in issued patents. The patent position of
pharmaceutical, biotechnology, and medical device companies, including ours, is generally uncertain
and involves complex legal and factual considerations. The standards that the U.S. Patent and
Trademark Office and its foreign counterparts use to grant patents are not always applied
predictably or uniformly and can change. There is also no uniform, worldwide policy regarding the
subject matter and scope of claims granted or allowable in pharmaceutical, biotechnology, or
medical device patents. Accordingly, we do not know the degree of future protection for our
proprietary rights or the breadth of claims that will be allowed in any patents issued to us or to
others. The legal systems of certain countries do not favor the aggressive enforcement of patents,
and the laws of foreign countries may not protect our rights to the same extent as the laws of the
United States. Therefore, the enforceability or scope of our owned or licensed patents in the
United States or in foreign countries cannot be predicted with certainty, and, as a result, any
patents that we own or license may not provide sufficient protection against competitors. We may
not be able to obtain or maintain patent protection for our pending patent applications, those we
may file in the future, or those we may license from third parties, including the University of
Pennsylvania, the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center (UT Southwestern), Academia
Sinica, and Redox Pharmaceuticals, among others.
While we believe that our patent rights are enforceable, we cannot assure you that any patents
that have issued, that may issue, or that may be licensed to us will be enforceable or valid, or
will not expire prior to the commercialization of our product candidates, thus allowing others to
more effectively compete with us. Therefore, any patents that we own or license may not adequately
protect our product candidates or our future products, which could have a material adverse effect
on our business, results of operations, and financial condition.
33
Table of Contents
If we are unable to protect the confidentiality of our proprietary information and know-how, the
value of our technology and products could be adversely affected.
In addition to patent protection, we also rely on other proprietary rights, including
protection of trade secrets, know-how, and confidential and proprietary information. To maintain
the confidentiality of trade secrets and proprietary information, we will seek to enter into
confidentiality agreements with our employees, consultants, and collaborators upon the commencement
of their relationships with us. These agreements generally require that all confidential
information developed by the individual or made known to the individual by us during the course of
the individuals relationship with us be kept confidential and not disclosed to third parties. Our
agreements with employees also generally provide that any inventions conceived by the individual in
the course of rendering services to us shall be our exclusive property. However, we may not obtain
these agreements in all circumstances, and individuals with whom we have these agreements may not
comply with their terms. In the event of unauthorized use or disclosure of our trade secrets or
proprietary information, these agreements, even if obtained, may not provide meaningful protection,
particularly for our trade secrets or other confidential information. To the extent that our
employees, consultants, or contractors use technology or know-how owned by third parties in their
work for us, disputes may arise between us and those third parties as to the rights in related
inventions.
Adequate remedies may not exist in the event of unauthorized use or disclosure of our
confidential information. The disclosure of our trade secrets would impair our competitive
position and may materially harm our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
We will rely heavily on licenses from third parties. Failure to comply with the provisions of
these licenses could result in the loss of our rights under the license agreements.
Many of the patents and patent applications in our patent portfolio are not owned by us, but
are licensed from third parties. For example, we rely on technology licensed from the University
of Pennsylvania, UT Southwestern, Academia Sinica, and Redox Pharmaceuticals, among others. Such
license agreements give us rights for the commercial exploitation of the patents resulting from the
respective patent applications, subject to certain provisions of the license agreements. Failure
to comply with these provisions could result in the loss of our rights under these license
agreements. Our inability to rely on these patents and patent applications, which are the basis of
our technology, would have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations and
financial condition.
We license patent rights to certain of our technology from third-party owners. If such owners do
not properly maintain or enforce the patents underlying such licenses, our competitive position and
business prospects will be harmed.
We have obtained licenses from, among others, the University of Pennsylvania, UT Southwestern,
Academia Sinica, and Redox Pharmaceuticals, that are necessary or useful for our business. In
addition, we intend to enter into additional licenses of third-party intellectual property in the
future.
Our success will depend in part on our ability or the ability of our licensors to obtain,
maintain, and enforce patent protection for our licensed intellectual property and, in particular,
those patents to which we have secured exclusive rights in our field. We or our licensors may not
successfully prosecute the patent applications which are licensed to us. Even if patents issue in
respect of these patent applications, we or our licensors may fail to maintain these patents, may
determine not to pursue litigation against other companies that are infringing these patents, or
may pursue such litigation less aggressively than we would. Without protection for the
intellectual property we have licensed, other companies might be able to offer substantially
identical products for sale, which could adversely affect our competitive business position and
harm our business, results of operations and financial condition.
Some jurisdictions may require us, or those from whom we license patents, to grant licenses to
third parties. Such compulsory licenses could be extended to include some of our product
candidates, which may limit our potential revenue opportunities.
Many countries, including certain countries in Europe, have compulsory licensing laws under
which a patent owner may be compelled to grant licenses to third parties. In addition, most
countries limit the enforceability of patents against government agencies or government
contractors. In these countries, the patent owner may be limited to monetary relief from an
infringement and may be unable to enjoin infringement, which could materially diminish the value of
the patent. If we or those from who we license patents are required to issue compulsory licenses,
it could materially adversely affect our business, results of operation and financial condition.
34
Table of Contents
Our commercial success depends significantly on our ability to operate without infringing the
patents and other proprietary rights of third parties.
Other entities may have or obtain patents or proprietary rights that could limit our ability
to manufacture, use, sell, offer for sale or import products, or impair our competitive position.
In addition, to the extent that a third party develops new technology that covers our products, we
may be required to obtain licenses to that technology, which licenses may not be available or may
not be available on commercially reasonable terms, if at all. If licenses are not available to us
on acceptable terms, we will not be able to market the affected products or conduct the desired
activities, unless we challenge the validity, enforceability or infringement of the third-party
patent, or circumvent the third-party patent, which would be costly and would require significant
time and attention of our management. Third parties may have or obtain valid and enforceable
patents or proprietary rights that could block us from developing products using our technology.
Our failure to obtain a license to any technology that we require may materially harm our business,
financial condition, and results of operations.
Additionally, RNAi is a relatively new scientific technology that has generated many different
patent applications from organizations and individuals seeking to obtain important patents in the
field. These applications claim many different methods, compositions, and processes relating to
the discovery, development, and commercialization of RNAi therapeutics. Because the field is so
new, very few of these patent applications have been fully processed by government patent offices
around the world, and there is a great deal of uncertainty about which patents will issue, when, to
whom, and with what claims. It is likely that there will be significant litigation and other
proceedings, such as interference and opposition proceedings in various patent offices, relating to
patent rights in RNAi technology. Others may attempt to invalidate our intellectual property
rights. Even if our rights are not directly challenged, disputes among third parties could impact
our intellectual property rights. Any challenge to our intellectual property rights could have a
material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, and financial condition.
If we become involved in patent litigation or other proceedings related to a determination of
rights, we could incur substantial costs and expenses, substantial liability for damages or be
required to stop our product development and commercialization efforts.
Third parties may sue us for infringing their patent rights. Likewise, we may need to resort
to litigation to enforce a patent issued or licensed to us or to determine the scope and validity
of proprietary rights of others. In addition, a third-party may claim that we have improperly
obtained or used its confidential or proprietary information. Furthermore, in connection with our
third-party license agreements, we generally have agreed to indemnify the licensor for costs
incurred in connection with litigation relating to intellectual property rights. The cost to us of
any litigation or other proceeding relating to intellectual property rights, even if resolved in
our favor, could be substantial, and the litigation would divert our managements efforts. Some of
our competitors may be able to sustain the costs of complex patent litigation more effectively than
we can because they have substantially greater resources. Uncertainties resulting from the
initiation and continuation of any litigation could limit our ability to continue our operations.
Our involvement in patent litigation and other proceedings could have a material adverse effect on
our business, results of operations, and financial condition.
If any parties successfully claim that our creation or use of proprietary technologies
infringes upon their intellectual property rights, we might be forced to pay damages, potentially
including treble damages, if we are found to have willfully infringed on such parties patent
rights. In addition to any damages we might have to pay, a court could require us to stop the
infringing activity or obtain a license. Any license required under any patent may not be made
available on commercially acceptable terms, if at all. In addition, such licenses are likely to be
non-exclusive and, therefore, our competitors may have access to the same technology licensed to
us. If we fail to obtain a required license and are unable to design around a patent, we may be
unable to effectively market some of our technology and products, which could limit our ability to
generate revenues or achieve profitability and possibly prevent us from generating revenue
sufficient to sustain our operations.
Adverse results in material litigation matters or governmental inquiries could have a material
adverse effect upon our business and financial condition.
We may from time to time become subject in the ordinary course of business to material legal
action related to, among other things, intellectual property disputes, professional liability,
contractual and employee-related matters, as well as inquiries from governmental agencies and
Medicare or Medicaid carriers requesting comment and information on allegations of billing
irregularities and other matters that are brought to their attention through billing audits, third
parties or other sources. The health care industry is subject to substantial federal and state
government
regulation and audit. Legal actions could result in substantial monetary damages as well as
damage to the Companys reputation with customers, which could have a material adverse effect upon
our results of operations and financial position.
35
Table of Contents
Medicare legislation and future legislative or regulatory reform of the health care system may
affect our ability to sell our products profitably.
In the United States, there have been a number of legislative and regulatory initiatives, at
both the federal and state government levels, to change the healthcare system in ways that, if
approved, could affect our ability to sell our products profitably. While many of the proposed
policy changes require congressional approval to implement, we cannot assure you that reimbursement
payments under governmental and private third party payer programs will remain at levels comparable
to present levels or will be sufficient to cover the costs allocable to patients eligible for
reimbursement under these programs. Any changes that lower reimbursement rates under Medicare,
Medicaid or private pay programs could negatively affect our business.
In addition, there are efforts underway to attempt the passage of significant healthcare
reform legislation. Any such health care reform may have an adverse effect on our business through
decreasing funds available to our customers and to us. Limitations or restrictions on Medicare and
Medicaid payments to our customers could adversely impact the liquidity of our customers, resulting
in their inability to pay us, or to timely pay us, for our products and services. This inability
could have a material adverse effect on our financial position, results of operations and
liquidity.
We are unable to predict what additional legislation or regulation, if any, relating to the
health care industry or third-party coverage and reimbursement may be enacted in the future or what
effect such legislation or regulation would have on our business.
RISKS RELATED TO INTERNATIONAL OPERATIONS
Failure to obtain regulatory approval outside the United States will prevent us from marketing our
product candidates abroad.
We intend to market certain of our existing and future product candidates in non-U.S.
markets. In order to market our existing and future product candidates in the European Union and
many other non-U.S. jurisdictions, we must obtain separate regulatory approvals. We have had
limited interactions with non-U.S. regulatory authorities, the approval procedures vary among
countries and can involve additional testing, and the time required to obtain approval may differ
from that required to obtain FDA approval or clearance. Approval or clearance by the FDA does not
ensure approval by regulatory authorities in other countries, and approval by one or more non-U.S.
regulatory authority does not ensure approval by other regulatory authorities in other countries or
by the FDA. The non-U.S. regulatory approval process may include all of the risks associated with
obtaining FDA approval or clearance. We may not obtain non-U.S. regulatory approvals on a timely
basis, if at all. We may not be able to file for non-U.S. regulatory approvals and may not receive
necessary approvals to commercialize our existing and future product candidates in any market,
which would have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations and financial
condition.
Non-U.S. governments often impose strict price controls, which may adversely affect our future
profitability.
We intend to seek approval to market certain of our existing and future product candidates in
both the United States and in non-U.S. jurisdictions. If we obtain approval in one or more
non-U.S. jurisdictions, we will be subject to rules and regulations in those jurisdictions relating
to our product. In some countries, particularly countries of the European Union, each of which has
developed its own rules and regulations, pricing is subject to governmental control. In these
countries, pricing negotiations with governmental authorities can take considerable time after the
receipt of marketing approval for a drug or medical device candidate. To obtain reimbursement or
pricing approval in some countries, we may be required to conduct a clinical trial that compares
the cost-effectiveness of our existing and future product candidates to other available products.
If reimbursement of our future product candidates is unavailable or limited in scope or amount, or
if pricing is set at unsatisfactory levels, we may be unable to generate revenues and achieve or
sustain profitability, which would have a material adverse effect on our business, results of
operations and financial condition.
36
Table of Contents
We may be exposed to liabilities under the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act, and any determination
that we violated the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act could have a material adverse effect on our
business.
We are subject to the Foreign Corrupt Practice Act, or FCPA, and other laws that prohibit U.S.
companies or their agents and employees from providing anything of value to a foreign official or
political party for the purposes of influencing any act or decision of these individuals in their
official capacity to help obtain or retain business, direct business to any person or corporate
entity or obtain any unfair advantage. We have operations and agreements with third parties and we
make sales in internationally. Our international activities create the risk of unauthorized
payments or offers of payments by our employees, consultants, sales agents or distributors, even
though they may not always be subject to our control. We discourage these practices by our
employees and agents. However, our existing safeguards and any future improvements may prove to be
less than effective, and our employees, consultants, sales agents or distributors may engage in
conduct for which we might be held responsible. Any failure by us to adopt appropriate compliance
procedures and ensure that our employees and agents comply with the FCPA and applicable laws and
regulations in foreign jurisdictions could result in substantial penalties or restrictions on our
ability to conduct business in certain foreign jurisdictions.
Violations of the FCPA may result in severe criminal or civil sanctions, and we may be subject
to other liabilities, which could negatively affect our business, operating results and financial
condition. In addition, the U.S. government may seek to hold our Company liable for successor
liability FCPA violations committed by companies in which we invest or that we acquire.
We are subject to risks associated with doing business globally.
Our operations, both within and outside the United States, are subject to risks inherent in
conducting business globally and under the laws, regulations and customs of various jurisdictions
and geographies. These risks include fluctuations in currency exchange rates, changes in exchange
controls, loss of business in government tenders that are held annually in many cases,
nationalization, increasingly complex labor environments, expropriation and other governmental
actions, changes in taxation, including legislative changes in U.S. and international taxation of
income earned outside of the United States, importation limitations, export control restrictions,
violations of U.S. or local laws, including the U.S. Foreign Corrupt Practices Act, dependence on a
few government entities as customers, pricing restrictions, economic destabilization, political and
economic instability, disruption or destruction in a significant geographic region due to the
location of manufacturing facilities, distribution facilities or customers regardless of cause,
including war, terrorism, riot, civil insurrection or social unrest, or natural or man-made
disasters, including famine, flood, fire, earthquake, storm or disease. Failure to comply with the
laws and regulations that affect our global operations, could have an adverse effect on our
business, financial condition or results of operations.
RISKS RELATED TO ACQUISITIONS
Acquisitions, investments and strategic alliances that we have made or may make in the future
may use significant resources, result in disruptions to our business or distractions of our
management, may not proceed as planned, and could expose us to unforeseen liabilities. We intend
to continue to expand our business through the acquisition of, investments in and strategic
alliances with companies, technologies, products, and services. Acquisitions, investments and
strategic alliances involve a number of special problems and risks, including, but not limited to:
| | difficulty integrating acquired technologies, products, services, operations, and personnel with the existing businesses; | ||
| | diversion of managements attention in connection with both negotiating the acquisitions and integrating the businesses; | ||
| | strain on managerial and operational resources as management tries to oversee larger operations; | ||
| | exposure to unforeseen liabilities of acquired companies; | ||
| | potential costly and time-consuming litigation, including stockholder lawsuits; |
37
Table of Contents
| | potential issuance of securities to equity holders of the company being acquired with rights that are superior to the rights of holders of our common stock, or which may have a dilutive effect on our stockholders; | ||
| | the need to incur additional debt or use cash; and | ||
| | the requirement to record potentially significant additional future operating costs for the amortization of intangible assets. |
As a result of these or other problems and risks, businesses we acquire may not produce the
revenues, earnings, or business synergies that we anticipated, and acquired products, services, or
technologies might not perform as we expected. As a result, we may incur higher costs and realize
lower revenues than we had anticipated. We may not be able to successfully address these problems
and we cannot assure you that the acquisitions will be successfully identified and completed or
that, if acquisitions are completed, the acquired businesses, products, services, or technologies
will generate sufficient revenue to offset the associated costs or other negative effects on our
business.
Any of these risks can be greater if an acquisition is large relative to our size. Failure to
manage effectively our growth through acquisitions could adversely affect our growth prospects,
business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows.
Funding may not be available for us to continue to make acquisitions, investments and strategic
alliances in order to grow our business.
We have made and anticipate that we may continue to make acquisitions, investments and
strategic alliances with complementary businesses, technologies, products and services to expand
our business. Our growth plans rely, in part, on the successful completion of future acquisitions.
At any particular time, we may need to raise substantial additional capital or to issue additional
equity to finance such acquisitions, investments, and strategic alliances. There is no assurance
that we will be able to secure additional funding on acceptable terms, or at all, or obtain the
stockholder approvals necessary to issue additional equity to finance such acquisitions,
investments, and strategic alliances. If we are unsuccessful in obtaining the financing, our
business would be adversely impacted.
RISKS RELATED TO OWNERSHIP OF OUR COMMON STOCK
The market price of our common stock may fluctuate significantly.
The market price of our common stock may fluctuate significantly in response to numerous
factors, some of which are beyond our control, such as:
| | the announcement of new products or product enhancements by us or our competitors; | ||
| | results of our clinical trials and other development efforts; | ||
| | developments concerning intellectual property rights and regulatory approvals; | ||
| | variations in our and our competitors results of operations; | ||
| | changes in earnings estimates or recommendations by securities analysts, if our common stock is covered by analysts; | ||
| | developments in the biotechnology, pharmaceutical, and medical device industry; | ||
| | the results of product liability or intellectual property lawsuits; | ||
| | future issuances of common stock or other securities, including debt; | ||
| | the addition or departure of key personnel; | ||
| | announcements by us or our competitors of acquisitions, investments, or strategic alliances; and | ||
| | general market conditions and other factors, including factors unrelated to our operating performance. |
38
Table of Contents
Further, the stock market in general, and the market for biotechnology, pharmaceutical, and
medical device companies in particular, has recently experienced extreme price and volume
fluctuations. Continued market fluctuations could result in extreme volatility in the price of our
common stock, which could cause a decline in the value of our common stock.
Trading of our common stock is limited and restrictions imposed by securities regulation and
certain lockup agreements may further reduce our trading, making it difficult for our stockholders
to sell shares.
Our common stock began trading on the American Stock Exchange, now known as the NYSE Amex, in
June 2007. To date, the liquidity of our common stock is limited, not only in terms of the number
of shares that can be bought and sold at a given price, but also through delays in the timing of
transactions and changes in security analyst and media coverage, if at all.
A substantial percentage of the outstanding shares of our common stock (including outstanding
shares of our preferred stock on an as converted basis) are restricted securities and/or are
subject to lockup agreements which limit sales for a period of time. These factors may result in
lower prices for our common stock than might otherwise be obtained and could also result in a
larger spread between the bid and ask prices for our common stock. In addition, without a large
float, our common stock is less liquid than the stock of companies with broader public ownership
and, as a result, the trading prices of our common stock may be more volatile. In the absence of
an active public trading market, an investor may be unable to liquidate his investment in our
common stock. Further, the limited liquidity could be an indication that the trading price is not
reflective of the actual fair market value of our common stock. Trading of a relatively small
volume of our common stock may have a greater impact on the trading price of our stock than would
be the case if our public float were larger.
Future sales of our common stock could reduce our stock price.
Some or all of the restricted shares of our common stock issued to former stockholders of
Froptix and Acuity in connection with the acquisition or held by other of our stockholders may be
offered from time to time in the open market pursuant to an effective registration statement, or
beginning April 2, 2008, pursuant to Rule 144. In addition, as described herein, a substantial
number of our shares of common stock were subject to lockup agreements which expired on March 27,
2009. We have also issued or agreed to issue a substantial number of securities in private
placement transactions with two year lockup restrictions expiring in each of December 2009, August
2010, and February 2011. In connection with our Series D Preferred Stock offering, shares were
issued with a three year lockup restriction that expires in September 2012. Sales of a substantial
number of shares of our common stock in the public market pursuant to Rule 144 or after the lockup
agreements lapse, or the perception that such sales could occur, could adversely affect the price
of our common stock.
Directors, executive officers, principal stockholders and affiliated entities own a majority of our
capital stock, and they may make decisions that you do not consider to be in the best interests of
our stockholders.
As of February 10, 2010, our directors, executive officers, principal stockholders, and
affiliated entities beneficially owned, in the aggregate a majority of our outstanding voting
securities. Frost Gamma Investments Trust (the Gamma Trust), of which Phillip Frost, M.D., the
Companys Chairman and CEO, is the sole trustee, is deemed to beneficially own in the aggregate
approximately 48.26% of the Companys common stock as of February 10, 2010. As a result, Dr. Frost
acting alone or with other members of management, would have the ability to control the election of
our Board of Directors, the adoption or amendment of provisions in the Companys Certificate of
Incorporation, the approval of mergers and other significant corporate transactions, and the
outcome of issues requiring approval by our stockholders. This concentration of ownership may also
have the effect of delaying or preventing a change in control of our company that may be favored by
other stockholders. This could prevent transactions in which stockholders might otherwise recover
a premium for their shares over current market prices.
Failure to maintain effective internal controls in accordance with Section 404 of the
Sarbanes-Oxley Act could have a material adverse effect on our business and operating results. In
addition, current and potential shareholders could lose confidence in our financial reporting,
which could have a material adverse effect on the price of our common stock.
Effective internal controls are necessary for us to provide reliable financial reports and
effectively prevent fraud. If we cannot provide reliable financial reports or prevent fraud, our
results of operation could be harmed.
39
Table of Contents
Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 requires annual management assessments of the
effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting and a report by our independent
registered public accounting firm on the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting
as of December 31, 2009. We continuously monitor our existing internal control over financial
reporting systems to confirm that they are compliant with Section 404, and we may identify
deficiencies that we may not be able to remediate in time to meet the deadlines imposed by the
Sarbanes-Oxley Act. This process may divert internal resources and will take a significant amount
of time and effort to complete.
If, at any time, it is determined that we are not in compliance with Section 404, we may be
required to implement new internal control procedures and reevaluate our financial reporting. We
may experience higher than anticipated operating expenses as well as increased independent auditor
fees during the implementation of these changes and thereafter. Further, we may need to hire
additional qualified personnel. If we fail to maintain the adequacy of our internal controls, as
such standards are modified, supplemented or amended from time to time, we may not be able to
conclude on an ongoing basis that we have effective internal control over financial reporting in
accordance with Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, which could result in our being unable to
obtain an unqualified report on internal control from our independent auditors. Failure to
maintain an effective internal control environment could also cause investors to lose confidence in
our reported financial information, which could have a material adverse effect on the price of our
common stock.
Compliance with changing regulations concerning corporate governance and public disclosure may
result in additional expenses.
There have been changing laws, regulations, and standards relating to corporate governance and
public disclosure, including the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, new regulations promulgated by the
Securities and Exchange Commission and rules promulgated by the NYSE Amex, the other national
securities exchanges and the NASDAQ. These new or changed laws, regulations, and standards are
subject to varying interpretations in many cases due to their lack of specificity, and, as a
result, their application in practice may evolve over time as new guidance is provided by
regulatory and governing bodies, which could result in continuing uncertainty regarding compliance
matters and higher costs necessitated by ongoing revisions to disclosure and governance practices.
As a result, our efforts to comply with evolving laws, regulations, and standards are likely to
continue to result in increased general and administrative expenses and a diversion of management
time and attention from revenue-generating activities to compliance activities. Our board members,
Chief Executive Officer, Chief Financial Officer, and Principal Accounting Officer could face an
increased risk of personal liability in connection with the performance of their duties. As a
result, we may have difficulty attracting and retaining qualified board members and executive
officers, which could harm our business. If our efforts to comply with new or changed laws,
regulations, and standards differ from the activities intended by regulatory or governing bodies,
we could be subject to liability under applicable laws or our reputation may be harmed, which could
materially adversely affect our business, results of operations and financial condition.
ITEM 1B. UNRESOLVED STAFF COMMENTS.
None.
ITEM 2. PROPERTIES.
Our principal corporate office is located at 4400 Biscayne Blvd, Miami, Florida. We lease
this space from Frost Real Estate Holdings, LLC, an entity which is controlled by Dr. Phillip
Frost, our Chairman of the Board and Chief Executive Officer. Pursuant to the lease agreement with
Frost Real Estate Holdings, we lease approximately 8,300 square feet, which encompasses space for
our corporate offices, administrative services, project management and pharmacology. The lease is
for a five-year term and currently requires annual rent of approximately $228,000, which amount
increases by approximately 4.5% per year.
We lease approximately 10,000 square feet of space in Hialeah, Florida from an entity
controlled by Dr. Phillip Frost, our Chairman and Chief Executive Officer, and Dr. Jane Hsiao, our
Vice Chairman and Chief Technical Officer, to house manufacturing and service operations for our
ophthalmic instrumentation business. We also lease an animal research facility at Mount Sinai
Hospital in Miami Beach, Florida. Our OTI subsidiary maintained offices in Toronto, Ontario,
Canada until late 2009, when it relocated to Miami. It also maintains a research and development
branch office in Kingston, Ontario, and an office in the United Kingdom at the University of Kent.
Pharma Genexx, our Chilean subsidiary, leases office space in Santiago, Chile, and through our
Mexican subsidiaries, we own a manufacturing facility and laboratory space consisting of
approximately 38,000 square feet.
40
Table of Contents
Table of Contents
PART II
| ITEM 5. | MARKET FOR REGISTRANTS COMMON EQUITY, RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS AND ISSUER PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES. |
Our common stock is traded publicly on the NYSE Amex (formerly the American Stock Exchange)
under the symbol OPK. The following table sets forth, for the periods indicated, the high and
low sales prices per share of our common stock during each of the quarters set forth below as
reported on the NYSE Amex:
| High | Low | |||||||
2009 |
||||||||
First Quarter |
$ | 1.70 | $ | 0.60 | ||||
Second Quarter |
1.87 | 0.98 | ||||||
Third Quarter |
2.76 | 1.55 | ||||||
Fourth Quarter |
2.43 | 1.55 | ||||||
2008 |
||||||||
First Quarter |
$ | 3.90 | $ | 2.00 | ||||
Second Quarter |
2.84 | 1.46 | ||||||
Third Quarter |
2.39 | 0.87 | ||||||
Fourth Quarter |
1.80 | 1.01 | ||||||
As of March 8, 2010, there were approximately 361 holders of record of our common stock.
The Company has not declared or paid any cash dividends on its common stock. No cash
dividends have been previously paid on our common stock and none are anticipated in fiscal 2010.
The Company also has shares of Series A and Series D Preferred Stock Outstanding that have
preferential dividend rights over any dividend payments to holders of common stock.
42
Table of Contents
| Stock Performance Graph |
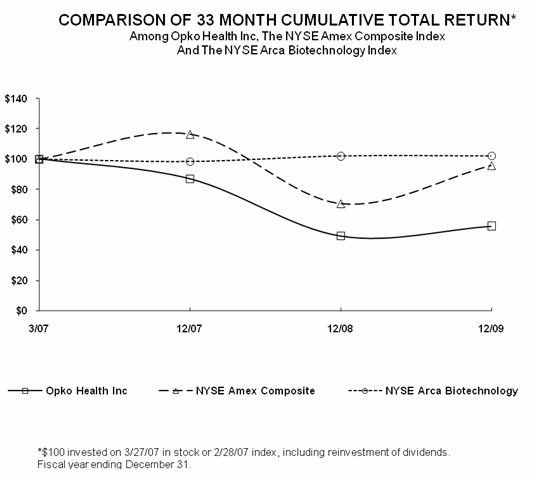
43
Table of Contents
| ITEM 6. | SELECTED FINANCIAL DATA. |
The following selected historical consolidated statement of operations data for the years
ended December 31, 2009, 2008, and 2007 and for the period from inception (June 23, 2006) through
December 31, 2006 and the consolidated balance sheet data as of December 31, 2009, 2008, 2007, and
2006, below are derived from our audited consolidated financial statements and related notes
thereto. This data should be read in conjunction with our Managements Discussion and Analysis of
Financial Condition and Results of Operation and our consolidated financial statements and the
related notes thereto.
| For the years ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||
| For the period | ||||||||||||||||
| from inception | ||||||||||||||||
| (June 23, 2006) | ||||||||||||||||
| through | ||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands, except share and per shares information) | 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | December 31, 2006 | ||||||||||||
Statement of operations data |
||||||||||||||||
Revenue |
$ | 13,147 | $ | 9,440 | $ | 847 | $ | | ||||||||
Cost of goods sold |
9,567 | 8,559 | 808 | | ||||||||||||
Gross margin |
3,580 | 881 | 39 | | ||||||||||||
Operating expenses: |
||||||||||||||||
Selling, general and administrative |
13,518 | 14,790 | 12,466 | 375 | ||||||||||||
Research and development |
12,881 | 21,562 | 10,850 | 508 | ||||||||||||
Write-off of acquired in-process research and
development |
2,000 | 1,398 | 243,761 | | ||||||||||||
Other operating expenses; primarily amortization of
intangible assets |
3,201 | 1,694 | 150 | | ||||||||||||
Total operating expenses |
31,600 | 39,444 | 267,227 | 883 | ||||||||||||
Operating loss |
(28,020 | ) | (38,563 | ) | (267,188 | ) | (883 | ) | ||||||||
Other (expense) income, net |
(2,034 | ) | (1,354 | ) | (671 | ) | 6 | |||||||||
Loss before income taxes and investment losses |
(30,054 | ) | (39,917 | ) | (267,859 | ) | (877 | ) | ||||||||
Income tax benefit |
294 | 83 | 83 | | ||||||||||||
Net loss before investment losses |
(29,760 | ) | (39,834 | ) | (267,776 | ) | (877 | ) | ||||||||
Loss from investments in investees |
(353 | ) | | (629 | ) | | ||||||||||
Net loss |
(30,113 | ) | (39,834 | ) | (268,405 | ) | (877 | ) | ||||||||
Preferred stock dividend |
(846 | ) | (217 | ) | (217 | ) | | |||||||||
Net loss attributable to common shareholders |
$ | (30,959 | ) | $ | (40,051 | ) | $ | (268,622 | ) | $ | (877 | ) | ||||
Loss per share, basic and diluted |
$ | (0.13 | ) | $ | (0.21 | ) | $ | (2.09 | ) | $ | (0.01 | ) | ||||
Weighted average number of common shares outstanding
basic and diluted |
233,191,617 | 187,713,041 | 128,772,080 | 58,733,556 | ||||||||||||
Balance sheet data |
||||||||||||||||
Total assets |
$ | 87,430 | $ | 21,764 | $ | 39,568 | $ | 116 | ||||||||
Working capital |
$ | 50,795 | $ | 5,754 | $ | 19,489 | $ | 21 | ||||||||
Long-term line of credit with related party, notes payable, and
capital lease obligations, net |
$ | 11,932 | $ | 11,867 | $ | 14,235 | $ | | ||||||||
Stockholders equity |
$ | 57,727 | $ | 359 | $ | 16,784 | $ | 21 | ||||||||
| ITEM 7. | MANAGEMENTS DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATION. |
This Annual Report on Form 10-K contains certain forward-looking statements within the meaning
of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995 (PSLRA), Section 27A of the Securities
Act of 1933, as amended (the Securities Act), and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of
1934, as amended, (the Exchange Act), about our expectations, beliefs, or intentions regarding
our product development efforts, business, financial condition, results of operations, strategies,
or prospects. You can identify forward-looking statements by the fact that these statements do not
relate strictly to historical or current matters. Rather, forward-looking statements relate to
anticipated or expected events, activities, trends, or results as of the date they are made.
Because forward-looking statements relate to matters that have not yet occurred, these statements
are inherently subject to risks and uncertainties that could cause our actual results to differ
materially from any future results expressed or implied by the forward-looking statements. Many
factors could cause our actual activities or results to differ materially from the activities and
results anticipated in forward-looking statements. These factors include those contained in Item
1A Risk Factors of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. We do not undertake any obligation to
update forward-looking statements. We intend that all forward-looking statements be subject to the
safe harbor provisions of PSLRA. These forward-looking statements are only predictions and reflect
our views as of the date they are made with respect to future events and financial performance.
44
Table of Contents
OVERVIEW
We are a specialty healthcare company involved in the discovery, development, and
commercialization of pharmaceutical products, medical devices, vaccines, diagnostic technologies,
and imaging systems. Initially focused on the treatment and management of ophthalmic diseases, we
have since expanded into other areas of major unmet medical need.
We expect to incur substantial losses as we continue the development of our product
candidates, continue our other research and development activities, and establish a sales and
marketing infrastructure in anticipation of the commercialization of our pharmaceutical product
candidates. We currently have limited commercialization capabilities, and it is possible that we
may never successfully commercialize any of our pharmaceutical product candidates. To date, we
have devoted substantially all of our efforts towards research and development. As of December 31,
2009, we had an accumulated deficit of $339.2 million. We do not currently generate revenue from
any of our pharmaceutical product candidates and have only generated limited revenue from our
operations in Chile and our instrumentation business. Our research and development activities are
budgeted to expand over a period of time and will require further resources if we are to be
successful. As a result, we believe that our operating losses are likely to be substantial over
the next several years. We will need to obtain additional funds to further develop our research
and development programs, and there can be no assurance that additional capital will be available
to us on acceptable terms, or at all.
RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
For The Years Ended December 31, 2009 and December 31, 2008
The results of operations for the year ended December 31, 2009 include the
post acquisition operations for
Pharma Genexx, S.A. (Pharma Genexx), a privately owned Chilean company engaged in the marketing,
sale, and distribution of pharmaceutical products, devices, and over-the-counter products for
government, private, and institutional markets in Chile, which we acquired on October 7, 2009. As
a result, our operating results for periods prior to October 7, 2009 do not include Pharma Genexx activity.
Revenue.
Revenue for the year ended December 31, 2009 was $13.1 million compared to $9.4
million for the year ended December 31, 2008. Revenue for 2009 increased as a result of the
revenue generated by Pharma Genexx after our acquisition on October 7, 2009. Partially offsetting
the revenue from Pharma Genexx were decreased revenue from our instrumentation business in international markets.
Revenue for 2008 primarily consisted of revenue from our instrumentation business in international
markets.
Gross margin. Gross margin for the year ended December 31, 2009 was $3.6 million compared to
$0.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2008. Gross margin improved during 2009 primarily as
a result of improved gross margin from our instrumentation business and post acquisition gross margin generated by
our pharmaceutical business. Gross margin during 2008 was negatively impacted
while we made a number of changes to our instrumentation manufacturing process in an effort to lower
the cost of goods sold and increase gross margins. Those improvements included changing suppliers
of components for our OCT SLO products and assembling a number of components in-house rather than
outsourcing those activities. We realized the benefits of those changes to our manufacturing
processes as increased gross margin during the year ended December 31, 2009.
Selling, general and administrative expense. Selling, general and administrative expense in
the year ended December 31, 2009 was $13.5 million as compared to $14.8 million during the year
ended December 31, 2008. Selling, general and administrative expense decreased primarily as a
result of decreased personnel costs, including equity-based compensation, and sales commissions to
certain international distributors in our instrumentation business, partially offset by increased
professional fees. Included in selling, general and administrative expenses were $3.2 million and
$4.2 million of equity based compensation expense for the years ended December 31, 2009 and 2008,
respectively.
Research and development expense. Research and development expense for the year ended
December 31, 2009 was $12.9 million as compared to $21.6 million during the year ended December 31,
2008. The decrease in research and development expense was primarily related to the termination of
the Phase III clinical trial of bevasiranib and related reduced personnel costs. Research and
development expense for the year ended December 31, 2009 consisted primarily of expenses related to
the Phase III clinical trial of bevasiranib through March 6, 2009 and the related costs of
analyzing the data generated by the trial. Research and development expense for the year ended
December 31, 2008 primarily consisted of expenses related to the Phase III clinical trial of
bevasiranib. Included in
research and development expense were $1.3 million and $2.5 million of equity based
compensation expense for the years ended December 31, 2009 and 2008, respectively.
45
Table of Contents
Write-off of acquired in-process research and development. On October 12, 2009, we entered
into an agreement to acquire certain assets from Schering Plough Corporations neurokinin-1
(NK-1) development program, of which, rolapitant is our lead pharmaceutical product candidate, in
an all cash transaction for $2.0 million at closing. We recorded this acquisition as an asset
acquisition and recorded the assets at fair value and allocated the entire purchase price to
acquired in-process research and development expense and recorded a charge of $2.0 million. On May
6, 2008, we acquired Vidus Ocular, Inc. in a stock for stock transaction. We recorded Vidus
assets and liabilities at fair value, and as a result, we recorded acquired in-process research and
development expense and recorded a charge of $1.4 million. We valued our common stock issued to
Vidus shareholders at the average closing price of the common stock on the date of the transaction
and two days prior to the transaction.
We record expense for in-process research and development projects accounted for as asset
acquisitions which have not reached technological feasibility and which have no alternative future
use. The NK-1 drug candidates have not reached a stage of technological feasibility and have no
alternative future use. At the time of our acquisition of Vidus, the accounting for business
combinations and asset acquisitions were the same and Vidus projects had not reached a stage of
technological feasibility and had no alternative future use. Effective January 1, 2009, in-process
research and development projects acquired in business combinations are capitalized.
Other operating expenses, principally amortization of intangible assets. Other operating
expenses were $3.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2009, compared to $1.7 million for the
year ended December 31, 2008. The increase is primarily the
result of the $1.1 million impairment of goodwill related to our instrumentation business. In addition, the increase reflects the
amortization expense related to the intangible assets acquired as part of our acquisition of Pharma
Genexx.
Other
income and expenses. Other expense was $2.0 million for the year ended December 31,
2009, compared to $1.4 million, net of $0.3 million of interest income for the year ended December
31, 2008. Other expenses primarily consist of interest expense incurred on our $12.0 million line
of credit, partially offset by interest earned on our cash and cash equivalents.
For The Year Ended December 31, 2008 and December 31, 2007
The results of operations for the year ended December 31, 2007 include those of Froptix for
the full period as well as the results of operations of Acuity Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (Acuity)
from March 27, 2007 through December 31, 2007, and of Ophthalmic Technologies, Inc. (OTI) from
November 28, 2007 through December 31, 2007, the date of our acquisitions.
Revenue. Revenue for the year ended December 31, 2008 was $9.4 million compared to $0.8
million for the year ended December 31, 2007. Revenue for 2008 primarily consisted of revenue from
sales of our OCT SLO device in international markets, and also included revenue from sales of our
ultrasound products. Revenue for the 2007 period was limited to the period from of our acquisition
of OTI on November 28, 2007 through December 31, 2007. Revenues during the 2007 period were also
primarily revenue from our OCT SLO and ultrasound products in international markets. In November
2008, we received 510(k) clearance from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration to begin marketing
the OCT SLO in the U.S., and we began marketing the device in the United States during 2009.
Gross margin. Gross margin for the year ended December 31, 2008 was $0.9 million compared to
$39 thousand for the year ended December 31, 2007. The increase in gross margin reflects the
full-year results for OTI during 2008, as compared to the 2007 period, which included revenue for
the period from our acquisition of OTI on November 28, 2007 through December 31, 2007. During
2008, we made a number of changes to our manufacturing process in effort to lower the cost of goods
sold and increase gross margins, including changing suppliers of components for out OCT SLO product
and assembling a number of components in-house rather than outsourcing those activities.
Throughout 2008, gross margin improved as a result of changes in our manufacturing processes and
realized reduced component pricing from suppliers as we increased volume purchases.
Selling, general and administrative expense. Selling, general and administrative expense in
the year ended December 31, 2008 was $14.8 million as compared to $12.5 million during the year
ended December 31, 2007, primarily as a result of increased personnel costs, including equity-based
compensation, and sales commissions to certain international distributors of our instrumentation
products. Selling, general and administrative expenses
during 2008 also increased as a result of reflecting a full 12 month period for all activities
as an operating public company. The 2007 period reflected only nine months as an operating public
company and one month of sales and marketing expenses as a result of our acquisition of OTI on
November 28, 2007. Included in selling, general and administrative expenses were $4.2 million and
$3.3 million of equity based compensation expense for the years ended December 31, 2008 and
December 31, 2007, respectively.
46
Table of Contents
Research and development expense. Research and development expense for the year ended December
31, 2008 was $21.6 million as compared to $10.9 million during the year ended December 31, 2007.
The increase during 2008 is primarily a result of expense related to our Phase III clinical trial
for bevasiranib. The Phase III clinical trial, which was initiated in July 2007, completed
enrollment in December 2008. In addition, the 2008 period includes a full year of activities for
both Acuity and OTI, which were acquired in March 2007 and November 2007, respectively. Research
and development expenses for the years ended December 31, 2008 and December 31, 2007 include
equity-based compensation of $2.5 million and $4.1 million, respectively. During the third quarter
of 2007, a reversal of equity-based compensation expense of $8.1 million was recorded as a result
of the termination of a consulting agreement prior to the vesting of any of the equity based awards
issued under the consulting agreement. Originally, we accrued $0.3 million for this expense during
2006 and $7.8 million during the first six months of 2007.
Write-off of acquired in-process research and development. On May 6, 2008, we acquired Vidus
in a stock for stock transaction. We recorded Vidus assets and liabilities at fair value, and as
a result, we recorded acquired in-process research and development expense and recorded a charge of
$1.4 million. On March 27, 2007, we acquired Acuity in a stock for stock transaction. We recorded
Acuitys assets and liabilities acquired at fair value. Approximately $243.8 million of the
purchase price was allocated to in-process research and development projects, which was immediately
charged to expense. We valued our common stock issued to Vidus and Acuity shareholders at the
average closing price of the common stock on the date of the transactions and two days prior to the
transactions. We record expense for in-process research and development projects which have not
reached technological feasibility and which have no alternative future use. At the time of our
acquisitions of Vidus and Acuity, neither companys projects had reached a stage of technological
feasibility and had no alternative future use.
Other income and expenses. Other expense was $1.4 million, net of $0.3 million of interest
income for the year ended December 31, 2008, compared to $0.7 million, net of $0.3 million of
interest income for the year ended December 31, 2007. Other expenses primarily consist of interest
expense incurred on our $12.0 million line of credit and our $4.0 million term loan, which was
repaid in January 2008, partially offset by the $4.0 million term loan being outstanding for only a
portion of 2008. The line of credit was drawn during 2007, and as a result, was only outstanding
during part of that period. In addition, the 2007 period includes the minority interest loss of
$0.6 million for a prorated portion of OTIs operating loss from the date of our investment in OTI
on April 13, 2007 through the date of our acquisition on November 28, 2007.
Liquidity And Capital Resources
At December 31, 2009, we had cash, cash equivalents and marketable securities of approximately
$42.7 million compared to $6.7 million on December 31, 2008. Cash used in operations during 2009
primarily reflects payment of liabilities related to the Phase III clinical trial for bevasiranib
and related shut down expenses of that trial, as well as other research and development activities,
and selling, general and administrative activities related to our corporate and instrumentation
operations. Since our inception, we have not generated sufficient gross margins to offset our
operating and other expenses and our primary source of cash has been from the private placement of
stock and credit facilities available to us.
On October 7, 2009, we acquired Pharma Genexx, a privately-owned Chilean company engaged in
the marketing, sales, commercialization and distribution of pharmaceutical products,
over-the-counter products and medical devices for government, private and institutional markets in
Chile for US$16 million in cash. In connection with our acquisition of Pharma Genexx, we have
entered into lines of credit agreements with 7 financial institutions in Chile in the aggregate
amount of $14.6 million, which lines of credit are used primarily as a source of working capital
for inventory purchases.
Effective September 21, 2009, the Company entered into an agreement pursuant to which the
Company invested $2.5 million in cash in Cocrystal Discovery, Inc., a privately held biopharmaceutical
company (Cocrystal), in exchange for 1,701,723 shares of
Cocrystals Convertible Series A Preferred Stock.
47
Table of Contents
On September 18, 2009, we entered into a securities purchase agreement (the Preferred
Purchase Agreement) with the private investors named therein (the Preferred Investors), pursuant
to which the Preferred Investors
agreed to purchase an aggregate of 1,209,677 shares (the Preferred Shares) of the Companys
newly-designated 8.0% Series D Cumulative Convertible Preferred Stock, par value $0.01 per share
(Series D Preferred Stock), at a purchase price of $24.80 per share, together with warrants to
purchase up to an aggregate of 3,024,196 shares of the Companys common stock, par value $.01 (the
Common Stock) at an exercise price of $2.48 per share (the Preferred Investment). Initially,
the Series D Preferred Stock is convertible into ten shares of the Companys Common Stock, and the
Preferred Shares purchase price was based on the average closing price of the Companys Common
Stock as reported on the NYSE Amex for the five days preceding the execution of the Preferred
Purchase Agreement. In connection with the Preferred Investment, the Company issued the Preferred
Shares on September 28, 2009 and raised approximately $30 million.
On June 10, 2009, we entered into a stock purchase agreement with Sorrento Therapeutics, Inc.
(Sorrento), pursuant to which we invested
$2.3 million in cash in Sorrento.
On May 26, 2009, May 29, 2009, and June 1, 2009, we entered into stock purchase agreements
with a total of seven accredited investors (Investors) pursuant to which the Investors agreed to
make a $31.0 million investment in the Company in exchange for 31,000,000 shares of our Common
Stock, par value $.01, at $1.00 per share. The purchase price represented a range of discounts of
approximately 16-21% to the average closing price of our Common Stock on the NYSE Amex for the five
trading days immediately preceding the closing date of the agreements.
On March 4, 2009, Frost Gamma Investments Trust (the Gamma Trust), of which Phillip Frost,
M.D., our Chairman and CEO, is the sole trustee, advanced $3.0 million to us under a Promissory
Note we issued to the Gamma Trust (the Note). The entire amount of this Note and all accrued
interest thereon was due and payable on May 4, 2009 or such earlier date following the closing of
the transaction contemplated by the Stock Purchase Agreement with the Gamma Trust, dated February
23, 2009. The Note bears interest at a rate equal to 11% per annum and may be prepaid in whole or
in part without penalty or premium. We repaid the Note in full, plus accrued interest of $48
thousand on April 27, 2009.
On February 23, 2009, we entered into a stock purchase agreement with the Gamma Trust pursuant
to which the Gamma Trust agreed to make a $20.0 million investment in exchange for 20,000,000
shares of our Common Stock, at $1.00 per share, representing an approximately 20% discount to the
average closing price of our Common Stock on the NYSE Amex for the five trading days immediately
preceding the effective date of Audit Committee and stockholder approval of the transaction. We
issued the Shares and received the proceeds of $20.0 million on April 27, 2009.
We have a fully-drawn $12.0 million line of credit with The Frost Group LLC, (the Frost
Group), a related party. We are obligated to pay interest upon maturity, compounded quarterly, on
outstanding borrowings under the line of credit at an 11% annual rate, which is due January 11,
2011. The line of credit is collateralized by all of our personal property except our intellectual
property.
We
believe the cash and cash equivalents on hand at December 31,
2009 and the amounts available to be borrowed under existing lines of
credit, are sufficient to meet
our anticipated cash requirements for operations and debt service for the next 12 months. We based
this estimate on assumptions that may prove to be wrong or are subject to change, and we may be
required to use our available cash resources sooner than we currently expect. If we acquire
additional assets or companies, accelerate our product development programs or initiate additional
clinical trials, including trials for rolapitant, we will need additional funds. Our future cash
requirements will depend on a number of factors, including possible acquisitions, the continued
progress of research and development of our product candidates, the timing and outcome of clinical
trials and regulatory approvals, the costs involved in preparing, filing, prosecuting, maintaining,
defending, and enforcing patent claims and other intellectual property rights, the status of
competitive products, the availability of financing, and our success in developing markets for our
product candidates. If we are not able to secure additional funding when needed, we may have to
delay, reduce the scope of, or eliminate one or more of our clinical trials or research and
development programs.
We expect to incur losses from operations for the foreseeable future. We expect to incur
substantial research and development expenses, including expenses related to the hiring of
personnel and additional clinical trials. We expect that selling, general and administrative
expenses will also increase as we expand our sales, marketing and administrative staff and add
infrastructure.
48
Table of Contents
We intend to finance additional research and development projects, clinical trials and our
future operations with a combination of private placements, payments from potential strategic
research and development, licensing and/or
marketing arrangements, public offerings, debt financing, and revenues from future product
sales, if any. There can be no assurance, however, that additional capital will be available to us
on acceptable terms, or at all.
The following table provides information as of December 31, 2009 with respect to the amounts
and timing of our known contractual obligation payments due by period.
| Contractual obligations | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | After 2014 | Total | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Open purchase orders |
$ | 7,152 | $ | | $ | | $ | | $ | | $ | | $ | 7,152 | |||||||||||||||
Operating leases |
448 | 428 | 261 | | | | 1,137 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Credit line |
4,319 | 12,000 | | | | | 16,319 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Total |
$ | 11,919 | $ | 12,428 | $ | 261 | $ | | $ | | $ | | $ | 24,608 | |||||||||||||||
The preceding table does not include information where the amounts of the obligations are not
currently determinable, including contractual obligations in connection with clinical trials, which
are payable on a per-patient basis and product license agreements that include payments upon
achievement of certain milestones. In addition to the principal balance as shown on our credit
line, we also must pay interest upon the maturity of the credit line in January 2011.
Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates
Accounting Estimates. The preparation of financial statements in conformity with generally
accepted accounting principles requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect
the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities
at the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of sales and expenses during the
reporting period. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
Equity-based compensation. We recognize equity based compensation as an expense in our
financial statements and that cost is measured at the fair value of the award and expensed over
their vesting period. Equity-based compensation arrangements to non-employees are recorded at
their fair value on the measurement date. We estimate the grant-date fair value of our stock
option grants using a valuation model known as the Black-Scholes-Merton formula or the
Black-Scholes Model and allocate the resulting compensation expense over the corresponding
requisite service period associated with each grant. The Black-Scholes Model requires the use of
several variables to estimate the grant-date fair value of stock options including expected term,
expected volatility, expected dividends and risk-free interest rate. We perform significant
analyses to calculate and select the appropriate variable assumptions used in the Black-Scholes
Model. We also perform significant analyses to estimate forfeitures of equity-based awards. We
are required to adjust our forfeiture estimates on at least an annual basis based on the number of
share-based awards that ultimately vest. The selection of assumptions and estimated forfeiture
rates is subject to significant judgment and future changes to our assumptions and estimates may
have a material impact on our Consolidated Financial Statements.
Goodwill and intangible assets. The allocation of the purchase price for acquisitions
requires extensive use of accounting estimates and judgments to allocate the purchase price to the
identifiable tangible and intangible assets acquired, including in-process research and
development, and liabilities assumed based on their respective fair values. Additionally, we must
determine whether an acquired entity is considered to be a business or a set of net assets, because
a portion of the purchase price can only be allocated to goodwill in a business combination.
Appraisals inherently require significant estimates and assumptions, including but not limited
to, determining the timing and estimated costs to complete the
in-process research and development projects, projecting
regulatory approvals, estimating future cash flows, and developing appropriate discount rates. We
believe the estimated fair values assigned to the Pharma Genexx assets acquired and liabilities
assumed are based on reasonable assumptions. However, the fair value estimates for the purchase
price allocation may change during the allowable allocation period, which is up to one year from
the acquisition date, if additional information becomes available that would require changes to our
estimates.
49
Table of Contents
Allowance for doubtful accounts and revenue recognition. Generally, we recognize revenue from
product sales when goods are shipped and title and risk of loss transfer to our customers. Certain
of our products are sold directly to end-users and require that we deliver, install and train the
staff at the end-users facility. As a result, we do not recognize revenue until the product is
delivered, installed and training has occurred. Return policies in certain international markets
for our medical device products provide for stringent guidelines in accordance with the terms of
contractual agreements with customers. Our estimates for sales returns are based upon the
historical patterns of
products returned matched against the sales from which they originated, and managements
evaluation of specific factors that may increase the risk of product returns. We analyze accounts receivable and historical bad debt levels, customer credit worthiness and
current economic trends when evaluating the adequacy of the allowance for doubtful accounts using
the specific identification method. Our reported net loss is directly affected by managements
estimate of the collectibility of accounts receivable. The allowance for
doubtful accounts recognized in our consolidated balance sheets at December 31, 2009 and December
31, 2008 was $0.5 million and $0.4 million, respectively.
Recent accounting pronouncements. In January 2010, the Financial Accounting Standards Board
(FASB), issued an amendment to the accounting for fair value measurements and disclosures. This
amendment details additional disclosures on fair value measurements, requires a gross presentation
of activities within a Level 3 rollforward, and adds a new requirement to disclose transfers in and
out of Level 1 and Level 2 measurements. The new disclosures are required of all entities that are
required to provide disclosures about recurring and nonrecurring fair value measurements. This
amendment is effective in the first interim or reporting period beginning after December 15, 2009,
with an exception for the gross presentation of Level 3 rollforward information, which is required
for annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2010, and for interim reporting periods
within those years. The adoption of this amendment is not expected to have a material impact on
our financial statement disclosures.
In October 2009, the FASB issued an amendment to the accounting for own-share lending
arrangements in contemplation of convertible debt issuance or other financing. This amendment
clarifies how an entity should account for an agreement between a company (share lender) and an
investment bank (share borrower) under which the company loans shares of its stock to the
investment bank, enabling the investment bank to use the shares to enter into equity derivative
contracts with the ultimate investors of the convertible debt. Under the amendment, at the date of
issuance, the share lending arrangement is required to be measured at fair value and recognized as
a debt issuance cost in the financial statements of the entity. The debt issuance cost should be
amortized under the effective interest method over the life of the financing arrangement as
interest cost. This amendment is effective for fiscal years beginning on or after December 15,
2009, and interim periods within those fiscal years. Early adoption is not permitted. The
adoption of this amendment requires retrospective application for all arrangements outstanding as
of the beginning of the fiscal year in which the guidance is initially applied. The adoption of
this amendment is not expected to have a material impact on our results of operations or financial
condition.
In October 2009, the FASB issued an amendment to the accounting for multiple-deliverable
revenue arrangements. This amendment provides guidance on whether multiple deliverables exist, how
the arrangements should be separated, and how the consideration paid should be allocated. As a
result of this amendment, entities may be able to separate multiple-deliverable arrangements in
more circumstances than under existing accounting guidance. This guidance amends the requirement
to establish the fair value of undelivered products and services based on objective evidence and
instead provides for separate revenue recognition based upon managements best estimate of the
selling price for an undelivered item when there is no other means to determine the fair value of
that undelivered item. The existing guidance previously required that the fair value of the
undelivered item reflect the price of the item either sold in a separate transaction between
unrelated third parties or the price charged for each item when the item is sold separately by the
vendor. If the fair value of all of the elements in the arrangement was not determinable, then
revenue was deferred until all of the items were delivered or fair value was determined. This
amendment will be effective prospectively for revenue arrangements entered into or materially
modified in fiscal years beginning on or after June 15, 2010. Early adoption and retrospective
application is also permitted. We are currently evaluating the potential effect of the adoption of
this amendment on our results of operations or financial condition.
In June 2009, the FASB issued an amendment to the accounting and disclosure requirements for
the consolidation of variable interest entities (VIEs). This amendment requires an enterprise to
qualitatively assess the determination of the primary beneficiary, or consolidator, of a VIE
based on whether the entity (i) has the power to direct matters that most significantly impact the
activities of the VIE, and (ii) has the obligation to absorb losses or the right to receive
benefits of the VIE that could potentially be significant to the VIE. The amendment changes the
consideration of kick-out rights in determining if an entity is a VIE and requires an ongoing
reconsideration of both whether an entity is a VIE and of the primary beneficiary. This amendment
is effective as of January 1, 2010, for interim periods within that first annual reporting period,
and for interim and annual reporting periods thereafter. Earlier adoption is prohibited. The
amendment requires companies to reassess, under the amended requirements, arrangements existing on
or before the effective date of the amendment that may fit within its scope and requires
retrospective application. We are currently evaluating the potential effect of the adoption of
this amendment but do not expect it will have a material impact on our results of operations or
financial condition.
50
Table of Contents
In June 2009, the FASB issued an amendment to the accounting and disclosure requirements for
transfers of financial assets. This amendment seeks to improve the relevance, representational
faithfulness and comparability of
the information that a reporting entity provides in its financial statements about a transfer
of financial assets; the effects of a transfer on its financial position, financial performance and
cash flows; and a transferors continuing involvement, if any, in transferred financial assets.
Additionally, on and after the effective date, this amendment eliminates the concept of a
qualifying special-purpose entity for accounting purposes. Therefore, formerly qualifying
special-purpose entities should be evaluated for consolidation by reporting entities on and after
the effective date in accordance with the applicable consolidation guidance. This amendment is
effective as of the beginning of each reporting entitys first annual reporting period that begins
after November 15, 2009, for interim periods within that first annual reporting period and for
interim and annual reporting periods thereafter. Earlier adoption is prohibited. The adoption of
this amendment is not expected to have a material impact on our results of operations or financial
condition.
| ITEM 7A. | QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK. |
In the normal course of doing business, we are exposed to the risks associated with foreign
currency exchange rates and changes in interest rates.
Foreign Currency Exchange Rate Risk Although we do not speculate in the foreign exchange
market, we may from time to time manage exposures that arise in the normal course of business
related to fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates by entering into offsetting positions
through the use of foreign exchange forward contracts. Certain firmly committed transactions are
hedged with foreign exchange forward contracts. As exchange rates change, gains and losses on the
exposed transactions are partially offset by gains and losses related to the hedging contracts.
Both the exposed transactions and the hedging contracts are translated at current spot rates, with
gains and losses included in earnings.
Our derivative activities, which consist of foreign exchange forward contracts, are initiated
to hedge forecasted cash flows that are exposed to foreign currency risk. The foreign exchange
forward contracts generally require us to exchange local currencies for foreign currencies based on
pre-established exchange rates at the contracts maturity dates. As exchange rates change, gains
and losses on these contracts are generated based on the change in the exchange rates that are
recognized in the consolidated statement of operations at maturity, and offset the impact of the
change in exchange rates on the foreign currency cash flows that are hedged. If the counterparties
to the exchange contracts do not fulfill their obligations to deliver the contracted currencies, we
could be at risk for currency related fluctuations. We enter into these contracts with
counterparties that we believe to be creditworthy and do not enter into any leveraged derivative
transactions. We had $6.3 million in foreign exchange forward contracts outstanding at December
31, 2009, and none at December 31, 2008, primarily to hedge Chilean-based operating cash flows
against US dollars. If Chilean Pesos were to strengthen in relation to the US dollar, our hedged
foreign currency cash-flows expense would be offset by a loss on the derivative contracts, with a
net effect of zero.
We do not engage in trading market risk sensitive instruments or purchasing hedging
instruments or other than trading instruments that are likely to expose us to significant market
risk, whether interest rate, foreign currency exchange, commodity price, or equity price risk.
Interest Rate Risk Our exposure to market risk relates to our cash and investments and to
our borrowings. We maintain an investment portfolio of money market funds. The securities in our
investment portfolio are not leveraged, and are, due to their very short-term nature, subject to
minimal interest rate risk. We currently do not hedge interest rate exposure. Because of the
short-term maturities of our investments, we do not believe that a change in market interest rates
would have a significant negative impact on the value of our investment portfolio except for
reduced income in a low interest rate environment. At December 31, 2009, we had cash and cash
equivalents of $42.7 million. The weighted average interest rate related to our cash and cash
equivalents for the year ended December 31, 2009 was 0%. As of December 31, 2009, the principal
value of our credit lines was $16.3 million, and have a weighted average interest rate of 9%.
The primary objective of our investment activities is to preserve principal while at the same
time maximizing yields without significantly increasing risk. To achieve this objective, we invest
our excess cash in debt instruments of the U.S. Government and its agencies, bank obligations,
repurchase agreements and high-quality corporate issuers, and money market funds that invest in
such debt instruments, and, by policy, restrict our exposure to any single corporate issuer by
imposing concentration limits. To minimize the exposure due to adverse shifts in interest rates,
we maintain investments at an average maturity of generally less than one month.
51
Table of Contents
| ITEM 8. | FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SUPPLEMENTARY DATA. |
| Page | ||||
| 53 | ||||
| 55 | ||||
| 56 | ||||
| 57 | ||||
| 58 | ||||
| 59 | ||||
52
Table of Contents
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
The Board of Directors and Shareholders of OPKO Health, Inc.
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of OPKO Health,
Inc. and subsidiaries as of December 31, 2009 and 2008, and the related
consolidated statements of operations, shareholders equity, and cash flows for
each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2009. These financial
statements are the responsibility of the Companys management. Our
responsibility is to express an opinion on these financial statements based on
our audits.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company
Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we
plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the
financial statements are free of material misstatement. An audit includes
examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in
the financial statements. An audit also includes assessing the accounting
principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as
evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our
audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, the financial statements referred to above present fairly, in
all material respects, the consolidated financial position of OPKO Health, Inc.
and subsidiaries at December 31, 2009 and 2008, and the consolidated results of
their operations and their cash flows for each of the three years in the period
ended December 31, 2009, in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting
principles.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company
Accounting Oversight Board (United States), OPKO Health, Inc. and
subsidiaries internal
control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2009, based on criteria
established in Internal Control-Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of
Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission and our report dated March
17, 2010 expressed an unqualified opinion thereon.
/s/ Ernst & Young LLP
Certified Public Accountants
Certified Public Accountants
Miami, Florida
March 17, 2010
March 17, 2010
53
Table of Contents
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
The Board of Directors and Shareholders of OPKO Health, Inc.
We have audited OPKO Health, Inc. and subsidiaries internal control over financial reporting as of
December 31, 2009, based on criteria established in Internal ControlIntegrated Framework issued
by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (the COSO criteria). OPKO
Health, Inc. and subsidiaries management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control
over financial reporting, and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over
financial reporting included in the accompanying Managements Annual Report on Internal Control
Over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the companys internal
control over financial reporting based on our audit.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight
Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain
reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was
maintained in all material respects. Our audit included obtaining an understanding of internal
control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, testing and
evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk,
and performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe
that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
A companys internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable
assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial
statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A
companys internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1)
pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the
transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that
transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance
with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company
are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company;
and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized
acquisition, use or disposition of the companys assets that could have a material effect on the
financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or
detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are
subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions or that
the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
As indicated in the accompanying Managements Annual Report on Internal Control Over Financial
Reporting, managements assessment of and conclusion on the effectiveness of internal control over
financial reporting did not include the internal controls of Pharma Genexx S.A., which is included
in the December 31, 2009 consolidated financial statements of OPKO Health, Inc. and subsidiaries
and constituted $28,024,000 and $17,145,000 of total and net assets, respectively, as of December 31, 2009 and
$4,418,000 and $176,000 of revenues and net loss, respectively, for the year then ended. Our audit of
internal control over financial reporting of
OPKO Health, Inc. and subsidiaries also did not include an evaluation of the internal control over
financial reporting of Pharma Genexx S.A.
In our opinion, OPKO Health, Inc. and subsidiaries maintained, in all material respects, effective
internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2009, based on the COSO criteria.
We have also audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight
Board (United States), the consolidated balance sheets of OPKO Health, Inc. and subsidiaries as of
December 31, 2009 and 2008, and the related consolidated statements of operations, shareholders
equity, and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2009, and our report dated March 17, 2010 expressed an unqualified opinion
thereon.
/s/ Ernst & Young LLP
Certified Public Accountants
Certified Public Accountants
Miami, Florida
March 17, 2010
March 17, 2010
54
Table of Contents
OPKO
Health, Inc. and Subsidiaries
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
(in thousands, except share data)
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
(in thousands, except share data)
| December 31, | ||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | |||||||
ASSETS |
||||||||
Current assets |
||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents |
$ | 42,658 | $ | 6,678 | ||||
Accounts receivable, net |
8,767 | 1,005 | ||||||
Inventory, net |
10,520 | 4,063 | ||||||
Current tax asset |
109 | | ||||||
Prepaid expenses and other current assets |
1,764 | 1,720 | ||||||
Total current assets |
63,818 | 13,466 | ||||||
Property and equipment, net |
593 | 659 | ||||||
Intangible assets, net |
12,722 | 6,336 | ||||||
Goodwill |
5,408 | 1,097 | ||||||
Investments |
4,447 | | ||||||
Deferred tax assets |
427 | | ||||||
Other assets |
15 | 206 | ||||||
Total assets |
$ | 87,430 | $ | 21,764 | ||||
LIABILITIES AND SHAREHOLDERS EQUITY |
||||||||
Current liabilities |
||||||||
Accounts payable |
$ | 4,784 | $ | 2,221 | ||||
Accrued expenses |
3,918 | 5,394 | ||||||
Current portion of lines of credit and notes payable |
4,321 | 97 | ||||||
Total current liabilities |
13,023 | 7,712 | ||||||
Long-term liabilities interest payable to related party |
3,409 | 1,826 | ||||||
Deferred tax liability |
1,339 | | ||||||
Line of credit with related party, net unamortized discount of $68 and
$133, respectively |
11,932 | 11,867 | ||||||
Total liabilities |
29,703 | 21,405 | ||||||
Commitments and contingencies |
||||||||
Shareholders equity |
||||||||
Series A Preferred stock $0.01 par value, 4,000,000 shares authorized;
1,025,934 and 953,756 shares issued and outstanding (liquidation
value of
$2,564 and $2,384) at December 31, 2009 and 2008, respectively |
10 | 10 | ||||||
Series C Preferred Stock $0.01 par value, 500,000 shares authorized;
No shares issued or outstanding |
| | ||||||
Series D Preferred Stock $0.01 par value, 2,000,000 shares authorized;
1,209,677 and 0 shares issued and outstanding (liquidation value of
$30,613 and $0) at December 31, 2009 and 2008, respectively |
12 | | ||||||
Common Stock $0.01 par value, 500,000,000 shares authorized;
253,762,552 and 199,020,379 shares issued and outstanding at
December 31, 2009 and 2008, respectively |
2,538 | 1,991 | ||||||
Treasury stock (45,154 and 18,000 shares at December 31, 2009
and 2008, respectively) |
(61 | ) | (24 | ) | ||||
Additional paid-in capital |
393,144 | 307,498 | ||||||
Accumulated other comprehensive income |
1,313 | | ||||||
Accumulated deficit |
(339,229 | ) | (309,116 | ) | ||||
Total shareholders equity |
57,727 | 359 | ||||||
Total liabilities and shareholders equity |
$ | 87,430 | $ | 21,764 | ||||
The accompanying Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements are an integral part of these statements.
55
Table of Contents
OPKO
Health, Inc. and Subsidiaries
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS
(in thousands, except share data)
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS
(in thousands, except share data)
| For the years ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | ||||||||||
Revenue |
$ | 13,147 | $ | 9,440 | $ | 847 | ||||||
Cost of goods sold, excluding amortization of intangible assets |
9,567 | 8,559 | 808 | |||||||||
Gross margin, excluding amortization of intangible assets |
3,580 | 881 | 39 | |||||||||
Operating expenses |
||||||||||||
Selling, general and administrative |
13,518 | 14,790 | 12,466 | |||||||||
Research and development |
12,881 | 21,562 | 10,850 | |||||||||
Write-off of acquired in-process research and
development |
2,000 | 1,398 | 243,761 | |||||||||
Other operating expenses, principally
amortization of intangible assets |
3,201 | 1,694 | 150 | |||||||||
Total operating expenses |
31,600 | 39,444 | 267,227 | |||||||||
Operating loss |
(28,020 | ) | (38,563 | ) | (267,188 | ) | ||||||
Other expense, net |
(2,034 | ) | (1,354 | ) | (671 | ) | ||||||
Loss before income taxes and investment losses. |
(30,054 | ) | (39,917 | ) | (267,859 | ) | ||||||
Income tax benefit |
294 | 83 | 83 | |||||||||
Loss before investment losses |
(29,760 | ) | (39,834 | ) | (267,776 | ) | ||||||
Loss from investments in investees |
(353 | ) | | (629 | ) | |||||||
Net loss |
(30,113 | ) | (39,834 | ) | (268,405 | ) | ||||||
Preferred stock dividend |
(846 | ) | (217 | ) | (217 | ) | ||||||
Net loss attributable to common shareholders |
$ | (30,959 | ) | $ | (40,051 | ) | $ | (268,622 | ) | |||
Loss per share, basic and diluted |
$ | (0.13 | ) | $ | (0.21 | ) | $ | (2.09 | ) | |||
Weighted
average number of common shares outstanding,
basic and diluted |
233,191,617 | 187,713,041 | 128,772,080 | |||||||||
The accompanying Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements are an integral part of these statements.
56
Table of Contents
OPKO Health, Inc. and Subsidiaries
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF SHAREHOLDERS EQUITY
(in thousands, except share data)
For the years ended December 31, 2007, 2008 and 2009
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF SHAREHOLDERS EQUITY
(in thousands, except share data)
For the years ended December 31, 2007, 2008 and 2009
| Additional | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Series A Preferred Stock | Series C Preferred Stock | Series D Preferred Stock | Common Stock | Treasury | Paid-In | Accumulated | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares | Dollars | Shares | Dollars | Shares | Dollars | Shares | Dollars | Shares | Dollars | Capital | Deficit | Total | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Balance at December 31, 2006 |
| $ | | | $ | | | $ | | 61,775,002 | $ | 618 | | $ | | $ | 280 | $ | (877 | ) | $ | 21 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Equity based compensation expense |
| | | | | | | | | 7,373 | | 7,373 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Issuance of equity securities for
net monetary assets at $0.42 per
share |
1,081,750 | 11 | | | | | 36,607,023 | 366 | | | 15,626 | | 16,003 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Issuance of equity securities to
acquire Acuity Pharmaceuticals,
Inc., at $2.65 per share |
| | 457,603 | 5 | | | 14,778,556 | 148 | | | 234,470 | | 234,623 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Issuance of equity securities to
acquire Ophthalmic
Technologies, Inc. at $2.57 per
share |
| | | | | | 2,682,928 | 27 | | | 6,905 | | 6,932 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Issuance of equity securities to
acquire software at $3.79 per
share |
| | | | | | 30,000 | | | | 114 | | 114 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Issuance of common stock in private
Placement to related party at
1.84 per share |
| | | | | | 10,869,565 | 109 | | | 19,891 | | 20,000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Issuance of common stock upon
automatic conversion of Series C
preferred stock |
| | (457,603 | ) | (5 | ) | | | 45,760,300 | 457 | | | (452 | ) | | | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Conversion of Series A preferred
stock |
(213,751 | ) | (2 | ) | | | | | 213,751 | 2 | | | | | | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Exercise of common stock options |
| | | | | | 641,972 | 6 | | | 117 | | 123 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Exercise of common stock warrants |
| | | | | | 4,985,511 | 50 | | | (50 | ) | | | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Preferred stock dividend |
86,800 | 1 | | | | | | | | | (1 | ) | | | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Net loss for the year ended
December 31, 2007 |
| | | | | | | | | | | (268,405 | ) | (268,405 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Balance at December 31, 2007 |
954,799 | 10 | | | | | 178,344,608 | 1,783 | | | 284,273 | (269,282 | ) | 16,784 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Equity-based compensation expense |
| | | | | | | | | | 6,730 | | 6,730 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Issuance of equity securities to
acquire Vidus Ocular, Inc. at
$1.65 per share |
| | | | | | 658,080 | 7 | | | 1,312 | | 1,319 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Correction of equity securities to
Acuity |
| | | | | | 57,408 | 1 | | | (1 | ) | | | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Exercise of common stock options |
| | | | | | 5,187,149 | 52 | | | 154 | | 206 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Exercise of common warrants |
| | | | | | 1,171,899 | 12 | | | 165 | | 177 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Issuance of common stock in private
placement to related party at 1.11 |
| | | | | | 13,513,514 | 135 | | | 14,865 | | 15,000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Series A preferred stock dividend |
86,678 | 1 | | | | | | | | | | | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Conversion of Series A preferred
Stock |
(87,721 | ) | (1 | ) | | | | | 87,721 | 1 | | | | | | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Other disposition of assets for stock |
| | | | | | | | (18,000 | ) | (24 | ) | | | (24 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Net loss for the year ended
December 31, 2008 |
| | | | | | | | | | | (39,834 | ) | (39,834 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Balance at December 31, 2008. |
953,756 | 10 | | | | | 199,020,379 | 1,991 | (18,000 | ) | (24 | ) | 307,498 | (309,116 | ) | 359 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Equity-based compensation
expense |
| | | | | | | | | | 4,498 | | 4,498 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Exercise of common stock
options |
| | | | | | 2,984,945 | 30 | | | 664 | | 694 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Exercise of common warrants |
| | | | | | 706,164 | 7 | | | 17 | | 24 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Issuance of common stock in
private placement with
related
parties at $1.00 per share |
| | | | | | 20,000,000 | 200 | | | 19,800 | | 20,000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Issuance of common stock in
private
placement, including
related
parties at $1.00 per share |
| | | | | | 31,000,000 | 310 | | | 30,680 | | 30,990 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Issuance of 8% Series D
Preferred
stock in private
placement,
including related parties
at $24.80
per share |
| | | | 1,209,677 | 12 | | | | | 29,988 | | 30,000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Series A preferred stock
dividend |
93,242 | 1 | | | | | | | | | (1) | | | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Conversion of Series A
preferred
Stock |
(21,064 | ) | (1 | ) | | | | | 21,064 | | | | | | (1 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Restricted stock grant |
| | | | | | 30,000 | | | | | | | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Purchase of shares at $3.55 |
| | | | | | | | (27,154 | ) | (37 | ) | | | (37 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Comprehensive loss |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Net loss for the year ended December 31, 2009
|
| | | | | | | | | | | (30,113 | ) | (30,113 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Cumulative translation
adjustment,
net |
1,313 | 1,313 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total comprehensive loss |
(28,800 | ) | (28,800 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Balance at December 31, 2009. |
1,025,934 | $ | 10 | | $ | | 1,209,677 | $ | 12 | 253,762,552 | $ | 2,538 | (45,154 | ) | $ | (61 | ) | $ | 393,144 | $ | (337,916 | ) | $ | 57,727 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The accompanying Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements are an integral part of these statements.
57
Table of Contents
OPKO
Health, Inc. and Subsidiaries
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
(in thousands)
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
(in thousands)
| For the year ended | |||||||||||||
| December 31, | |||||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | |||||||||||
Cash flows from operating activities: |
|||||||||||||
Net loss |
$ | (30,113 | ) | $ | (39,834 | ) | $ | (268,405 | ) | ||||
Adjustments to reconcile net loss to net cash used in
operating activities: |
|||||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization |
2,357 | 1,823 | 184 | ||||||||||
Impairment
of goodwill |
1,097 | | | ||||||||||
Write-off of acquired in-process research and development |
2,000 | 1,398 | 243,761 | ||||||||||
Accretion of debt discount related to notes payable |
123 | 190 | 279 | ||||||||||
Losses from investments in investees |
353 | | 629 | ||||||||||
Equity based compensation employees and non-employees. |
4,498 | 6,730 | 7,373 | ||||||||||
Provision for bad debts |
73 | 204 | | ||||||||||
Provision for inventory obsolescence |
279 | 255 | | ||||||||||
Foreign exchange |
122 | | | ||||||||||
Loss on disposal of assets |
| 148 | | ||||||||||
Changes in: |
|||||||||||||
Accounts receivable |
(1,271 | ) | 590 | (554 | ) | ||||||||
Inventory |
(928 | ) | (2,104 | ) | (317 | ) | |||||||
Prepaid expenses and other current assets |
431 | 25 | (789 | ) | |||||||||
Other assets |
(276 | ) | | | |||||||||
Accounts payable |
(1,019 | ) | (1,225 | ) | (607 | ) | |||||||
Accrued expenses |
(1,062 | ) | 2,506 | 1,497 | |||||||||
Net cash used in operating activities |
(23,336 | ) | (29,294 | ) | (16,949 | ) | |||||||
Cash flows from investing activities: |
|||||||||||||
Investments in investees |
(4,800 | ) | | (5,000 | ) | ||||||||
Acquisition of businesses, net of cash |
(15,632 | ) | 48 | 2,751 | |||||||||
Acquisition of rolapident |
(2,000 | ) | | | |||||||||
Purchase of marketable securities |
(9,997 | ) | | | |||||||||
Maturities of marketable securities |
9,997 | | | ||||||||||
Capital expenditures |
(172 | ) | (378 | ) | (489 | ) | |||||||
Net cash used in investing activities |
(22,604 | ) | (330 | ) | (2,738 | ) | |||||||
Cash flows from financing activities: |
|||||||||||||
Issuance of common stock for cash to related party |
30,990 | 15,000 | 20,000 | ||||||||||
Issuance of common stock |
20,000 | | 16,284 | ||||||||||
Issuance of Series D preferred stock and warrants,
including related parties |
30,000 | | | ||||||||||
Borrowings under line of credit with related party |
| | 8,000 | ||||||||||
Proceeds from bridge loan with related party |
3,000 | | | ||||||||||
Repayment of bridge loan with related party |
(3,000 | ) | | | |||||||||
Insurance
financing and borrowings on lines of credit |
529 | 371 | 152 | ||||||||||
Proceeds from the exercise of stock options and warrants. |
718 | 383 | 123 | ||||||||||
Repayments of notes payable and capital lease obligations |
(317 | ) | (2,825 | ) | (1,615 | ) | |||||||
Net cash provided by financing activities |
81,920 | 12,929 | 42,944 | ||||||||||
Net change in cash and cash equivalents |
35,980 | (16,695 | ) | 23,257 | |||||||||
Cash and
cash equivalents at beginning of year |
6,678 | 23,373 | 116 | ||||||||||
Cash and
cash equivalents at end of year |
$ | 42,658 | $ | 6,678 | $ | 23,373 | |||||||
The accompanying Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements are an integral part of these statements.
58
Table of Contents
OPKO
Health, Inc. and Subsidiaries
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 1. Business and Organization
We are a specialty healthcare company involved in the discovery, development, and
commercialization of pharmaceutical products, medical devices, vaccines, diagnostic technologies,
and imaging systems. Initially focused on the treatment and management of ophthalmic diseases, we
have since expanded into other areas of major unmet medical need. We are a Delaware corporation,
headquartered in Miami, Florida.
On March 27, 2007, pursuant to the terms of a Merger Agreement and Plan of Reorganization,
Froptix Corporation (Froptix), a development stage research and development company, controlled
by The Frost Group, LLC (the Frost Group) and Acuity Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (Acuity), a
development stage research and development company, and eXegenics were part of a three-way merger
(the Merger). Per that agreement, eXegenics issued new capital stock to acquire all of the
issued and outstanding capital stock of Froptix and Acuity. The Frost Group members include the
Frost Gamma Investment Trust (the Gamma Trust) of which Phillip Frost, M.D., our Chairman and
CEO, is the sole trustee, Jane Hsiao, the Companys Vice Chairman and Chief Technical Officer,
Steven D. Rubin, the Companys Executive Vice President Administration and a director, and Rao
Uppaluri, the Companys Chief Financial Officer.
On June 8, 2007, we changed our name to OPKO Health, Inc. (OPKO or the Company) from
eXegenics, Inc. (eXegenics). Through March 26, 2007, eXegenics was a public shell company whose
assets consisted of cash and nominal other assets.
Note 2. Acquisitions and Investments
On October 12, 2009, we entered into an asset purchase agreement (the Schering Agreement)
with Schering-Plough Corporation (Schering) to acquire rolapitant, our lead pharmaceutical
product candidate, and other assets relating to Scherings neurokinin-1 (NK-1) receptor
antagonist program. Under the terms of the Schering Agreement, we paid Schering $2 million in cash
upon closing and agreed to pay up to an additional $27 million upon certain development milestones.
Rolapitant, the lead product in the NK-1 program, successfully completed Phase II clinical testing
for prevention of nausea and vomiting related to cancer chemotherapy and surgery, and other
indications. Phase I clinical testing has also been completed for a second compound in the same
class. Development of rolapitant and the other assets had been
stopped at the time of our acquisition and there were no ongoing
clinical trials. None of the assets acquired have alternative future
uses, nor have they reached a stage of technological
feasability.
The table below reflects the estimated fair value of the net assets acquired at the date of
acquisition:
| (in thousands) | ||||
In-process research and development |
$ | 2,000 |
On October 1, 2009, we entered into a definitive agreement to acquire Pharma Genexx S.A.
(Pharma Genexx), a privately-owned Chilean company engaged in the representation, importation,
commercialization and distribution of pharmaceutical products, over-the-counter products and
medical devices for government, private and institutional markets in Chile. Pursuant to a stock
purchase agreement with Pharma Genexx and its shareholders, Farmacias Ahumada S.A., FASA Chile
S.A., and Laboratorios Volta S.A., we acquired all of the outstanding stock of Pharma Genexx in
exchange for $16 million in cash. A portion of the proceeds will remain in escrow for a period of
time to satisfy indemnification claims. The transaction closed on October 7, 2009.
The following table summarizes the estimated fair value of the net assets acquired and
liabilities assumed in the acquisition of Pharma Genexx at the date of acquisition:
| (in thousands) | ||||
Current assets (including cash of $368) |
$ | 12,208 | ||
Intangible assets |
7,826 | |||
Goodwill |
4,983 | |||
Other assets |
20 | |||
Accounts payable and accrued expenses |
(9,037 | ) | ||
Total purchase price |
$ | 16,000 | ||
59
Table of Contents
Effective September 21, 2009, the Company entered into an agreement pursuant to which the
Company invested $2.5 million in cash in Cocrystal Discovery, Inc., a privately held biopharmaceutical
company (Cocrystal) in exchange for 1,701,723 shares of
Cocrystals Convertible Series A
Preferred Stock. A group of investors led by the Frost Group (the Frost Investors), previously
invested $5 million in Cocrystal, and agreed to invest an additional $5 million payable in two
equal installments in September 2009 and March 2010. As a result of an amendment to the Frost
Investor agreements dated June 9, 2009, OPKO, rather than the Frost Investors, made the first
installment investment ($2.5 million) on September 21, 2009. Following the first investment, the
members of the Frost Group owned a total of 2,948,645 shares of Cocrystal, representing 33.65% of
Cocrystals voting stock on an as converted basis and the Gamma Trust owned a majority of those
shares, owning 2,768,257 shares. On Deccember 31, 2009 we owned approximately 20% of Cocrystals outstanding stock. Following the final installment investment of $2.5 million in
Cocrystal by the Frost Investors in or around March 2010, the Company will own approximately 16% of
Cocrystal and members of the Frost Group will own approximately 4,422,967 shares, representing 42%
of Cocrystals voting stock on an as converted basis, including 4,152,386 held by the Gamma Trust.
Dr. Frost, Mr. Rubin, and Dr. Hsiao currently serve on the Board of Directors of Cocrystal and
represent 50% of its board.
We have determined that Cocrystal has insufficient resources to carry out its principal
activities without additional subordinated financial support. As such, Cocrystal meets the
definition of a variable interest entity ("VIE"). In order to determine the primary beneficiary of the VIE, we evaluated the
related party group to identify who had the most significant power to control Cocrystal. The Gamma
Trust holds in excess of 32% of the voting stock of Cocrystal on a fully diluted basis as of the
date of our investment and after the March 2010 investment by the Frost Investors, will hold in
excess of 42% of the voting stock. In addition, the Gamma Trust influenced the redesign of
Cocrystal and can significantly influence the success of Cocrystal through its board representation
and voting power. As such, we have determined that the Gamma Trust is the primary beneficiary
within the related party group. As a result of our determination that we are not the primary
beneficiary, we have accounted for our investment in Cocrystal under the equity method.
On June 10, 2009, we entered into a stock purchase agreement with Sorrento Therapeutics, Inc.
(Sorrento), a privately held company with a technology for generating fully human monoclonal
antibodies, pursuant to which we invested $2.3 million in Sorrento. In exchange for the
investment, we acquired approximately one-third of the outstanding common shares of Sorrento and
received a fully-paid, exclusive license to the Sorrento antibody library for the discovery and
development of therapeutic antibodies in the field of ophthalmology. On September 21, 2009,
QuikByte Software, Inc., a Colorado corporation (Quikbyte), acquired Sorrento pursuant to a
Merger Agreement dated July 14, 2009 (the Sorrento Merger) by and among QuikByte, Sorrento, and
certain other parties named therein. At the effective time of the Sorrento Merger, all of the
issued and outstanding shares of Sorrento common stock (the Sorrento Shares) were converted into
the right to receive shares of QuikByte common stock, par value $0.0001 per share (the QuikByte
Common Stock).
On September 18, 2009, QuikByte entered into a Stock Purchase Agreement (the QuikByte Stock
Purchase Agreement) with investors (the QuikByte Investors) pursuant to which QuikByte received
an aggregate investment of $2.0 million in exchange for shares of QuikByte Common Stock (the
QuikByte Financing). The QuikByte Investors included Dr. Frost and other members of OPKO
management. Upon completion of the Sorrento Merger, QuickByte changed its name to Sorrento
Therapeutics, Inc. After giving effect to the Sorrento Financing, OPKO owned approximately
53,113,732 shares of Sorrento Common Stock, or approximately 24% of Sorrentos total outstanding
common stock at December 31, 2009. The closing stock price for
Sorrento's common stock, a thinly traded stock, as
quoted on the over-the-counter markets was $1.92 per share on December 31, 2009.
On May 6, 2008, we completed the acquisition of Vidus Ocular, Inc. (Vidus), a privately-held
company that is developing Aquashunt, a shunt to be used in the treatment of glaucoma. Pursuant
to a Securities Purchase Agreement with Vidus, each of its stockholders, and the holders of
convertible promissory notes issued by Vidus, we acquired all of the outstanding stock and
convertible debt of Vidus in exchange for (i) the issuance and delivery at closing of 658,080
shares of our common stock (the Closing Shares); (ii) the issuance of 488,420 shares of our
common stock to be held in escrow pending the occurrence of certain development milestones (the
Milestone Shares); and (iii) the issuance of options to acquire 200,000 shares of our common
stock. Additionally, in the event that the stock price for our common stock at the time of receipt
of approval or clearance by the U.S. Food & Drug Administration of a pre-market notification 510(k)
relating to the Aquashunt is not at or above a specified price, we will be obligated to issue an
additional 413,850 shares of our common stock. A portion of the Closing Shares and the Milestone
Shares remained in escrow for a period of one year to satisfy indemnification claims.
60
Table of Contents
We accounted for the Vidus acquisition as an asset acquisition. We valued the common stock
issued to Vidus stockholders at the average closing price on the date of the acquisition and the
two days prior to the transaction, or
$1.65 per share. In addition, we valued the options to acquire our common stock that were
issued to the founders of Vidus using the Black-Scholes-Merton pricing model and recorded the value of
those options as part of the purchase price of Vidus, or $1.17 per common stock option. All other
contingent consideration will be valued and added to the purchase price if the milestones occur.
The table below reflects the estimated fair value of the net assets acquired at the date of
acquisition:
| (in thousands) | ||||
Current assets (cash of $48) |
$ | 48 | ||
In-process research and development |
1,398 | |||
Accounts payable and accrued expenses |
(127 | ) | ||
Total purchase price |
$ | 1,319 | ||
The portion of the purchase price allocated to in-process research and development of $1.4
million was immediately expensed.
On April 13, 2007, we invested $5 million in exchange for common shares of Ophthalmic
Technologies, Inc. (OTI), equaling one-third of the outstanding equity of OTI. On November 28,
2007, we acquired the remaining outstanding shares of OTI and issued approximately 2.7 million
shares of our common stock based upon a purchase price of $10.0 million and a value of $3.55 per
share. OTI provides diagnostic and imaging systems to eye care professionals worldwide through its
distributor network which covers over 50 countries. The minority interest results in OTI from
April 13, 2007 through our acquisition of OTI on November 28, 2007 have been included in our
financial statements.
The following table summarizes the estimated fair value of the net assets acquired and
liabilities assumed in the acquisition OTI at the date of acquisition:
| (in thousands) | ||||
Current assets (including cash of $1,616) |
$ | 4,682 | ||
Intangible assets |
8,087 | |||
Other assets |
602 | |||
Goodwill |
1,732 | |||
Accounts payable and accrued expenses |
(3,374 | ) | ||
Total purchase price |
$ | 11,729 | ||
On
March 27, 2007, we acquired Acuity in a stock-for-stock transaction. We valued our common
stock issued to Acuity shareholders at the average closing price of the common stock on the date of
acquisition and the two days prior to the transaction. Acuitys primary focus prior to our
acquisition had been on the development of its lead compound, bevasiranib, for the treatment of Wet
Age-Related Macular Degeneration, or Wet AMD.
The following table summarizes the estimated fair value of the net assets acquired and
liabilities assumed in the acquisition of Acuity at the date of acquisition:
| (in thousands) | ||||
Current assets (including cash of $1,135) |
$ | 1,350 | ||
Property and equipment |
85 | |||
In-process research and development |
243,761 | |||
Accounts payable and accrued expenses |
(3,154 | ) | ||
Line of credit and term loan |
(7,419 | ) | ||
Total purchase price |
$ | 234,623 | ||
The portion of the purchase price allocated to in-process research and development of $243.8
million relates to the acquisition of Acuity and was immediately expensed. The majority of our
research and development expenses have been focused on our most advanced compound, bevasiranib. In
March 2009, we terminated the Phase III clinical trial of bevasiranib. Acuitys second compound,
ACU-NCT-001, did not reach technological feasibility during 2008 and has since been abandoned, and
its other projects are still in various early stages of development.
61
Table of Contents
The purchase price of Acuity includes $1.5 million of costs incurred by us to acquire Acuity,
including $1.3 million of costs associated with the issuance of warrants to the Frost Group as a
result of the increase of the credit line with Acuity.
The following table summarizes that fair value assigned to our major intangible assets
classes:
| Fair value | Weighted average | |||||||
| (in thousands) | assigned | amortization period | ||||||
Customer relationships |
$ | 7,259 | 3 years | |||||
Technology |
4,597 | 10 years | ||||||
Product registrations |
3,829 | 10 years | ||||||
Covenants not to compete |
317 | 3 years | ||||||
Tradename |
578 | 3 years | ||||||
Other |
7 | Indefinite | ||||||
Total amortizing intangible assets |
16,587 | |||||||
Goodwill |
5,408 | Indefinite | ||||||
Total intangible assets acquired |
$ | 21,995 | ||||||
All of the intangible
assets acquired and goodwill acquired relate to our acquisitions of
Pharma Genexx and OTI. The weighted average period prior to the next renewal or extension for our product
registrations is 2.7 years. We do not anticipate capitalizing the cost of product registration renewals,
rather we expect to expense, as incurred costs related to the activities required to renew our product registrations. We do not anticipate goodwill to be tax deductible for income tax purposes.
The
following table includes the pro forma results for the years ended
December 31, 2009 and 2008 of the combined companies as though
the acquisitions of Pharma Genexx and Vidus had been completed as of the beginning of each period, respectively, and for the 2008 period includes $0.5 million related to Vidus.
| For the year ended December 31, | |||||||||
| (in thousands, except per share amounts) | 2009 | 2008 | |||||||
Revenue |
$ | 25,615 | $ | 20,365 | |||||
Net loss |
$ | (28,443 | ) | $ | (39,713 | ) | |||
Basic and diluted loss per share |
$ | (0.12 | ) | $ | (0.21 | ) | |||
This unaudited pro forma financial information is presented for informational purposes only.
The unaudited pro forma financial information may not necessarily reflect our future results of
operations or what the results of operations would have been had we owned and operated each company
as of the beginning of the periods presented.
Note 3. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
Basis of Presentation. The accompanying consolidated financial statements have been prepared
in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States and with the
instructions to Form 10-K and of Regulation S-X. The consolidated financial statements include the
accounts of the Company and its wholly-owned subsidiaries. All significant intercompany
transactions and balances have been eliminated in consolidation.
Use of Estimates. The preparation of financial statements in conformity with accounting
principles generally accepted in the United States of America requires management to make estimates
and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of
contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts
of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. Actual results could differ from those
estimates.
Cash and Cash Equivalents. We consider all non-restrictive, highly liquid short-term
investments purchased with a maturity of three months or less on the date of purchase to be cash
equivalents.
Inventories. Inventories are valued at the lower of cost or market (net realizable value).
Cost is determined by the first-in, first-out method.
Property and Equipment. Property and equipment are recorded at cost. Depreciation is
provided using the straight-line method over the estimated useful lives of the assets, generally
five to ten years and includes amortization expense for assets capitalized under capital leases.
The estimated useful life by asset class are as follows: software 3 years, machinery and
equipment 5-8 years, furniture and fixtures 5-10 years and leasehold improvements the
lesser of their useful life or the lease term. Expenditures for repairs and maintenance are
charged to expense as incurred, while betterments reduce accumulated
depreciation. Depreciation expense was $0.2
million, $0.1 million, and $35 thousand for the years ended
December 31, 2009, 2008 and 2007, respectively.
62
Table of Contents
Goodwill and Intangible Assets. Goodwill represents the difference between the purchase
price and the estimated fair value of the net assets acquired when accounted for by the purchase
method of accounting and arose from our acquisitions of OTI and Pharma Genexx. Refer to Note 2.
We do not amortize goodwill, however, we perform an annual impairment test of goodwill during the
fourth quarter. During the fourth quarter of 2009, we performed an impairment test and determined
the goodwill related to our instrumentation business was impaired and written down to $0. We
evaluate our goodwill for impairment annually and whenever events and changes in circumstances
suggest that the carrying amount may not be recoverable.
We amortize intangible assets with definite lives on a straight-line basis over their
estimated useful lives, ranging from 3 to 10 years, and review for impairment at least annually, or
sooner when events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of such assets may
not be recoverable. We use the straight-line method of
amortization as there is no reliably determinable pattern in which
the economic benefits of our intangible assets are consumed or
otherwise used up. Amortization expense was $3.2 million and $1.7 million for the years ended
December 31, 2009 and 2008, respectively. Included in the amortization expense for the year ended
December 31, 2009, is $1.1 million related to the impairment of the goodwill related to our
instrumentation segment. In addition, the 2009 year included amortization related to the
acquisition of Pharma Genexx. Amortization expense for the years ending December 31, 2010, 2011,
2012, 2013, and 2014 is expected to be $3.3 million, $2.2 million, $1.8 million, $0.8 million, and
$0.8 million, respectively.
Impairment of Long-Lived Assets. Long-lived assets, such as property and equipment, are
reviewed for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying
amount of an asset may not be recoverable. Recoverability of assets to be held and used is
measured by a comparison of the carrying amount of an asset to estimated undiscounted future cash
flows expected to be generated by the asset. If the carrying amount of an asset exceeds its
estimated future cash flows, then an impairment charge is recognized by the amount by which the
carrying amount of the asset exceeds the fair value of the asset.
Fair Value Measurements. The carrying amounts of our cash and cash equivalents, accounts
receivable, accounts payable, and accrued expenses approximate their fair value due to the
short-term maturities of these instruments. Investments are considered available-for-sale as of
December 31, 2009 and 2008, and are carried at fair value.
Short-term investments include bank deposits, corporate notes, U.S. treasury securities and
U.S. government agency securities with original maturities of greater than 90 days and remaining
maturities of less than one year. Long-term investments include corporate notes, U.S. treasury
securities and U.S. government agency securities with maturities greater than one year.
In evaluating the fair value information, considerable judgment is required to interpret the
market data used to develop the estimates. The use of different market assumptions and/or
different valuation techniques may have a material effect on the estimated fair value amounts.
Accordingly, the estimates of fair value presented herein may not be indicative of the amounts that
could be realized in a current market exchange. Refer to Note 17.
Derivative financial instruments. We record derivative financial instruments on our balance
sheet at their fair value and the changes in the fair value are recognized in income when they
occur, the only exception being derivatives that qualify as hedges. To qualify the derivative
instrument as a hedge, we are required to meet strict hedge effectiveness and contemporaneous
documentation requirements at the initiation of the hedge and assess the hedge effectiveness on an
ongoing basis over the life of the hedge. At December 31, 2009, the forward contracts did not meet
the documentation requirements to be designated as hedges. Accordingly, we recognize all changes
in fair values in income.
Research and Development. Research and development costs are charged to expense as incurred.
We record expense for in-process research and development projects acquired as asset acquisitions
which have not reached technological feasibility and which have no alternative future use. For
in-process research and development projects acquired in business combinations, the in-process
research and development project is capitalized and evaluated for impairment until the development
process has been completed. Once the development process has been completed the asset will be
amortized over its remaining useful life.
Income Taxes. Income taxes are accounted for under the asset-and-liability method. Deferred
tax assets and liabilities are recognized for the future tax consequences attributable to
differences between the financial statement carrying amounts of existing assets and liabilities and
the respective tax bases and operating loss and tax credit carryforwards. Deferred tax assets and
liabilities are measured using enacted tax rates expected to apply to taxable income in the years
in which those temporary differences are expected to be recovered or settled. The effect on
deferred tax assets and liabilities of a change in tax rates is recognized in operations in the
period that includes the
enactment date. We periodically evaluate the realizability of our net deferred tax assets.
Our tax accruals are analyzed periodically and adjustments are made as events occur to warrant such
adjustment.
63
Table of Contents
Loss Per Common Share. Basic and diluted earnings or loss per common share is based on the
net loss increased by dividends on preferred stock divided by the weighted average number of common
shares outstanding during the period. In the periods in which their effect would be anti-dilutive,
no effect has been given to outstanding options, warrants or convertible preferred stock in the
diluted computation. The diluted loss per share does not include the weighted average impact of
the outstanding options, warrants, and other contingent consideration of 17,743,032, 24,022,713,
and 30,508,179 shares for the years ended December 31, 2009, 2008, and 2007 respectively, because
their inclusion would have been anti-dilutive. As of December 31, 2009, the holders of our Series
A Preferred Stock and Series D Preferred Stock could convert their Preferred Shares into
approximately 1,025,934 and 12,344,081 shares of our Common Stock, respectively.
Revenue Recognition. Generally, we recognize revenue from product sales when goods are
shipped and title and risk of loss transfer to our customers. Certain of our products are sold
directly to end-users and require that we deliver, install and train the staff at the end-users
facility. As a result, we do not recognize revenue until the product is delivered, installed and
training has occurred.
Allowance for Doubtful Accounts. We analyze accounts receivable and historical bad debt levels, customer credit worthiness and
current economic trends when evaluating the adequacy of the allowance for doubtful accounts using
the specific identification method. Our reported net loss is directly affected by managements
estimate of the collectibility of accounts receivable. Estimated allowances for sales returns are based upon our
history of product returns. The amount of allowance for doubtful accounts at December 31, 2009 and
2008 was $0.5 million and $0.4 million, respectively.
Product Warranties. Product warranties are accrued at the time we record revenue for a
product. The costs of warranties are recorded as a component of cost of sales. We estimate
warranty costs based on our estimated historical experience and adjust for any known product
reliability issues.
| (in thousands) | 2009 | 2008 | ||||||
Beginning balance |
$ | 259 | $ | 227 | ||||
Accrual for product sold |
257 | 259 | ||||||
Settlements in kind or expired |
(259 | ) | (227 | ) | ||||
Ending balance |
$ | 257 | $ | 259 | ||||
Equity-Based Compensation. We measure the cost of employee services received in exchange for
an award of equity instruments based on the grant-date fair value of the award. That cost is
recognized in the statement of operations over the period during which an employee is required to
provide service in exchange for the award. We record excess tax benefits, realized from the
exercise of stock options as a financing cash inflow rather than as a reduction of taxes paid in
cash flow from operations. Refer to Note 8. Equity-based compensation arrangements to
non-employees are recorded at their fair value on the measurement date. The measurement of
equity-based compensation is subject to periodic adjustment as the underlying equity instruments
vest.
Comprehensive income or loss. Our comprehensive loss for the year ended December 31, 2009
includes net loss for the year and the cumulative translation adjustment, net, for the translation
of our Chilean subsidiarys results and comprehensive loss for the years ended December 31, 2008
and 2007 is comprised entirely of our net loss.
Segment reporting. Our chief operating decision-maker (CODM) is comprised of our executive
management with the oversight of our board of directors. Our CODM review our operating results and
operating plans and make resource allocation decisions on a company-wide or aggregate basis.
Accordingly, we have aggregated our three operating segments, instrumentation, pharmaceutical
operating business and our pharmaceutical and device research and development activities into two
reporting segments, instrumentation and pharmaceutical.
Recent accounting pronouncements: In January 2010, the Financial Accounting Standards Board
(FASB) issued an amendment to the accounting for fair value measurements and disclosures. This
amendment details additional disclosures on fair value measurements, requires a gross presentation
of activities within a Level 3 rollforward, and adds a new requirement to disclose transfers in and
out of Level 1 and Level 2 measurements. The new disclosures are required of all entities that are
required to provide disclosures about recurring and nonrecurring fair value measurements. This
amendment is effective in the first interim or reporting period beginning after December 15, 2009,
with an exception for the gross presentation of Level 3 rollforward information, which is required
for annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2010, and for interim reporting periods
within those years. The adoption of this amendment is not expected to have a material impact on
our financial statement disclosures.
64
Table of Contents
In October 2009, the FASB issued an amendment to the accounting for own-share lending
arrangements in contemplation of convertible debt issuance or other financing. This amendment
clarifies how an entity should account for an agreement between a company (share lender) and an
investment bank (share borrower) under which the company loans shares of its stock to the
investment bank, enabling the investment bank to use the shares to enter into equity derivative
contracts with the ultimate investors of the convertible debt. Under the amendment, at the date of
issuance, the share lending arrangement is required to be measured at fair value and recognized as
a debt issuance cost in the financial statements of the entity. The debt issuance cost should be
amortized under the effective interest method over the life of the financing arrangement as
interest cost. This amendment is effective for fiscal years beginning on or after December 15,
2009, and interim periods within those fiscal years. Early adoption is not permitted. The
adoption of this amendment requires retrospective application for all arrangements outstanding as
of the beginning of the fiscal year in which the guidance is initially applied. The adoption of
this amendment is not expected to have a material impact on our results of operations or financial
condition.
In October 2009, the FASB issued an amendment to the accounting for multiple-deliverable
revenue arrangements. This amendment provides guidance on whether multiple deliverables exist, how
the arrangements should be separated, and how the consideration paid should be allocated. As a
result of this amendment, entities may be able to separate multiple-deliverable arrangements in
more circumstances than under existing accounting guidance. This guidance amends the requirement
to establish the fair value of undelivered products and services based on objective evidence and
instead provides for separate revenue recognition based upon managements best estimate of the
selling price for an undelivered item when there is no other means to determine the fair value of
that undelivered item. The existing guidance previously required that the fair value of the
undelivered item reflect the price of the item either sold in a separate transaction between
unrelated third parties or the price charged for each item when the item is sold separately by the
vendor. If the fair value of all of the elements in the arrangement was not determinable, then
revenue was deferred until all of the items were delivered or fair value was determined. This
amendment will be effective prospectively for revenue arrangements entered into or materially
modified in fiscal years beginning on or after June 15, 2010. Early adoption and retrospective
application is also permitted. We are currently evaluating the potential effect of the adoption of
this amendment on our results of operations or financial condition.
In June 2009, the FASB issued an amendment to the accounting and disclosure requirements for
the consolidation of VIEs. This amendment requires an enterprise to
qualitatively assess the determination of the primary beneficiary, or consolidator, of a VIE
based on whether the entity (i) has the power to direct matters that most significantly impact the
activities of the VIE, and (ii) has the obligation to absorb losses or the right to receive
benefits of the VIE that could potentially be significant to the VIE. The amendment changes the
consideration of kick-out rights in determining if an entity is a VIE and requires an ongoing
reconsideration of both whether an entity is a VIE and of the primary beneficiary. This amendment
is effective as of January 1, 2010, for interim periods within that first annual reporting period,
and for interim and annual reporting periods thereafter. Earlier adoption is prohibited. The
amendment requires companies to reassess, under the amended requirements, arrangements existing on
or before the effective date of the amendment that may fit within its scope and requires
retrospective application. We are currently evaluating the potential effect of the adoption of
this amendment but do not expect it will have a material impact on our results of operations or
financial condition.
In June 2009, the FASB issued an amendment to the accounting and disclosure requirements for
transfers of financial assets. This amendment seeks to improve the relevance, representational
faithfulness and comparability of the information that a reporting entity provides in its financial
statements about a transfer of financial assets; the effects of a transfer on its financial
position, financial performance and cash flows; and a transferors continuing involvement, if any,
in transferred financial assets. Additionally, on and after the effective date, this amendment
eliminates the concept of a qualifying special-purpose entity for accounting purposes. Therefore,
formerly qualifying special-purpose entities should be evaluated for consolidation by reporting
entities on and after the effective date in accordance with the applicable consolidation guidance.
This amendment is effective as of the beginning of each reporting entitys first annual reporting
period that begins after November 15, 2009, for interim periods within that first annual reporting
period and for interim and annual reporting periods thereafter. Earlier adoption is prohibited.
The adoption of this amendment is not expected to have a material impact on our results of
operations or financial condition.
65
Table of Contents
Note 4. Composition of Certain Financial Statement Captions
| December 31, | ||||||||
| (in thousands) | 2009 | 2008 | ||||||
Accounts receivable, net |
||||||||
Accounts receivable |
$ | 9,118 | $ | 1,412 | ||||
Less allowance for doubtful accounts |
(351 | ) | (407 | ) | ||||
| $ | 8,767 | $ | 1,005 | |||||
Inventories, net |
||||||||
Raw materials (components) |
$ | 3,764 | $ | 2,635 | ||||
Work in-process |
1,365 | 934 | ||||||
Finished products |
5,632 | 749 | ||||||
Less inventory reserve |
(241 | ) | (255 | ) | ||||
| $ | 10,520 | $ | 4,063 | |||||
Prepaid expenses and other current assets |
||||||||
Prepaid supplies and clinical |
$ | 599 | $ | 677 | ||||
Other receivables |
441 | 633 | ||||||
Prepaid insurance |
162 | 267 | ||||||
Tax credit recoverable |
414 | 143 | ||||||
Other |
148 | | ||||||
| $ | 1,764 | $ | 1,720 | |||||
Property and equipment, net |
||||||||
Machinery and equipment |
$ | 388 | $ | 248 | ||||
Furniture and fixtures |
207 | 207 | ||||||
Software |
207 | 152 | ||||||
Leasehold improvements |
237 | 264 | ||||||
Less accumulated depreciation |
(446 | ) | (212 | ) | ||||
| $ | 593 | $ | 659 | |||||
Intangible assets, net |
||||||||
Customer relationships |
$ | 7,259 | $ | 2,978 | ||||
Product registrations |
3,829 | | ||||||
Technology |
4,597 | 4,597 | ||||||
Tradename |
578 | 195 | ||||||
Covenants not to compete |
317 | 317 | ||||||
Other |
7 | 7 | ||||||
Less accumulated amortization |
(3,865 | ) | (1,758 | ) | ||||
| $ | 12,722 | $ | 6,336 | |||||
Accrued expenses |
||||||||
Income taxes payable |
$ | 492 | $ | | ||||
Accrued royalties |
315 | 317 | ||||||
Accrued distributor commissions |
372 | 349 | ||||||
Product warranties medical device products |
257 | 259 | ||||||
Clinical trials |
163 | 2,098 | ||||||
Customer deposits |
307 | 345 | ||||||
Professional fees |
223 | 331 | ||||||
Employee benefits |
340 | 390 | ||||||
Other |
1,449 | 1,305 | ||||||
| $ | 3,918 | $ | 5,394 | |||||
66
Table of Contents
The
changes to goodwill include $0.2 million from the foreign
exchange translation and reflect the carrying value of the assets and liabilities valued in
connection with the Pharma Genexx acquisition, partially offset by the impairment of $1.1 million
of goodwill related to our instrumentation business. As a result of competition in the U.S. market, the broad global
economic conditions, and pricing pressures globally, we determined that goodwill was impaired for
the instrumentation reporting unit. The impairment loss was determined by
calculating the fair value of the instrumentation reporting unit based on a discounted net
present-value calculation. The purchase price allocation of the assets acquired in the
Pharma Genexx acquisition are subject to change while contingencies that existed on the acquisition
date are resolved.
The following table reflects the changes in the allowance for doubtful accounts, provision for
inventory reserve and tax valuation allowance accounts:
| Beginning | Charged to | Charged to | Ending | |||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | balance | expense | Written-off | other | balance | |||||||||||||||
2009 |
||||||||||||||||||||
Allowance for doubtful
accounts |
$ | (407 | ) | (73 | ) | 130 | $ | (350 | ) | |||||||||||
Provision for inventory
reserve |
$ | (255 | ) | (279 | ) | 293 | $ | (241 | ) | |||||||||||
Tax valuation allowance |
$ | (35,197 | ) | (16,699 | ) | | 199 | $ | (51,697 | ) | ||||||||||
2008 |
||||||||||||||||||||
Allowance for doubtful
accounts |
$ | (465 | ) | (204 | ) | 150 | 112 | $ | (407 | ) | ||||||||||
Provision for inventory
reserve |
$ | | (255 | ) | | | (255 | ) | ||||||||||||
Tax valuation allowance |
$ | (16,924 | ) | $ | (19,137 | ) | $ | | $ | 864 | $ | (35,197 | ) | |||||||
Note 5. Debt
We have a fully-drawn $12.0 million line of credit with the Frost Group. We are obligated to
pay interest upon maturity, compounded quarterly, on outstanding borrowings under the line of
credit at an 11% annual rate, which is due January 11, 2011. The line of credit is collateralized
by all of our personal property except our intellectual property.
In connection of our acquisition of Pharma Genexx, we have entered into lines of credit
agreements with 7 financial institutions in Chile. Those lines of credit are used primarily as a
source of working capital for inventory purchases. The following table summarizes the lines of
credit:
| (in thousands) | Amount outstanding at December 31, | |||||||||||||||
| Interest rate | Maximum | |||||||||||||||
| Lender | on borrowings | borrowings | 2009 | 2008 | ||||||||||||
The Frost Group LLC |
11 | % | $ | 12,000 | $ | 12,000 | $ | 12,000 | ||||||||
Itau Bank |
Libor +2.8% | 2,000 | 270 | | ||||||||||||
Bank of Chile |
Libor +2.8% | 2,000 | 988 | | ||||||||||||
BICE Bank |
Libor +2.8% | 2,000 | 1,459 | | ||||||||||||
Santander Bank |
Libor +2.8% | 2,600 | 324 | | ||||||||||||
Corp Banca |
Libor +2.8% | | 62 | | ||||||||||||
BBVA Bank |
Libor +2.8% | 3,500 | 1,216 | | ||||||||||||
Scotiabank |
Libor +2.8% | 2,500 | | | ||||||||||||
Total |
$ | 26,600 | $ | 16,319 | $ | 12,000 | ||||||||||
67
Table of Contents
On March 4, 2009, the Gamma Trust advanced $3.0 million to us pursuant to a Promissory Note we
issued to the Gamma Trust (the Note). The entire amount of this advance and all accrued interest
thereon was due and payable on the earlier of May 4, 2009, or such earlier date following the
closing of the stock purchase transaction with the Gamma Trust
discussed in Note 6. The Note bore
interest at a rate equal to 11% per annum and may be prepaid in whole or in part without penalty or
premium. We repaid the Note and $48 thousand of interest on April 27, 2009.
Note 6. Equity Offerings
Effective as of September 18, 2009, we entered into a securities purchase agreement (the
Preferred Purchase Agreement) with the private investors named therein (the Preferred
Investors), pursuant to which the Preferred Investors agreed to purchase an aggregate of 1,209,677
shares (the Preferred Shares) of the Companys newly-designated 8.0% Series D Cumulative
Convertible Preferred Stock, par value $0.01 per share (Series D Preferred Stock) (Refer to Note
7) at a purchase price of $24.80 per share, together with warrants (the Warrants) to
purchase up to an aggregate of 3,024,196 shares of the Companys
common stock, par value $.01 at an exercise price of $2.48 per share (the Preferred Investment).
Initially, the Series D Preferred Stock was convertible into ten shares of the Companys Common
Stock, and the Preferred Shares purchase price was based on the average closing price of the
Companys Common Stock as reported on the NYSE Amex for the five days preceding the execution of
the Preferred Purchase Agreement. In connection with the Preferred Investment, the Company issued
the Preferred Shares and Warrants and received an aggregate of $30.0 million
in cash on September 28, 2009.
The Company agreed to issue the Preferred Shares and the Warrants in reliance upon the
exemption from registration under Section 4(2) of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (the
Act). The Preferred Shares issued in the Preferred Investment, including the shares of the
Companys Common Stock into which the Preferred Shares and Warrants may be converted, are
restricted securities as that term is defined by Rule 144 under the Act, subject to a three year
contractual lockup, and no registration rights have been granted.
On May 26, 2009, May 29, 2009, and June 1, 2009, we entered into stock purchase agreements
with a total of seven accredited investors (Investors) pursuant to which the Investors agreed to
make a $31.0 million investment in the Company in exchange for 31,000,000 shares of our Common
Stock at $1.00 per share, representing a range of discounts of approximately 16-21% to the average
closing price of our Common Stock on the NYSE Amex for the five trading days immediately preceding
the closing date of the agreements. The shares issued were restricted securities and were exempt from registration requirements under Section 4(2) of the Act
because the transaction did not involve a public offering.
On February 23, 2009, we entered into a Stock Purchase Agreement with the Gamma Trust,
pursuant to which the Gamma Trust agreed to make a $20.0 million cash investment in the Company in
exchange for 20,000,000 shares (the Shares) of our Common Stock, at $1.00 per share, representing
an approximately 20% discount to the average closing price of our Common Stock on the NYSE Amex for
the five trading days immediately preceding the effective date of Audit Committee and stockholder
approval of the transaction. We issued the Shares and received the proceeds on April 27,
2009. The Shares issued were restricted securities, subject to a two-year lockup and no registration rights were granted.
On September 10, 2008, we issued 13,513,514 shares of our Common Stock to a group of
investors, including members of the Frost Group, in exchange for $15.0 million. The shares were
issued at $1.11 per share, representing an approximately 40% discount to the five-day average
closing price of our Common Stock on the NYSE Amex. The Shares issued were restricted securities,
subject to a two year lockup, and no registration rights have been granted. The issuance of the
Shares was exempt from the registration requirements under Section 4(2) of the Act because the
transaction did not involve a public offering.
Note 7. Shareholders Equity
Our authorized capital stock consists of 500,000,000 shares of common stock, par value $.01
per share, and 10,000,000 shares of preferred stock, par value $.01 per share.
Common Stock
Subject to the rights of the holders of any shares of preferred stock currently outstanding or
which may be issued in the future, the holders of the common stock are entitled to receive
dividends from our funds legally available when, as and if declared by our board of directors, and
are entitled to share ratably in all of our assets available for distribution to holders of common
stock upon the liquidation, dissolution or winding-up of our affairs subject to the liquidation
preference, if any, of any then outstanding shares of preferred stock. Holders of our common stock
do not have any preemptive, subscription, redemption or conversion rights. Holders of our common
stock are entitled to one vote per share on all matters which they are entitled to vote upon at
meetings of stockholders or upon actions taken by written consent pursuant to Delaware corporate
law. The holders of our common stock do not have cumulative voting rights, which means that the
holders of a plurality of the outstanding shares can elect all of our directors. All of the shares
of our common stock currently issued and outstanding are fully-paid and nonassessable. No
dividends have been paid to holders of our common stock since our incorporation, and no cash
dividends are anticipated to be declared or paid in the reasonably foreseeable future.
68
Table of Contents
In
addition to our equity-based compensation plans, we have issued warrants to purchase our common
stock. Refer to Note 8 for additional information on our share-based compensation plans. The
table below provides additional information for warrants outstanding as of December 31, 2009.
| Weighted | ||||||||||
| Number of | average | |||||||||
| Warrants | warrants | exercise price | Expiration date | |||||||
Outstanding at December 31, 2008
|
27,245,466 | |||||||||
Issued
|
3,024,196 | |||||||||
Exercised
|
(1,075,500 | ) | ||||||||
Expired
|
| |||||||||
Outstanding and Exercisable at
December 31, 2009
|
29,194,162 | $ | 0.89 | Various from September 2014 through March, 2017 | ||||||
Of the 1,075,500 warrants exercised to purchase common stock, 369,336 shares were surrendered
in lieu of a cash payment via the net exercise feature of the warrant agreements.
Preferred Stock
Under our certificate of incorporation, our board of directors has the authority, without
further action by stockholders, to designate up to 10 million shares of preferred stock in one or
more series and to fix or alter, from time to time, the designations, powers and rights of each
series of preferred stock and the qualifications, limitations or restrictions of any series of
preferred stock, including dividend rights, dividend rate, conversion rights, voting rights, rights
and terms of redemption (including sinking fund provisions), redemption price or prices, and the
liquidation preference of any wholly issued series of preferred stock, any or all of which may be
greater than the rights of the common stock, and to establish the number of shares constituting any
such series.
Series A Preferred Stock
Of the authorized preferred stock, 4,000,000 shares have been designated Series A preferred
stock. Dividends are payable on the Series A preferred stock in the amount of $0.25 per share,
payable annually in arrears. At the option of our board of directors, dividends will be paid
either (i) wholly or partially in cash or (ii) in newly issued shares of Series A preferred stock
valued at $2.50 per share to the extent cash dividend is not paid.
Holders of Series A preferred stock have the right to convert their shares, at their option
exercisable at any time, into shares of our common stock on a one-for-one basis subject to
anti-dilution adjustments. These anti-dilution adjustments are triggered in the event of any
subdivision or combination of our outstanding common stock, any payment by us of a stock dividend
to holders of our common stock or other occurrences specified in the certificate of designations
relating to the Series A preferred stock. We may elect to convert the Series A preferred stock
into common stock or a substantially equivalent preferred stock in the case of a merger or
consolidation in which we do not survive, a sale of all or substantially all of our assets or a
substantial reorganization of us.
Each share of Series A preferred stock is entitled to one vote on all matters on which the
common stock has the right to vote. Holders of Series A preferred stock are also entitled to vote
as a separate class on any proposed adverse change in the rights, preferences or privileges of the
Series A preferred stock and any increase in the number of authorized shares of Series A preferred
stock. In the event of any liquidation or winding up of the Company, the holders of the Series A
preferred stock will be entitled to receive $2.50 per share plus any accrued and unpaid dividends
before any distribution to the holders of the common stock and any other class of series of
preferred stock ranking junior to it.
We may redeem the outstanding shares of Series A preferred stock for $2.50 per share (plus
accrued and unpaid dividends), at any time.
69
Table of Contents
Series C Preferred Stock
Of the authorized preferred stock, 500,000 shares were designated Series C preferred stock.
On June 22, 2007, 457,603 shares of Series C preferred stock were issued and outstanding and held by 30
stockholders. Cumulative dividends were payable on the Series C preferred stock in the amount of
$1.54 per share when declared by the board of directors. On June 22, 2007, all outstanding shares
(457,603 shares) of Series C preferred stock automatically converted into shares of common stock,
on a one-hundred-for-one basis.
8% Series D Cumulative Convertible Preferred Stock
Of the authorized preferred stock, 2,000,000 shares were designated 8% Series D Cumulative
Convertible Preferred Stock (Series D Preferred Stock). Holders of the Series D Preferred Stock
are entitled to receive, when, as and if declared by the Companys Board of Directors, dividends on
each share of Series D Preferred Stock at a rate per annum equal to 8.0% of the sum of (a) $24.80,
plus (b) any and all declared and unpaid and accrued dividends thereon, subject to adjustment for
any stock split, combination, recapitalization or other similar corporate action (the Liquidation
Amount). All dividends shall be cumulative, whether or not earned or declared, accruing on an
annual basis from the issue date of the Series D Preferred Stock. As of December 31, 2009 we had approximately $0.51 per Series D Preferred Share, or $0.6 million of Series D Preferred Stock dividends in arrears.
The Holders of Series D Preferred Stock have the right to receive notice of any meeting of
holders of the Companys Common Stock or Series D Preferred Stock and to vote (on an as-converted
into Common Stock basis) upon any matter submitted to a vote of the holders of Common Stock or
Series D Preferred Stock. Except as otherwise expressly set forth in the Companys Amended and
Restated Certificate of Incorporation, as amended from time to time, the holders of Series D
Preferred Stock will vote on each matter submitted to them with the holders of Common Stock and all
other classes and series of the Companys capital stock entitled to vote on such matter, taken
together as a single class.
With respect to dividend distributions (other than required dividends to the holders of the
Companys Series A Preferred Stock) and distributions upon liquidation, winding up or dissolution
of the Company, the Series D Preferred Stock ranks senior to all classes of Common Stock, the
Companys Series A Preferred Stock, the Companys Series C Preferred Stock, and to each other class
of the Companys capital stock existing now or hereafter created that are not specifically
designated as ranking senior to or pari passu with the Series D Preferred Stock.
Upon the occurrence of a Liquidation Event (as defined in the Certificate of Designation),
holders of Series D Preferred Stock are entitled to be paid, subject to applicable law, out of the
assets of the Company available for distribution to its stockholders, an amount in cash (the
Liquidation Payment) for each share of Series D Preferred Stock equal to the greater of (x) the
Liquidation Amount for each such share of Series D Preferred Stock outstanding plus (i) any
declared and unpaid dividends and (ii) accrued dividends or (y) the amount for each share of Series
D Preferred Stock the holders would be entitled to receive pursuant to the Liquidation Event if all
of the shares of Series D Preferred Stock had been converted into Common Stock as of the date
immediately prior to the date fixed for determination of stockholders entitled to receive a
distribution in such Liquidation Event. Such Liquidation Payment will be paid before any cash
distribution will be made or any other assets distributed in respect of any class of securities
junior to the Series D Preferred Stock, including, without limitation, Common Stock and the
Companys Series A Preferred Stock.
The holder of any share of Series D Preferred Stock may at any time and from time to time
convert such share into such number of fully paid and nonassessable shares of Common Stock as is
determined by dividing (A) the Liquidation Amount of the share by (B) the Conversion Price, which
is initially $2.48, subject to adjustment as provided in the Certificate of Designation.
Initially, the Series D Preferred Stock is convertible into 10 shares of the Companys Common
Stock.
The Company may, at any time, convert the outstanding Series D Preferred Stock into such
number of fully paid and non-assessable shares of Common Stock as is determined by dividing (A) the
Liquidation Amount of the shares by (B) the Conversion Price, but only if the closing bid price of
the Common Stock exceeds $5.00 per share during any thirty (30) consecutive trading days prior to
each conversion. Initially, the Series D Preferred Stock is convertible into 10 shares of the
Companys Common Stock.
To the extent it is lawfully able to do so, the Company may redeem all of the then outstanding
shares of Series D Preferred Stock by paying in cash an amount per share equal to $24.80 plus all
declared or accrued unpaid dividends on such shares, subject to adjustment for any stock dividends
or distributions, splits, subdivisions, combinations, reclassifications, stock issuances or similar
events with respect to the Common Stock.
70
Table of Contents
Note 8. Equity-Based Compensation
We maintain equity-based incentive compensation plans that provide for grants of stock options
and restricted stock to our directors, officers, key employees and certain outside consultants.
Our 2007 Equity Incentive Plan includes all options assumed from the companies combined in the
Merger discussed in Note 1. Stock options granted under the 1996 Stock Option Plan, 2000 Stock
Option Plan and the plans assumed from Froptix and Acuity
are exercisable for a period of up to 10 years from date of grant. Equity awards granted
under the 2007 Equity Incentive Plan are exercisable for a period up to 7 years. Vesting periods
range from immediate to 5 years.
We classify the cash flows resulting from the tax benefit that arises when the tax deductions
exceed the compensation cost recognized for those equity awards (excess tax benefits) as financing
cash flows. There were no excess tax benefits for the years ended December 31, 2009, 2008, and
2007.
Equity-based compensation arrangements to non-employees are accounted for at their fair value
on the measurement date. The measurement of equity-based compensation is subject to periodic
adjustment over the waiting time of the equity instruments.
Valuation and Expense Information
We recorded equity based compensation expense of $4.5 million, $6.7 million, and $7.4 million
for the years ended December 31, 2009, 2008 and 2007, respectively, all of which were reflected as
operating expense. Of the $4.5 million of equity based compensation expense recorded in the year
ended December 31, 2009, $3.2 was recorded as selling, general and administrative expense and $1.3
million was recorded as research and development expenses. Of the $6.7 million of equity based
compensation expense recorded in the year ended December 31, 2008, $4.2 million was recorded as
selling, general and administrative expense and $2.5 million was recorded as research and
development expenses. For the year ended December 31, 2007, of the $7.4 million of expense
recorded, $4.4 million was recorded as selling, general and administration expense and $3.0 million
was recorded as research and development expense. During the third quarter of 2007, a reversal of
equity-based compensation expense of $8.1 million was recorded as a result of the termination of a
consulting agreement prior to the vesting of any of the equity based awards issued under a
consulting agreement. Originally, we accrued $0.3 million for this expense during 2006 and $7.8
million during the first six months of 2007 as research and development expense.
We estimate forfeitures of stock options and recognize compensation cost only for those awards
expected to vest. Forfeiture rates are determined for all employees and non-employee directors
based on historical experience and our estimate of future vesting. Estimated forfeiture rates are
adjusted from time to time based on actual forfeiture experience.
As of December 31, 2009, there was $8.3 million of unrecognized compensation cost related to
the stock options granted under our stock plans. That cost is expected to be recognized over a
weighted-average period of 2.2 years.
Stock Options
We estimate the fair value of each stock option on the date of grant using a Black-Scholes
option-pricing formula, applying the following assumptions, and amortized the fair value to expense
over the options vesting period using the straight-line attribution approach for employees and
non-employee directors, and for awards issued to non-employees we recognize compensation expense on
a graded basis, with most of the compensation expense being recorded during the initial periods of
vesting:
| Year Ended | Year Ended | Year Ended | ||||
| December 31, 2009 | December 31, 2008 | December 31, 2007 | ||||
Expected term (in years) |
0.6 - 7.9 | 1.6 - 8.9 | 3.5 - 9.7 | |||
Risk-free interest rate |
1.4% - 3.0% | 1.5% - 3.7% | 3.2% - 5.2% | |||
Expected volatility |
70% - 77% | 70% - 75% | 73% - 76% | |||
Expected dividend yield |
0% | 0% | 0% |
Expected Term: The expected term of the stock options to employees and non-employee directors
was calculated using the shortcut method. We believe this method is appropriate as our equity
shares have been publicly traded for a limited period of time and as such we do not have sufficient
historical exercise data to provide a reasonable basis upon which to estimate expected term. The
expected term of stock options issued to non-employee consultants is the remaining contractual life
of the options issued.
71
Table of Contents
Risk-Free Interest Rate: The risk-free interest rate is based on the rates paid on securities
issued by the U.S. Treasury with a term approximating the expected life of the option.
Expected Volatility: The expected volatility was based on a peer group of publicly-traded
stocks historical trading which we believe will be representative of the volatility over the
expected term of the options. We believe the peer groups historical volatility is appropriate as
our equity shares have been publicly traded for a limited period of time.
Expected Dividend Yield: We do not intend to pay dividends on common stock for the foreseeable
future. Accordingly, we used a dividend yield of zero in the assumptions.
We maintain incentive stock plans that provide for the grants of stock options to our
directors, officers, employees and non-employee consultants. As of December 31, 2009, there were
13,371,586 shares of common stock reserved for issuance under our 2007 Incentive Plan. We intend
to issue new shares upon the exercise of options. Stock options granted under these plans have
been granted at an option price equal to the closing market value of the stock on the date of the
grant. Options granted under these plans to employees typically become exercisable over four years
in equal annual installments after the date of grant, and to non-employee directors become
exercisable in full after one-year after the grant date, subject to, in each case, continuous
service with the Company during the applicable vesting period. The Company assumed options to
grant common stock as part of the Merger, which reflected various vesting schedules, including
monthly vesting to employees and non-employee consultants.
A summary of option activity under our stock plans as of December 31, 2009, and the changes
during the year is presented below:
| Weighted | ||||||||||||||||
| Weighted | average | |||||||||||||||
| average | remaining | Aggregate | ||||||||||||||
| Number of | exercise | contractual | intrinsic value | |||||||||||||
| Options | options | price | term (years) | (in thousands) | ||||||||||||
Outstanding at December 31, 2008 |
11,977,437 | $ | 2.06 | 6.1 | $ | 7,807 | ||||||||||
Granted |
5,538,500 | $ | 1.60 | |||||||||||||
Exercised |
(2,984,945 | ) | $ | 0.23 | ||||||||||||
Forfeited |
(1,324,936 | ) | $ | 0.96 | ||||||||||||
Expired |
(582,500 | ) | $ | 3.59 | ||||||||||||
Outstanding at December 31, 2009 |
12,623,556 | $ | 2.36 | 5.5 | $ | 4,544 | ||||||||||
Vested and expected to vest at
December 31, 2009 |
11,839,931 | $ | 2.35 | 5.5 | $ | 4,341 | ||||||||||
Exercisable at December 31, 2009 |
5,107,138 | $ | 2.41 | 5.1 | $ | 2,919 | ||||||||||
The total intrinsic value of stock options exercised for the years ended December 31, 2009,
2008, and 2007 were $3.8 million, $9.5 million, and $2.3 million, respectively.
The weighted average grant date fair value of stock options granted for the years ended
December 31, 2009, 2008 and 2007 were $0.99, $1.13, and $2.73, respectively. The total fair value
of stock options vested during the years ended December 31, 2009, 2008 and 2007 were $5.1 million,
$4.1 million and $1.0 million, respectively. The following table provides the grant date fair
value for each of the following groups of stock option activity during 2009:
| Weighted | ||||||||
| average grant | ||||||||
| Options | Number of options | date fair value | ||||||
Nonvested at December 31, 2008 |
6,116,674 | $ | 2.28 | |||||
Granted |
5,538,500 | $ | 0.99 | |||||
Forfeited |
1,324,936 | $ | 2.15 | |||||
Nonvested at December 31, 2009 |
7,516,418 | $ | 1.47 | |||||
72
Table of Contents
Restricted Stock
In 2009, the Company issued 30,000 shares of restricted stock to one of its independent board
members. The restricted stock was granted under our 2007 Equity Incentive Plan with a term of 7
years and vesting occurring 5 years after the grant date with certain events which would accelerate
the vesting of the award. The restricted stock
was valued using the grant date fair value which was equivalent to the closing price on the
grant date. We record the cost of restricted stock over the vesting period.
Note 9. Income Taxes
Loss
before income taxes was taxable in the U.S., Canada, and Chile.
The benefit/(expense) for incomes taxes consists of the following:
| For the Year | For the Year | For the Year | ||||||||||
| Ended | Ended | Ended | ||||||||||
| December 31, | December 31, | December 31, | ||||||||||
| (in thousands) | 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | |||||||||
Current |
||||||||||||
Federal |
$ | | $ | | $ | | ||||||
State |
| | | |||||||||
Foreign |
140 | 83 | 83 | |||||||||
| 140 | 83 | 83 | ||||||||||
Deferred |
||||||||||||
Federal |
15,602 | 17,075 | 5,274 | |||||||||
State |
985 | 1,137 | 334 | |||||||||
Foreign |
266 | 925 | 106 | |||||||||
Change in valuation allowance |
(16,699 | ) | (19,137 | ) | (5,714 | ) | ||||||
| 154 | | | ||||||||||
Total, net |
$ | 294 | $ | 83 | $ | 83 | ||||||
Deferred income tax assets and liabilities as of December 31, 2009 and 2008 are comprised of
the following:
| (in thousands) | December 31, 2009 | December 31, 2008 | ||||||
Deferred income tax assets: |
||||||||
Federal net operating loss |
$ | 26,690 | $ | 17,075 | ||||
State net operating loss |
4,816 | 3,246 | ||||||
Foreign net operating loss |
1,198 | 1,622 | ||||||
Capitalized research and development
Expense |
4,378 | 5,098 | ||||||
Research and development tax credit |
6,492 | 5,186 | ||||||
Canadian research and development pool |
1,464 | 1,202 | ||||||
Canadian Tax Credits |
1,089 | | ||||||
Amortization and depreciation |
258 | 236 | ||||||
Accruals |
555 | 511 | ||||||
Other |
6,663 | 3,486 | ||||||
Deferred income tax assets |
53,603 | 37,662 | ||||||
Deferred income tax liabilities: |
||||||||
Intangible assets |
(3,114 | ) | (2,459 | ) | ||||
Other |
| (6 | ) | |||||
Deferred income tax liabilities |
(3,114 | ) | (2,465 | ) | ||||
Net deferred income tax assets |
50,489 | 35,197 | ||||||
Valuation allowance |
(51,697 | ) | (35,197 | ) | ||||
Net deferred income tax liabilities |
$ | (1,208 | ) | $ | | |||
The change in deferred income tax assets, liabilities and valuation allowances at December 31,
2009 reflect the acquisition of various legal entities, including the tax attributes. The
acquisitions were accounted for under U.S. GAAP as asset acquisitions. As of December 31, 2009, we
have Federal, state, and foreign net operating loss
carryforwards of approximately $123.2 million,
$101.4 million, and $4.7 million, respectively, that expire at various dates through 2029. We
have research and development tax credit carryforwards of approximately $7.6
million that expire in varying amounts through 2029. We have determined a full valuation
allowance is required against all of our tax assets that we do not expect to be utilized by the
turning of deferred income tax liabilities.
73
Table of Contents
Under Section 382 of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended, certain significant
changes in ownership may restrict the future utilization of our income tax loss carryforwards and
income tax credit carryforwards in the United States. The annual limitation is equal to the value
of our stock immediately before the ownership change, multiplied by the long-term tax-exempt rate
(i.e., the highest of the adjusted Federal long-term rates in effect for any month in the
three-calendar-month period ending with the calendar month in which the change date occurs). This
limitation may be increased under the IRC§ 338 Approach (IRS approved methodology for determining
recognized Built-In Gain). As a result, federal net operating losses and tax credits may expire
before we are able to fully utilize them.
During 2008, we conducted a study to determine the impact of the various ownership changes
that occurred during 2007 and 2008. As a result, we have concluded that the annual utilization of
our net operating loss carryforwards (NOLs) and tax credits is subject to a limitation pursuant
to Internal Revenue Code section 382. Under the tax law, such NOLs and tax credits are subject to
expiration from 15 to 20 years after they were generated. As a result of the annual limitation
that may be imposed on such tax attributes and the statutory expiration period, some of these tax
attributes may expire prior to our being able to use them. As we have established a valuation
allowance against all of our net deferred tax assets, including such NOLs and tax credits, there is
no current impact on these financial statements as a result of the annual limitation. This study
did not conclude as to whether eXegenics pre-merger NOLs were limited under Section 382. As such,
of the $123.2 million of federal net operating loss carryforwards, at least approximately $52.0 million
may not be able to be utilized.
Adoption of FASB ASC Topic 740 (formerly FIN 48)
Prior to January 1, 2007, we recognized income taxes with respect to uncertain tax positions
based upon SFAS No. 5, Accounting for Contingencies, or SFAS No. 5 (codified primarily in FASB
ASC Topic 450, Contingencies). Under former SFAS No. 5, we would record a liability associated
with an uncertain tax position if the liability was both probable and estimable. Prior to January
1, 2007, the liabilities recorded under SFAS No. 5 including interest and penalties related to
income tax exposures, would have been recognized as incurred within income taxes in our
consolidated statements of operations. We recorded no such liabilities in 2006.
Effective January 1, 2007, we adopted FIN 48, Accounting for Uncertainty in Income Taxes
(codified primarily in FASB ASC Topic 740, Income Taxes). Formerly FIN 48, ASC 740 clarifies the
accounting for uncertainty in income taxes recognized in financial statements in accordance with
former SFAS No. 109, Accounting for Income Taxes (codified primarily in FASB ASC Topic 740,
Income Taxes). ASC 740 prescribes a recognition threshold and measurement attribute for the
financial statement recognition and measurement of a tax position taken or expected to be taken in
a tax return. ASC 740 requires that we determine whether the benefit of our tax positions are more
likely than not to be sustained upon audit, based on the technical merits of the tax position. For
tax positions that are more likely than not to be sustained upon audit, we recognize the greatest
amount of the benefit that is more likely than not to be sustained in our consolidated financial
statements. For tax positions that are not more likely than not to be sustained upon audit, we do
not recognize any portion of the benefit in our consolidated financial statements. The provisions
of ASC 740 also provide guidance on derecognition, classification, interest and penalties,
accounting in interim periods, and disclosure.
Our policy for interest and penalties under ASC 740, related to income tax exposures, was not
impacted as a result of the adoption of the recognition and measurement provisions of ASC 740.
Therefore, we continue to recognize interest and penalties as incurred within income taxes in our
consolidated statements of operations, when applicable.
There was no change to our accumulated deficit as of January 1, 2007 as a result of the
adoption of the recognition and measurement provisions of ASC 740.
Uncertain Income Tax Positions
We file Federal income tax returns in the U.S., Canada, Chile, and Taiwan jurisdictions, as
well as with various U.S. states and the Ontario province in Canada. We are subject to tax audits
in all jurisdictions for which we file tax
returns. Tax audits by their very nature are often complex and can require several years to
complete. There are currently no tax audits that have commenced with respect to income returns in
any jurisdiction.
U.S. Federal: Under the tax statute of limitations applicable to the Internal Revenue Code, we
are no longer subject to U.S. federal income tax examinations by the Internal Revenue Service for
years before 2005. However, because we are carrying forward income tax attributes, such as net
operating losses and tax credits from 2005 and earlier tax years, these attributes can still be
audited when utilized on returns filed in the future.
State: Under the statutes of limitation applicable to most state income tax laws, we are no
longer subject to state income tax examinations by tax authorities for years before 2005 in states
in which we have filed income tax returns. Certain states may take the position that we are
subject to income tax in such states even though we have not filed income tax returns in such
states and, depending on the varying state income tax statutes and administrative practices, the
statute of limitations in such states may extend to years before 2005.
74
Table of Contents
Foreign: Under the statutes of limitations applicable to our foreign operations, we are no
longer subject to tax examination for years before 2005 in jurisdictions we have filed income tax
returns.
As a result of our January 1, 2007 implementation of ASC 740, the total amount of gross tax
benefits, excluding the offsetting full valuation allowance, that became unrecognized, was
approximately $0.4 million. There were no accrued interest and penalties resulting from such
unrecognized tax benefits. As of December 31, 2009 and December 31, 2008, the total amount of
gross unrecognized tax benefits was approximately $6.8 million and $3.6 million, respectively, and
accrued interest and penalties on such unrecognized tax benefits was $0 in each period.
The following table rolls forward the 2009 activity in our gross unrecognized income tax benefits.
| (in thousands) | ||||
Unrecognized tax benefits January 1, 2009 |
$ | 3,619 | ||
Gross increases tax positions in prior period |
3,199 | |||
Gross decreases tax positions in prior period |
| |||
Unrecognized tax benefits at December 31, 2009 |
$ | 6,818 | ||
There are no net unrecognized tax benefits that, if recognized, would impact the effective tax
rate as of December 31, 2009 as a result of the full valuation allowance.
Other Income Tax Disclosures
The significant elements contributing to the difference between the federal statutory tax rate
and the effective tax rate are as follows:
| For the Year Ended | For the Year Ended | For the Year Ended | ||||||||||
| (in thousands) | December 31, 2009 | December 31, 2008 | December 31, 2007 | |||||||||
Federal Statutory rate |
35.0 | % | 35.0 | % | 35.0 | % | ||||||
State income taxes, net of federal
benefit |
3.7 | 3.6 | 3.9 | |||||||||
Foreign income taxes |
0.1 | | | |||||||||
Acquired in-process research and
development |
(2.6 | ) | (1.4 | ) | (35.3 | ) | ||||||
Research and development tax credits |
6.7 | 10.7 | (0.1 | ) | ||||||||
OID |
5.0 | | | |||||||||
Impairment of Goodwill |
(1.4 | ) | | | ||||||||
Other permanent items |
9.8 | | | |||||||||
Change in valuation allowance |
(55.3 | ) | (48.0 | ) | (2.1 | ) | ||||||
Other |
0.0 | 0.3 | (1.4 | ) | ||||||||
Total |
1.0 | % | 0.2 | % | 0.0 | % | ||||||
No income taxes were paid prior to 2009; we will be paying income tax in Chile for the 2009
year.
The following table reconciles our losses before income taxes between U.S. and foreign
jurisdictions:
| For the Year Ended | For the Year Ended | For the Year Ended | ||||||||||
| (in thousands) | December 31, 2009 | December 31, 2008 | December 31, 2007 | |||||||||
Pre-tax loss |
||||||||||||
U.S. |
$ | (29,214 | ) | $ | (37,153 | ) | $ | (267,542 | ) | |||
Foreign |
(840 | ) | (2,764 | ) | (317 | ) | ||||||
Total |
$ | (30,054 | ) | $ | (39,917 | ) | $ | (267,859 | ) | |||
75
Table of Contents
Note 10. Supplemental Cash Flow Information
Supplemental cash flow information is summarized as follows:
| For the Year Ended | For the Year Ended | For the Year Ended | ||||||||||
| (in thousands) | December 31, 2009 | December 31, 2008 | December 31, 2007 | |||||||||
Interest paid |
$ | 95 | $ | 101 | $ | 370 | ||||||
Non-cash financing |
||||||||||||
Issuance of
capital stock to
acquire
Acuity |
$ | | $ | | $ | 243,623 | ||||||
Issuance of
capital stock to
acquire
OTI |
$ | | $ | | $ | 6,932 | ||||||
Issuance of
capital stock to
acquire
Vidus and Other |
$ | | $ | 1,319 | $ | 114 | ||||||
76
Table of Contents
Note 11. Related Party Transactions
Effective September 21, 2009, we entered into an agreement pursuant to which the we invested
$2.5 million in Cocrystal in exchange for 1,701,723 shares of
Cocrystals Convertible Series A Preferred Stock.
A group of Investors, led by the Frost Group (the CoCrystal Investors), previously invested $5
million in Cocrystal, and agreed to invest an additional $5 million payable in two equal
installments in September 2009 and March 2010. As a result of an amendment to the CoCrystal
Investors agreements dated June 9, 2009, OPKO, rather than the CoCrystal Investors, made the first
installment investment ($2.5 million) on September 21, 2009. Refer to Note 2.
On September 18, 2009, we entered into the Preferred Purchase Agreement with various
investors. Refer to Note 6. Included among the investors is the Gamma Trust, Hsu Gamma
Investment, L.P, a limited partnership controlled by Jane H. Hsiao and Oracle Partners LP, a
limited partnership in which Dr. Frost is a limited partner.
On July 20, 2009, the Company entered into a worldwide exclusive license agreement with
Academia Sinica in Taipei, Taiwan, for a new technology to develop protein vaccines against
influenza and other viral infections. Dr. Alice Yu, a member of our board of directors, is a
Distinguished Research Fellow and Associate Director at the Genomics Research Center, Academia
Sinica.
On June 16, 2009, we entered into an agreement to lease approximately 10,000 square feet of
space in Hialeah, Florida to house manufacturing and service operations for our ophthalmic
instrumentation business (the Hialeah Facility) from an entity controlled by Dr. Frost and Dr.
Jane Hsiao. Pursuant to the terms of a lease agreement, which is effective as of February 1, 2009,
gross rent is $0.1 million per year for a one-year lease which may be extended, at our option, for
one additional year. From April 2008 through January 2009, we leased 20,000 square feet at the
Hialeah Facility from a third party landlord pursuant to a lease agreement which contained an
option to purchase the facility. We initially elected to exercise the option to purchase the
Hialeah Facility in September 2008. Prior to closing, however, we assigned the right to purchase
the Hialeah Facility to an entity controlled by Drs. Frost and Hsiao and leased a smaller portion
of the facility as a result of several factors, including our inability to obtain outside financing
for the purchase, current business needs, the reduced operating costs for the smaller space, and
the minimization of risk and expense of unutilized space.
On June 10, 2009, we entered into a stock purchase agreement with Sorrento, pursuant to which
we invested $2.3 million in Sorrento. In exchange for the investment, we acquired approximately
one-third of the outstanding common shares of Sorrento and received a fully-paid, exclusive license
to the Sorrento antibody library for the discovery and development of therapeutic antibodies in the
field of ophthalmology. Refer to Note 2. Dr. Richard Lerner, a member of our Board of Directors,
serves as a consultant and scientific advisory board member to Sorrento and owns less than one
percent of its shares.
On May 26, 2009, May 29, 2009, and June 1, 2009, we entered into stock purchase agreements
with a total of seven accredited investors pursuant to which we agreed to sell an aggregate of 31
million shares of the Companys Common Stock in exchange for $31 million. Under the terms of each
investment, OPKO issued shares to the investors at a price of $1.00 per share. Refer to Note 6.
Oracle Partners, LP and Vector Group Ltd. were among the investors in the transaction and purchased
4 million and 5 million shares of our Common Stock, respectively. Dr. Frost may also be deemed to
beneficially own 11.5% of Vector Group Ltd.s outstanding stock.
On March 4, 2009, the Gamma Trust advanced $3.0 million to us under a Promissory Note we
issued to the Gamma Trust, which was repaid in full on April 27, 2009. Refer to Note 5.
In March 2009, we paid the $45 thousand filing fee to the Federal Trade Commission in
connection with filings made by us and Dr. Frost, under the Hart-Scott-Rodino Antitrust
Improvements Act of 1976 (HSR). The filings permitted Dr. Frost and his affiliates to acquire
additional shares of our Common Stock upon expiration of the HSR waiting period on March 23, 2009.
On February 23, 2009, we entered into a Stock Purchase Agreement with the Gamma Trust, of
which Dr Frost is the sole trustee. Refer to Note 6.
On September 10, 2008, in exchange for a $15.0 million cash investment in the Company, we
issued 13,513,514 shares of our Common Stock to a group of investors which included members of the
Frost Group. The shares were issued at a price of $1.11 per share, representing an approximately
40% discount to the 5 day average trading price of our stock on the NYSE Amex. Refer to Note 6.
77
Table of Contents
On December 5, 2007, we issued 10,869,565 shares of the our Common Stock to members of the
Frost Group in exchange for a $20 million cash investment, or $1.84 per share, representing an
approximately 40% discount to the average trading price of our stock on the NYSE Amex for the five
days preceding the date our board of directors and stockholders approved the issuance of the
shares. The shares issued in the private placement were restricted securities, subject to a two
year lockup, and no registration rights have been granted.
In November 2007, we entered into an office lease with Frost Real Estate Holdings, LLC, an
entity affiliated with Dr. Frost. The lease is for approximately 8,300 square feet of space in an
office building in Miami, Florida, where the Companys principal executive offices are located. We
had previously been leasing this space from Frost Real Estate Holdings on a month-to-month basis
while the parties were negotiating the lease. The lease provides for payments of approximately
$18 thousand per month in the first year increasing annually to $24 thousand per month in the fifth year,
plus applicable sales tax. The rent is inclusive of operating expenses, property taxes and
parking. The rent for the first year was reduced to reflect a $30 thousand credit for the costs of
tenant improvements. From January 1, 2008 through October 1, 2008, we leased an additional 1,100
square feet of general office and laboratory space on a ground floor annex of our corporate office
building pursuant to an addendum to the Lease, which required us to pay annual rent of $19 thousand per
year for the annex space.
On September 19, 2007, we entered into an exclusive technology license agreement with Winston
Laboratories, Inc. (Winston). Under the terms of the license agreement, Winston granted us an
exclusive license to the proprietary rights of certain products in exchange for the payment of an
initial licensing fee, royalties, and payments on the occurrence of certain milestones. Drs.
Frost, Uppaluri and Hsiao and Mr. Rubin beneficially own approximately 30% of Winston
Pharmaceuticals, Inc. and Dr. Uppaluri has served as a member of Winstons board of directors since
September 2008. In connection with the license agreement, we reimbursed Winston $29 thousand, $3
thousand and $0 for the years ended December 31, 2009, 2008 and 2007, respectively, for services
provided by Winston personnel to assist us with the clinical program for the product we licensed.
OPKO provided Winston notice of termination of the license agreement on February 23, 2010.
In June 2007, we paid the $125,000 filing fee to the Federal Trade Commission in connection
with filings made by us and Dr. Frost under the Hart-Scott-Rodino Antitrust Improvements Act of
1976 (HSR). The filings permitted Dr. Frost and his affiliates to acquire additional shares of
our common stock upon expiration of the HSR waiting period on July 12, 2007.
As part of the Mergers, we assumed a line of credit with the Frost Group from Acuity and
amended and restated that line of credit to increase borrowing availability. In connection with
the increase of the borrowing availability, we issued 4,000,000 warrants to the Frost Group. Refer
to Note 5.
We reimburse Dr. Frost for Company-related use by Dr. Frost and our other executives of an
airplane owned by a company that is beneficially owned by Dr. Frost. We reimburse Dr. Frost in an
amount equal to the cost of a first class airline ticket between the travel cities for each
executive, including Dr. Frost, traveling on the airplane for Company-related business. We do not
reimburse Dr. Frost for personal use of the airplane by Dr. Frost or any other executive; nor do we
pay for any other fixed or variable operating costs of the airplane. For the fiscal years ending
December 31, 2009, 2008, and 2007, we reimbursed Dr. Frost approximately $92 thousand, $108 thousand, and $0,
respectively, for Company-related travel by Dr. Frost and other OPKO executives.
During the years ending December 31, 2009, 2008 and 2007, we reimbursed SafeStitch Medical,
Inc. (SafeStitch) approximately $0, $49 thousand and $0, respectively, for time SafeStitchs personnel
spent assisting us with the implementation of certain quality and control standard operating
procedures at our manufacturing facility in Toronto, Ontario. Dr. Hsiao serves as chairman of the
board of directors for SafeStitch; and Steven Rubin and Richard Pfenniger, each of whom are members
of our board of directors, also serve on the board of directors of SafeStitch.
Note 12. Employee Benefit Plans
Effective January 1, 2007, the OPKO Health Savings and Retirement Plan, or the Plan, permits
employees to contribute up to 50% of qualified pre-tax annual compensation up to annual statutory
limitations. The discretionary company match for employee contributions to the Plan is 100% of up
to the first 4% of the participants earnings contributed to the Plan. Our matching contributions
to the plan were approximately $0.2 million and $0.2 million in the years ended December 31, 2009
and 2008, respectively.
78
Table of Contents
Note 13. Commitments and Contingencies
In the event of a termination of an existing employee of OTI, we would become obligated at
such employees sole option to acquire up to 10% of the shares issued to the employee in connection
with the acquisition of OTI at a price of $3.55 per share. In connection with the potential
obligation, we have recorded approximately $0.2 million in accrued expenses as of December 31, 2009
based on the estimated fair value of the unexercised put option.
On May 6, 2008, we completed the acquisition of Vidus Ocular, Inc. (Vidus). Pursuant to a
Securities Purchase Agreement with Vidus, each of its stockholders, and the holders of convertible
promissory notes issued by Vidus, we acquired all of the outstanding stock and convertible debt of
Vidus in exchange for (i) the issuance and delivery at closing of 658,080 shares of our Common
Stock (the Closing Shares); (ii) the issuance of 488,420 shares of our Common Stock to be held in
escrow pending the occurrence of certain development milestones (the Milestone Shares); and (iii)
the issuance of options to acquire 200,000 shares of our Common Stock. Additionally, in the event
that the stock price for our Common Stock at the time of receipt of approval or clearance by the
U.S. Food & Drug Administration of a pre-market notification 510(k) relating to the Aquashunt is
not at or above a specified price, we will be obligated to issue an additional 413,850 shares of
our Common Stock.
On May 7, 2007, Ophthalmic Imaging Systems (OIS) sued Steven Verdooner, its former president
and our then Executive Vice President, Instrumentation, in California Superior Court for the County
of Sacramento. OIS later amended its complaint to add claims against the Company and the Frost
Group alleging breach of fiduciary duty, intentional interference with contract and intentional
interference with prospective economic advantage. Trial in the matter was scheduled to commence on
April 28, 2009. In order to avoid the expense and uncertainty of litigation, and without making
any admission of wrongdoing or liability, we entered into a settlement agreement to fully and
finally resolve the lawsuit on May 4, 2009. The impact of the settlement was not material to the
Company.
We are a party to other litigation in the ordinary course of business. We do not believe that
any such litigation will have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, or
results of operations.
We expect to incur losses from operations for the foreseeable future. We expect to incur
substantial research and development expenses, including expenses related to the hiring of
personnel and additional clinical trials. We expect that selling, general and administrative
expenses will also increase as we expand our sales, marketing and administrative staff and add
infrastructure. We intend to finance additional research and development projects, clinical trials
and our future operations with a combination of private placements, payments from potential
strategic research and development, licensing and/or marketing arrangements, public offerings, debt
financing and revenues from future product sales, if any. There can be no assurance, however, that
additional capital will be available to us on acceptable terms, or at all.
Note 14. Strategic Alliances
We plan to develop a portfolio of product candidates through a combination of internal
development and external partnerships. We have completed strategic deals with the Trustees of the
University of Pennsylvania, the University of Florida Research Foundation, the University of Texas
Southwestern, Academia Sinica, and Redox Pharmaceuticals, among others. In connection with these
license agreements, upon the achievement of certain milestones we are obligated to make certain
payments and upon sales of products developed under the license agreements, have royalty
obligations. At this time, we are unable to estimate the timing and amounts of payments as the
obligations are based on future development of the licensed products.
79
Table of Contents
Note 15. Leases
We conduct certain of our operations under operating lease agreements. Rent expense was
approximately $0.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2009, and $0.6 million for the year
ended December 31, 2008.
As of December 31, 2009, the aggregate future minimum lease payments under all non-cancelable
operating leases with initial or remaining lease terms in excess of one year are as follows:
| Year Ending | (in thousands) | |||
2010 |
$ | 448 | ||
2011 |
428 | |||
2012 |
261 | |||
2013 |
| |||
2014 |
| |||
Total minimum lease commitments |
$ | 1,137 | ||
Note 16. Segments
We currently manage our operations in two reportable segments, pharmaceutical and
instrumentation segments. The pharmaceutical segment consists of two operating segments, our (i)
pharmaceutical research and development segment which is focused on the research and development of
pharmaceutical products, diagnostic tests and vaccines, and (ii) the pharmaceutical operations we
acquired in Chile through the acquisition of Pharma Genexx. The instrumentation segment consists
of ophthalmic instrumentation products and the activities related to the research, development,
manufacture and commercialization of those products. There are no inter-segment sales. We
evaluate the performance of each segment based on operating profit or loss. There is no
inter-segment allocation of interest expense and income taxes.
80
Table of Contents
Information regarding our operations and assets for the two segments and the unallocated
corporate operations as well as geographic information are as follows:
| For the years ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | |||||||||
Revenue |
||||||||||||
Pharmaceutical |
$ | 4,418 | $ | | $ | | ||||||
Instrumentation |
8,729 | 9,440 | 847 | |||||||||
Corporate |
| | | |||||||||
| $ | 13,147 | $ | 9,440 | $ | 847 | |||||||
Operating loss |
||||||||||||
Pharmaceutical |
$ | (11,920 | ) | $ | (19,437 | ) | $ | (255,303 | ) | |||
Instrumentation |
(6,843 | ) | (9,704 | ) | (2,119 | ) | ||||||
Corporate |
(9,257 | ) | (9,422 | ) | (9,766 | ) | ||||||
| $ | (28,020 | ) | $ | (38,563 | ) | $ | (267,188 | ) | ||||
Depreciation and
amortization |
||||||||||||
Pharmaceutical |
$ | 507 | $ | 29 | $ | 20 | ||||||
Instrumentation |
1,797 | 1,753 | 153 | |||||||||
Corporate |
53 | 41 | 11 | |||||||||
| $ | 2,357 | $ | 1,823 | $ | 184 | |||||||
Net loss of investees |
||||||||||||
Pharmaceutical |
$ | (353 | ) | $ | | $ | | |||||
Instrumentation |
| | (629 | ) | ||||||||
Corporate |
| | | |||||||||
| $ | (353 | ) | $ | | $ | (629 | ) | |||||
Revenue |
||||||||||||
United States |
$ | 813 | $ | 112 | $ | | ||||||
Chile |
4,418 | | | |||||||||
All others |
7,916 | 9,328 | 847 | |||||||||
| $ | 13,147 | $ | 9,440 | $ | 847 | |||||||
| As of December 31, | |||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | ||||||||||
Assets |
|||||||||||
Pharmaceutical |
$ | 28,813 | $ | 389 | |||||||
Instrumentation |
12,262 | 14,117 | |||||||||
Corporate |
46,355 | 7,258 | |||||||||
| $ | 87,430 | $ | 21,764 | ||||||||
During
the year ended December 31, 2009, no customers represented greater
than 10% of total revenue. During the year ended December 31, 2008, four
customers represented 18%, 17%, 13% and 11%, respectively, of our revenue. During the year
ended December 31, 2007 four customers represented 19%, 18%, 13% and 11%, respectively, of our revenue. As of December 31, 2009, two customers
represented 32% and 19% of our accounts receivable balance. As of
December 31, 2008, two customers represented 47% and 19% of our
accounts receivable balance.
Note 17. Fair Value Measurement
We record fair value at an exit price, representing the amount that would be received to sell
an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants. As
such, fair value is a market-based measurement that should be determined based on assumptions that
market participants would use in pricing an asset or liability. We utilize a three-tier fair value
hierarchy, which prioritizes the inputs used in measuring fair value. These tiers include: Level
1, defined as observable inputs such as quoted prices in active markets; Level 2, defined as inputs
other than quoted prices in active markets that are either directly or indirectly observable; and
Level 3, defined as unobservable inputs in which little or no market data exists, therefore
requiring an entity to develop its own assumptions.
81
Table of Contents
As
of December 31, 2009, we held money market funds that qualify as
cash equivalents and forward contracts for inventory purchases (Refer
to Note 18) that are
required to be measured at fair value on a recurring basis. Our other
assets and liabilities carrying value approximate their fair value
due to their short-term nature.
In addition, the OTI put options were valued at fair value utilizing the Black-Scholes-Merton
valuation method. Refer to Note 13. During the years December 31, 2009, 2008, and 2007, we
recorded a reversal of expense of $35 thousand, expense of $0.1 million and reversal of expense of $10 thousand,
respectively, reflecting our stock price fluctuations.
Any future fluctuation in fair value related to these instruments that is judged to be
temporary, including any recoveries of previous write-downs, would be recorded in accumulated other
comprehensive income or loss. If we determine that any future valuation adjustment was
other-than-temporary, we would record a charge to the consolidated statement of operations as
appropriate.
Our financial assets and liabilities measured at fair value on a recurring basis, are as
follows:
| Fair value measurements as of December 31, 2009 | ||||||||||||||||
| Quoted prices | ||||||||||||||||
| in active | Significant | |||||||||||||||
| markets for | other | Significant | ||||||||||||||
| identical | observable | unobservable | ||||||||||||||
| assets | inputs | inputs | ||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | (Level 1) | (Level 2) | (Level 3 | Total | ||||||||||||
Assets: |
||||||||||||||||
Money market funds |
$ | 41,299 | $ | | $ | | $ | 41,299 | ||||||||
Liabilities: |
||||||||||||||||
OTI put option |
$ | | $ | 176 | $ | | $ | 176 | ||||||||
Forward contracts |
| 151 | | 151 | ||||||||||||
Total liabilities |
$ | | $ | 327 | $ | | $ | 327 | ||||||||
Note 18. Derivative Contracts
We enter into foreign currency forward exchange contracts to cover the risk of exposure to
exchange rate differences arising from inventory purchases on letters of credit. Under these
forward contracts, for any rate above or below the fixed rate, we receive or pay the difference
between the spot rate and the fixed rate for the given amount at the settlement date.
We record derivative financial instruments on our balance sheet at their fair value as an accrued expense and the
changes in the fair value are recognized in
income in other expense net when they occur, the only exception being
derivatives that qualify as hedges. To qualify the derivative instrument as a hedge, we are
required to meet strict hedge effectiveness and contemporaneous documentation requirements at the
initiation of the hedge and assess the hedge effectiveness on an ongoing basis over the life of the
hedge. At December 31, 2009, the forward contracts did not meet the documentation requirements to
be designated as hedges. Accordingly, we recognize all changes in fair values in income.
The outstanding contracts at the end of the year 2009 have been valued at fair value, and
their maturity details are as follows:
| (In thousands) | Fair value at | |||||||||||
| Days until maturity | Contract value | December 31, 2009 | Effect on loss | |||||||||
0 to 30 |
$ | 433 | $ | 448 | $ | (15 | ) | |||||
31 to 60 |
458 | 489 | (31 | ) | ||||||||
61 to 90 |
924 | 978 | (54 | ) | ||||||||
91 to 120 |
723 | 728 | (5 | ) | ||||||||
121 to 180 |
796 | 822 | (26 | ) | ||||||||
More than 180 |
2,970 | 2,990 | (20 | ) | ||||||||
Total |
$ | 6,304 | $ | 6,455 | $ | (151 | ) | |||||
82
Table of Contents
Note 19. Selected Quarterly Financial Data (Unaudited)
| For the 2009 Quarters Ended | ||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | March 31, 2009 | June 30, 2009 | September 30, 2009 | December 31, 2009 | ||||||||||||
Revenue |
$ | 2,301 | $ | 2,347 | $ | 1,501 | $ | 6,998 | ||||||||
Gross margin |
740 | 583 | 446 | 1,811 | ||||||||||||
Net loss attributable to
common shareholders |
(9,055 | ) | (5,734 | ) | (6,426 | ) | (9,744 | ) | ||||||||
Basic and diluted loss
per share |
$ | (0.05 | ) | $ | (0.03 | ) | $ | (0.03 | ) | $ | (0.04 | ) | ||||
| For the 2008 Quarters Ended | ||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | March 31, 2008 | June 30, 2008 | September 30, 2008 | December 31, 2008 | ||||||||||||
Revenue |
$ | 2,824 | $ | 879 | $ | 4,050 | $ | 1,687 | ||||||||
Gross (deficit) margin |
(506 | ) | (146 | ) | 1,081 | 452 | ||||||||||
Net (loss) income attributable to
common shareholders |
(10,935 | ) | (10,934 | ) | (8,380 | ) | (9,801 | ) | ||||||||
Basic and diluted (loss) income
per share |
$ | (0.06 | ) | $ | (0.06 | ) | $ | (0.04 | ) | $ | (0.05 | ) | ||||
Due to rounding, the quarterly per share amounts may not mathematically compute to the annual
amount.
On October 7, 2009 we acquired Pharma Genexx. The results of operations include
the results of Pharma Genexx after that date. During the fourth quarter of 2008, we recorded a
reversal of stock-based compensation expense of $0.5 million related to an error recorded in the
first quarter of 2008. As a result of the error, stock based compensation expense was overstated
by $0.5 million during the first quarter of 2008. The quarterly information was not restated due
to immateriality.
Note 20. Subsequent Events
We have reviewed all subsequent events and transactions that occurred after the date of our December 31,
2009 consolidated balance sheet date as of March 17, 2010, through the time of filing this
Annual Report on Form 10-K on March 17, 2010.
On February 17, 2010, we entered into an agreement to acquire Pharmacos Exakta, S.A. de C.V.
(Exakta), a privately-owned Mexican company, engaged in the manufacture, marketing and
distribution of ophthalmic and other pharmaceutical products for government and private markets
since 1957. Pursuant to a purchase agreement with Exakta and its shareholders, and an affiliate of
the shareholders, Inmobiliaria Chapalita, S.A. de C.V. (Inmobiliaria), the Company acquired all
of the outstanding stock of Exakta and real property owned by Inmobiliaria for a total aggregate
purchase price of $4 million, of which an aggregate of $1.6 million was paid in cash and $2.4
million was paid in shares of Common Stock based on the average closing price of the Companys
Common Stock as reported on the NYSE Amex for the ten trading days ending on February 12, 2010. A
portion of the proceeds will remain in escrow for a period of time for working capital adjustments
and to satisfy indemnification claims.
| ITEM 9. | CHANGES IN AND DISAGREEMENTS WITH ACCOUNTANTS ON ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE. |
None.
83
Table of Contents
| ITEM 9A. | CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES. |
Disclosure Controls and Procedures
The Companys management, under the supervision and with the participation of the Companys
Chief Executive Officer (CEO) and Chief Financial Officer (CFO), has evaluated the
effectiveness of the Companys disclosure controls and procedures as defined in Securities and
Exchange Commission (SEC) Rule 13a-15(e) as of December 31, 2009. Based on that evaluation, CEO
and CFO have concluded that the Companys disclosure
controls and procedures are effective to ensure that information the Company is required to
disclose in reports that it files or submits under the Securities Exchange Act is accumulated and
communicated to management, including the CEO and CFO, as appropriate, to allow timely decisions
regarding required disclosure and is recorded, processed, summarized, and reported within the time
periods specified in the SECs rules and forms.
Managements Annual Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
Our management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over
financial reporting, as such term is defined in Rule 13a-15(f) under the Securities Exchange Act of
1934, as amended. Our internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide
reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of
financial statements according to generally accepted accounting principles. All internal control
systems, no matter how well designed, have inherent limitations. Therefore, even those systems
determined effective could provide only reasonable assurance with respect to financial statement
preparation and presentation.
Our management conducted an evaluation of the effectiveness of our internal control over
financial reporting as of December 31, 2009, based on the framework in Internal Control -
Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway
Commission. As permitted, our managements assessment of and conclusion on the effectiveness of
our internal controls did not include the internal controls of Pharma Genexx, because it was
acquired by us in a purchase business combination during the fourth quarter of fiscal 2009.
Based on our evaluation under the framework in Internal Control Integrated Framework,
management concluded that our internal control over financial reporting was effective as of
December 31, 2009.
The effectiveness of the Companys internal control over financial reporting as of December
31, 2009 has been audited by Ernst & Young LLP, our independent registered public accounting firm,
who also audited our consolidated financial statements included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K,
as stated in their report which appears with our accompanying consolidated financial statements.
Changes to the Companys Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
Beginning in the fourth quarter of 2009, we began implementing a new accounting system, as
well as standards and procedures at Pharma Genexx, S.A., upgrading and establishing controls over
accounting systems, and adding employees who are trained and experienced in the preparation of
financial statements in accordance with U.S. GAAP to ensure that we have in place appropriate
internal control over financial reporting at Pharma Genexx. Other than as set forth above with
respect to Pharma Genexx, there have been no changes to the Companys internal control over
financial reporting that occurred during the Companys fourth fiscal quarter that have materially
affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, the Companys internal control over
financial reporting. Pharma Genexx, S.A.s assets constituted $28.0 million and $17.1 million of total and net assets, respectively,
as of December 31, 2009 and $4.4 million and $0.2 million of revenues and net loss, respectively, for the year ended December 31, 2009.
| ITEM 9B. | OTHER INFORMATION. |
None.
84
Table of Contents
PART III
The information required in Items 10 (Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance),
Item 11 (Executive Compensation), Item 12 (Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and
Management and Related Stockholder Matters), Item 13 (Certain Relationships and Related
Transactions, and Director Independence), and Item 14 (Principal Accounting Fees and Services) is
incorporated by reference to the Companys definitive proxy statement for the 2010 Annual Meeting
of Stockholders to be filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission within 120 days of December
31, 2009.
85
Table of Contents
PART IV
| ITEM 15. | EXHIBITS, FINANCIAL STATEMENT SCHEDULES. |
| (a)(1) Financial Statements: See Part II, Item 8 of this report. |
| (2) | Financial Statement Schedules: See Part II, Item 8 of this report. | ||
| (3) | Exhibits: See below. |
| Exhibit | ||||
| Number | Description | |||
| 2.1(1) | Merger Agreement and Plan of Reorganization, dated as of March 27,
2007, by and among Acuity Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Froptix Corporation,
eXegenics, Inc., e-Acquisition Company I-A, LLC, and e-Acquisition
Company II-B, LLC. |
|||
| 2.2(5)+ | Securities Purchase Agreement dated May 6, 2008, among Vidus Ocular,
Inc., OPKO Instrumentation, LLC, OPKO Health, Inc., and the
individual sellers and noteholders named therein. |
|||
| 3.1(2) | Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation. |
|||
| 3.2(4) | Amended and Restated By-Laws. |
|||
| 3.3(9) | Certificate of Designation of Series D Preferred Stock. |
|||
| 4.1(1) | Form of Common Stock Warrant. |
|||
| 4.2(9) | Form of Common Stock Warrant. |
|||
| 10.1(1) | Form of Lockup Agreement. |
|||
| 10.2(1) | License Agreement, dated as March 31, 2003, by and between the
Trustees of the University of Pennsylvania and Acuity
Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (Reich/Tolentino). |
|||
| 10.3(1) | License Agreement, dated as March 31, 2003, by and between the
Trustees of the University of Pennsylvania and Acuity
Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (Reich/Gewirtz). |
|||
| 10.4(1) | First Amendment to License Agreement, dated as August 1, 2003, by and
between the Trustees of the University of Pennsylvania and Acuity
Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (Reich/Tolentino). |
|||
| 10.5(1) | First Amendment to License Agreement, dated as August 1, 2003, by and
between the Trustees of the University of Pennsylvania and Acuity
Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (Gewirtz). |
|||
| 10.6(1) | Credit Agreement, dated as of March 27, 2007, by and among eXegenics,
Inc., The Frost Group, LLC, and Acuity Pharmaceuticals, LLC. |
|||
| 10.7(1) | Amended and Restated Subordination Agreement, dated as of March 27,
2007, by and among The Frost Group, LLC, Horizon Technology Funding
Company LLC, Acuity Pharmaceuticals, LLC, and eXegenics, Inc. |
|||
| 10.8(4) | Share Purchase Agreement, dated April 11, 2007, by and between
Ophthalmic Technologies, Inc. and eXegenics, Inc. |
|||
| 10.9(3) | Lease Agreement dated November 13, 2007, by and between Frost Real
Estate Holdings, LLC and the Company. |
|||
| 10.10(4) | Share Purchase Agreement, dated as of November 28, 2007, by and among
Ophthalmic Technologies, Inc., OTI Holdings Limited, and the
Shareholders named therein. |
|||
86
Table of Contents
| Exhibit | ||||
| Number | Description | |||
| 10.11(4) | Exchange and Support Agreement, dated as of November 28, 2007, by and
among OPKO Health, Inc. and OTI Holdings Limited and the holders of
exchangeable shares named therein. |
|||
| 10.12(4) | Stock Purchase Agreement, dated December 4, 2007, by and between
members of The Frost Group, LLC and the Company. |
|||
| 10.13(4)* | OPKO Health, Inc. 2007 Equity Incentive Plan. |
|||
| 10.14(5) | Form of Director Indemnification Agreement. |
|||
| 10.15(5) | Form of Officer Indemnification Agreement. |
|||
| 10.16(6) | Stock Purchase Agreement, dated August 8, 2008 by and among the
Company and the Investors named therein. |
|||
| 10.17(7) | Stock Purchase Agreement, dated February 23, 2009 by and between the
Company and Frost Gamma Investments Trust. |
|||
| 10.18(7) | Promissory Note to Frost Gamma Investments Trust, dated March 4, 2009. |
|||
| 10.19(8) | Form of Stock Purchase Agreement for transactions between the Company
and Nora Real Estate SA., Vector Group Ltd., Oracle Partners LP,
Oracle Institutional Partners, LP., Chung Chia Company Limited, Gold
Sino Assets Limited and Grandtime Associates Limited. |
|||
| 10.20(8) | Stock Purchase Agreement, dated June 10, 2009, by and among the
Company and Sorrento Therapeutics, Inc. |
|||
| 10.21(9) | Form of Securities Purchase Agreement Series D Preferred Stock. |
|||
| 10.22(10)* | Form of Restricted Share Award Agreement (Director). |
|||
| 10.23(10) | Cocrystal Discovery, Inc. Agreements. |
|||
| 10.24 | Stock Purchase Agreement, dated October 1, 2009, by and among the
OPKO Chile Limitada and Inversones OPKO Limitada, subsidiaries of the
Company, and the Sellers named therein. |
|||
| 10.25+ | Asset Purchase Agreement, dated October 12, 2009, by and between the
Company and Schering Corporation. |
|||
| 21 | Subsidiaries of the Company. |
|||
| 23.1 | Consent of Ernst & Young LLP. |
|||
| 31.1 | Certification by Phillip Frost, Chief Executive Officer, pursuant to
Exchange Act Rules 13a-14 and 15d-14. |
|||
| 31.2 | Certification by Rao Uppaluri, Chief Financial Officer, pursuant to
Exchange Act Rules 13a-14 and 15d-14. |
|||
| 32.1 | Certification by Phillip Frost, Chief Executive Officer, pursuant to
18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as adopted pursuant to Section 906 of the
Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. |
|||
| 32.2 | Certification by Rao Uppaluri, Chief Financial Officer, pursuant to
18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as adopted pursuant to Section 906 of the
Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. |
|||
87
Table of Contents
| * | Denotes management contract or compensatory plan or arrangement. | |
| + | Certain confidential material contained in the document has been omitted and filed separately with the Securities and Exchange Commission. | |
| (1) | Filed with the Companys Current Report on Form 8-K filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on April 2, 2007, and incorporated herein by reference. | |
| (2) | Filed with the Companys Current Report on Form 8-A filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on June 11, 2007, and incorporated herein by reference. | |
| (3) | Filed with the Companys Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on November 14, 2007 for the Companys three-month period ended September 30, 2007, and incorporated herein by reference. | |
| (4) | Filed with the Companys Annual Report on Form 10-K filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on March 31, 2008 and incorporated herein by reference. | |
| (5) | Filed with the Companys Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on August 8, 2008 for the Companys three-month period ended June 30, 2008, and incorporated herein by reference. | |
| (6) | Filed with the Companys Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on November 12, 2008 for the Companys three-month period ended September 30, 2008, and incorporated herein by reference. | |
| (7) | Filed with the Companys Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on May 8, 2009 for the Companys three-month period ended March 31, 2009, and incorporated herein by reference. | |
| (8) | Filed with the Companys Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on August 7, 2009 for the Companys three-month period ended June 30, 2009, and incorporated herein by reference. | |
| (9) | Filed with the Companys Current Report on Form 8-K filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on September 24, 2009, and incorporated herein by reference. | |
| (10) | Filed with the Companys Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on November 9, 2009 for the Companys three-month period ended September 30, 2009, and incorporated herein by reference. |
88
Table of Contents
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934,
the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto
duly authorized.
| OPKO HEALTH, INC. |
||||
| By: | /s/ Dr. Phillip Frost | |||
| Dr. Phillip Frost, | ||||
| Chairman of the Board and Chief Executive Officer | ||||
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been
signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the
dates indicated.
| Signature | Title | Date | ||
/s/ Dr. Phillip Frost, M.D.
|
Chairman of the Board and Chief
Executive Officer (Principal Executive Officer) |
March 17, 2010 | ||
| /s/ Dr. Jane H. Hsiao
|
Vice Chairman and Chief Technical Officer | March 17, 2010 | ||
| /s/ Steven D. Rubin
|
Director and Executive Vice President Administration | March 17, 2010 | ||
| /s/ Rao Uppaluri
|
Senior Vice President and Chief
Financial Officer (Principal Financial Officer) |
March 17, 2010 | ||
| /s/ Adam Logal
|
Executive Director of Finance, Chief
Accounting Officer and Treasurer (Principal Accounting Officer) |
March 17, 2010 | ||
| /s/ Robert Baron
|
Director | March 17, 2010 | ||
| /s/ Thomas E. Beier
|
Director | March 17, 2010 | ||
| /s/ Pascal J. Goldschmidt, M.D.
|
Director | March 17, 2010 | ||
| /s/ Richard A. Lerner, M.D.
|
Director | March 17, 2010 | ||
| /s/ John A. Paganelli
|
Director | March 17, 2010 | ||
| /s/ Richard C. Pfenniger, Jr.
|
Director | March 17, 2010 | ||
| /s/ Alice Lin-Tsing Yu, M.D., Ph.D.
|
Director | March 17, 2010 |
89
Table of Contents
EXHIBIT INDEX
| Exhibit | ||||
| Number | Description | |||
| 10.24 | Stock Purchase Agreement, dated October 1,
2009, by and among the OPKO Chile Limitada
and Inversones OPKO Limitada, subsidiaries of
the Company, and the Sellers named therein. |
|||
| 10.25+ | Asset Purchase Agreement, dated October 12,
2009, by and between the Company and Schering
Corporation. |
|||
| 21 | Subsidiaries of the Company. |
|||
| 23.1 | Consent of Ernst & Young LLP. |
|||
| 31.1 | Certification by Phillip Frost, Chief
Executive Officer, pursuant to Exchange Act
Rules 13a-14 and 15d-14. |
|||
| 31.2 | Certification by Rao Uppaluri, Chief
Financial Officer, pursuant to Exchange Act
Rules 13a-14 and 15d-14. |
|||
| 32.1 | Certification by Phillip Frost, Chief
Executive Officer, pursuant to 18 U.S.C.
Section 1350, as adopted pursuant to Section
906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. |
|||
| 32.2 | Certification by Rao Uppaluri, Chief
Financial Officer, pursuant to 18 U.S.C.
Section 1350, as adopted pursuant to Section
906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. |
|||
| + | Certain confidential material contained in the document has been omitted and filed separately with the Securities and Exchange Commission. |
90